7-4: Parallel Lines and Proportional Parts
... G1.2.2: Construct and justify arguments and solve multistep problems involving angle measure, side length, perimeter, and area of all types of triangles. G2.3.4: Use theorems about similar triangles to solve problems with and without use of coordinates. ...
... G1.2.2: Construct and justify arguments and solve multistep problems involving angle measure, side length, perimeter, and area of all types of triangles. G2.3.4: Use theorems about similar triangles to solve problems with and without use of coordinates. ...
Geometry Retest Test 3 Review
... Review for Retest of Test 3 Geometry On a separate sheet of paper, copy the question. Show all work on those marked. 1. mDEF = 63° and mCEF = 32°. Find the measure of mDEC. Show work. Classify the angle. C F E D 2. Determine the values of x and y in the diagram. (not drawn to scale) x ...
... Review for Retest of Test 3 Geometry On a separate sheet of paper, copy the question. Show all work on those marked. 1. mDEF = 63° and mCEF = 32°. Find the measure of mDEC. Show work. Classify the angle. C F E D 2. Determine the values of x and y in the diagram. (not drawn to scale) x ...
3.1 Pairs of Lines and Angles
... Think of each segment in the diagram as part of a line. Complete the statement with parallel, skew, or perpendicular. ...
... Think of each segment in the diagram as part of a line. Complete the statement with parallel, skew, or perpendicular. ...
Main Street ACADEMY LESSON PLAN 2011-2012
... 3. If the figure is a pentagon, then it has five sides. Write the converse: ________________________________________________ ...
... 3. If the figure is a pentagon, then it has five sides. Write the converse: ________________________________________________ ...
Geometry Course Objectives Student Study Guide
... • Determine the measure of central and inscribed angles and their intercepted arcs • Find segment lengths, angle measures, and intercepted arc measures formed by chords, secants, and tangents intersecting inside and outside circles Comparing Congruent and Similar Geometric Figures Similarity and Con ...
... • Determine the measure of central and inscribed angles and their intercepted arcs • Find segment lengths, angle measures, and intercepted arc measures formed by chords, secants, and tangents intersecting inside and outside circles Comparing Congruent and Similar Geometric Figures Similarity and Con ...
02 Spherical Geometry Basics
... due south. We are, from now on, going to rule out pairs of antipodal points such as the north and south poles, because there are infinitely many geodesics between them. Otherwise, just as in geometry for the plane, each two (non-antipodal) points determine a unique geodesic. In the plane, this is th ...
... due south. We are, from now on, going to rule out pairs of antipodal points such as the north and south poles, because there are infinitely many geodesics between them. Otherwise, just as in geometry for the plane, each two (non-antipodal) points determine a unique geodesic. In the plane, this is th ...
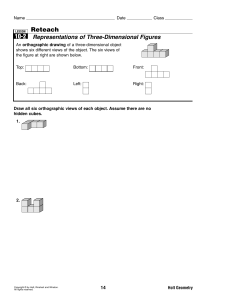
10-2 Reteach Representations of Three
... An isometric drawing is drawn on isometric dot paper and shows three sides of a figure from a corner view. A solid and an isometric drawing of the solid are shown. ...
... An isometric drawing is drawn on isometric dot paper and shows three sides of a figure from a corner view. A solid and an isometric drawing of the solid are shown. ...
Perspective (graphical)

Perspective (from Latin: perspicere to see through) in the graphic arts is an approximate representation, on a flat surface (such as paper), of an image as it is seen by the eye. The two most characteristic features of perspective are that objects are smaller as their distance from the observer increases; and that they are subject to foreshortening, meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight are shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight.Italian Renaissance painters including Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca Pacoima studied linear perspective, wrote treatises on it, and incorporated it into their artworks, thus contributing to the mathematics of art.