5th Grade | Unit 9 - Amazon Web Services
... intersecting lines. Lines in the same plane that are not parallel. line. An infinite set of points forming a straight path that continues in both directions. line segment. A part of a line bounded by two endpoints. obtuse angle. An angle measuring greater than 90°. parallel lines. Lines in the same ...
... intersecting lines. Lines in the same plane that are not parallel. line. An infinite set of points forming a straight path that continues in both directions. line segment. A part of a line bounded by two endpoints. obtuse angle. An angle measuring greater than 90°. parallel lines. Lines in the same ...
Relating Graph Thickness to Planar Layers and Bend Complexity
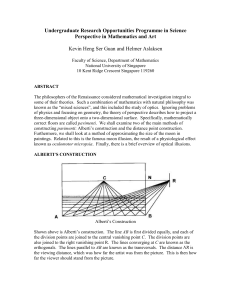
... edges E 0 ⊆ E is called a crossing-free edge set in Γ, if the corresponding polygonal chains correspond to a planar polyline drawing, i.e., no two polylines that correspond to a pair of edges in E 0 intersect, except possibly at their common endpoints. The layer complexity of Γ is the minimum intege ...
... edges E 0 ⊆ E is called a crossing-free edge set in Γ, if the corresponding polygonal chains correspond to a planar polyline drawing, i.e., no two polylines that correspond to a pair of edges in E 0 intersect, except possibly at their common endpoints. The layer complexity of Γ is the minimum intege ...
Geometry - Carl Junction Schools
... 4d. Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. 4e. Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. ...
... 4d. Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. 4e. Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. ...
Technical drawing

Technical drawing, also known as drafting or draughting, is the act and discipline of composing drawings that visually communicate how something functions or is to be constructed.Technical drawing is essential for communicating ideas in industry and engineering.To make the drawings easier to understand, people use familiar symbols, perspectives, units of measurement, notation systems, visual styles, and page layout. Together, such conventions constitute a visual language, and help to ensure that the drawing is unambiguous and relatively easy to understand. These drafting conventions are condensed into internationally accepted standards and specifications that transcend the barrier of language making technical drawings a universal means of communicating complex mechanical concepts.This need for precise communication in the preparation of a functional document distinguishes technical drawing from the expressive drawing of the visual arts. Artistic drawings are subjectively interpreted; their meanings are multiply determined. Technical drawings are understood to have one intended meaning.A drafter, draftsperson, or draughtsman is a person who makes a drawing (technical or expressive). A professional drafter who makes technical drawings is sometimes called a drafting technician. Professional drafting is a desirable and necessary function in the design and manufacture of complex mechanical components and machines. Professional draftspersons bridge the gap between engineers and manufacturers, and contribute experience and technical expertise to the design process.