Significance of Wesak - Year 11-12 Studies of Religion 2Unit 2013-4
... Wesak is the most important of the public puja festivals within Buddhism and it is enjoyed and celebrated by all within the community. Puja is worship; the ritual that honours a God or a Goddess as a divine guest, usually in a temple but can also be a domestic ritual. Wesak is so called because it i ...
... Wesak is the most important of the public puja festivals within Buddhism and it is enjoyed and celebrated by all within the community. Puja is worship; the ritual that honours a God or a Goddess as a divine guest, usually in a temple but can also be a domestic ritual. Wesak is so called because it i ...
Who is the founder of Buddhism? The Buddhist tradition is founded
... The Buddhist tradition is founded on and inspired by the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama. He was called the Buddha and lived in the 4th or 5th century B.C. in India. Why is Siddhartha Gautama so important to Buddhists? Siddhartha Gautama found the path to Enlightenment. By doing so he was led from t ...
... The Buddhist tradition is founded on and inspired by the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama. He was called the Buddha and lived in the 4th or 5th century B.C. in India. Why is Siddhartha Gautama so important to Buddhists? Siddhartha Gautama found the path to Enlightenment. By doing so he was led from t ...
Making Sense of Ch`an - 羅致廉醫生| DR. Robert CL Law
... •Reign of Indian Emperor Asoka (272231) who converted and established the Buddha's Dharma on a national level for the first time in Buddhist history. •He ruled from Burma to Iran and from Nepal to South India • In the 3rd Century B.C. during the time of Emperor Asoka, the Third Council was held at P ...
... •Reign of Indian Emperor Asoka (272231) who converted and established the Buddha's Dharma on a national level for the first time in Buddhist history. •He ruled from Burma to Iran and from Nepal to South India • In the 3rd Century B.C. during the time of Emperor Asoka, the Third Council was held at P ...
buddhism ppt - Valhalla High School
... Did not demand rigorous asceticism Popular with merchants who used Buddhist monasteries as inns Taught in vernacular language to reach a popular audience Holy sites and shrines facilitated pilgrimages ...
... Did not demand rigorous asceticism Popular with merchants who used Buddhist monasteries as inns Taught in vernacular language to reach a popular audience Holy sites and shrines facilitated pilgrimages ...
Buddhism glossary - Religion 21 Home
... Siddhartha Gautama. The personal name of the historical Buddha. six realms. Gods, asuras (anti-gods), humans, animals, hungry ghosts, hell beings — the six states in which one can be reborn. stupa. A monument which usually contains relics and which is an object of devotion. Sukhavati. The ‘Pure Land ...
... Siddhartha Gautama. The personal name of the historical Buddha. six realms. Gods, asuras (anti-gods), humans, animals, hungry ghosts, hell beings — the six states in which one can be reborn. stupa. A monument which usually contains relics and which is an object of devotion. Sukhavati. The ‘Pure Land ...
The Differences between Theravada and Mahayana
... According to the Sri Lanka chronicles: of Dipavamsa (Chronicle of the Island, 4th AC), Mahavamsa (Great Chronicle, 5th AC) and the Samantapasadika (Commentary on the Vinaya), the term Theravada was first introduced into the history of Buddhism after the first Buddhist Council (synod) held at Rajagah ...
... According to the Sri Lanka chronicles: of Dipavamsa (Chronicle of the Island, 4th AC), Mahavamsa (Great Chronicle, 5th AC) and the Samantapasadika (Commentary on the Vinaya), the term Theravada was first introduced into the history of Buddhism after the first Buddhist Council (synod) held at Rajagah ...
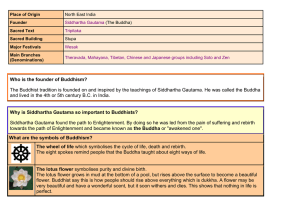
The Buddhist tradition is founded on and inspired by the teachi
... The Buddhist tradition is founded on and inspired by the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama. He was called the Buddha and lived in the 4th or 5th century B.C. in India. Why is Siddhartha Gautama so important to Buddhists? Siddhartha Gautama found the path t ...
... The Buddhist tradition is founded on and inspired by the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama. He was called the Buddha and lived in the 4th or 5th century B.C. in India. Why is Siddhartha Gautama so important to Buddhists? Siddhartha Gautama found the path t ...
Buddhism - A Cultural Approach
... Found in southern Asia. The monastic life is the best way to achieve nirvana. Focus on wisdom and meditation. Goal is to become a “Buddha,” or “Enlightened One.” Over 100,000,000 followers today. ...
... Found in southern Asia. The monastic life is the best way to achieve nirvana. Focus on wisdom and meditation. Goal is to become a “Buddha,” or “Enlightened One.” Over 100,000,000 followers today. ...
File - Year 11-12 Studies of Religion 2Unit 2013-4
... and a hospice can present the best environment for a peaceful death. However, no Buddhist hospice would practice assisted suicide. This is because assisted suicide is equivalent to intentional killing and therefore constitutes a breakage of the first precept. ...
... and a hospice can present the best environment for a peaceful death. However, no Buddhist hospice would practice assisted suicide. This is because assisted suicide is equivalent to intentional killing and therefore constitutes a breakage of the first precept. ...
An Outline of Buddhist Traditions
... What is called the Theravada Tradition (The School of the Elders) is practiced in South East Asian countries – Burma, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam and Sri Lanka. This tradition has preserved the methods of meditation and freeing the mind based on what the Historical Buddha taught - mindfulness, calm and ...
... What is called the Theravada Tradition (The School of the Elders) is practiced in South East Asian countries – Burma, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam and Sri Lanka. This tradition has preserved the methods of meditation and freeing the mind based on what the Historical Buddha taught - mindfulness, calm and ...
Chinese Buddhists attempted to unify the Buddhist
... Theravada Buddhism, the Way of the Elders, became the major religious tradition in South and Southeast Asia. The Elders refers to the teachers who received the teachings directly from the Buddha, transmitting them to later disciples. In the period prior to the famous Buddhist King Asoka (3rd.c. BCE) ...
... Theravada Buddhism, the Way of the Elders, became the major religious tradition in South and Southeast Asia. The Elders refers to the teachers who received the teachings directly from the Buddha, transmitting them to later disciples. In the period prior to the famous Buddhist King Asoka (3rd.c. BCE) ...
Buddhism PowerPoint - School District 308
... People that follow the Buddha’s teachings are called Buddhists. The teaching of Buddhism reflect Hindu ideas. He rejected many of the ideas contained in the Vedas, including animal sacrifice. Buddha has 4 guiding principles that are at the heart of his teaching. They are known as The Four Noble ...
... People that follow the Buddha’s teachings are called Buddhists. The teaching of Buddhism reflect Hindu ideas. He rejected many of the ideas contained in the Vedas, including animal sacrifice. Buddha has 4 guiding principles that are at the heart of his teaching. They are known as The Four Noble ...
Buddhism and Confucianism
... Beliefs continued • By following the Four Noble Truths and in effect the Eight Fold Path, one moves closer to the destination of Nirvana. • Nirvana is considered a place of peace and harmony. ...
... Beliefs continued • By following the Four Noble Truths and in effect the Eight Fold Path, one moves closer to the destination of Nirvana. • Nirvana is considered a place of peace and harmony. ...
Slide 1 - SD308.org
... Origins of Buddhism 4 Noble Truths Eightfold Path HW – Study Guides due Wednesday India Test Thursday ...
... Origins of Buddhism 4 Noble Truths Eightfold Path HW – Study Guides due Wednesday India Test Thursday ...
"Awakened One" (Buddha): Prince Siddhartha Gautama, who would
... greatest is an absolute achievement free of comparison. What does that mean? It means that to be the greatest is not an achievement that can be attained through competition. You can't win greatness - but you can achieve it. That means everyone can be the greatest. Here's an example: For a healthy an ...
... greatest is an absolute achievement free of comparison. What does that mean? It means that to be the greatest is not an achievement that can be attained through competition. You can't win greatness - but you can achieve it. That means everyone can be the greatest. Here's an example: For a healthy an ...
Buddhism… - Joshua ISD
... Over the past two centuries, especially since the later half of the 20th century, Buddhism has made inroads into the Western world through… ...
... Over the past two centuries, especially since the later half of the 20th century, Buddhism has made inroads into the Western world through… ...
Buddhism - WordPress.com
... Hun armies eventually gained control of northern and central India After the fall of the Guptas, weak, decentralized rule characterized India though there was ...
... Hun armies eventually gained control of northern and central India After the fall of the Guptas, weak, decentralized rule characterized India though there was ...
Mahayana
Mahāyāna (Sanskrit: महायान mahāyāna, literally the ""Great Vehicle"") is one of two (or three, under some classifications) main existing branches of Buddhism and a term for classification of Buddhist philosophies and practice. The Buddhist tradition of Vajrayana is sometimes classified as a part of Mahayana Buddhism, but some scholars may consider it as a different branch altogether.According to the teachings of Mahāyāna traditions, ""Mahāyāna"" also refers to the path of the Bodhisattva seeking complete enlightenment for the benefit of all sentient beings, also called ""Bodhisattvayāna"", or the ""Bodhisattva Vehicle"". A bodhisattva who has accomplished this goal is called a samyaksaṃbuddha, or ""fully enlightened Buddha"". A samyaksaṃbuddha can establish the Dharma and lead disciples to enlightenment. Mahayana Buddhists teach that enlightenment can be attained in a single lifetime, and this can be accomplished even by a layperson.The Mahāyāna tradition is the largest major tradition of Buddhism existing today, with 53.2% of practitioners, compared to 35.8% for Theravāda and 5.7% for Vajrayāna in 2010.In the course of its history, Mahāyāna Buddhism spread from India to various other Asian countries such as Bangladesh, China, Japan, Vietnam, Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Tibet, Bhutan, Malaysia, and Mongolia. Major traditions of Mahāyāna Buddhism today include Zen, Chinese Chán, Pure Land, Tiantai, and Nichiren. It may also include the Vajrayāna Buddhist traditions of Shingon, Tendai and Tibetan Buddhism, which add esoteric teachings to the Mahāyāna tradition.