1. a) The sagittal plane divides the brain into left and right sides. The
... ANS) parts. Somatin PNS refers to the parts of the PNS that are under voluntary control. Conversely, visceral PNS refers to the parts of the PNS that are autoregulated and not under voluntary control e.g., heart muscle. Affarent refers to information transport towards something. Effarent refers to ...
... ANS) parts. Somatin PNS refers to the parts of the PNS that are under voluntary control. Conversely, visceral PNS refers to the parts of the PNS that are autoregulated and not under voluntary control e.g., heart muscle. Affarent refers to information transport towards something. Effarent refers to ...
The Central Nervous System
... region of the premotor area. Present only on left side of the brain, directs muscles involved in speech production. ...
... region of the premotor area. Present only on left side of the brain, directs muscles involved in speech production. ...
COGS107ALocationterminology
... Section definitions (midsagittal, parasagittal, coronal, horizontal) Lobes (frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, limbic), regions in each, and dividing sulci (longitudinal fissure, lateral (Sylvian) fissure, calcarine sulcus, central sulcus, parietooccipital sulcus) Major divisions of CNS: myelen ...
... Section definitions (midsagittal, parasagittal, coronal, horizontal) Lobes (frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, limbic), regions in each, and dividing sulci (longitudinal fissure, lateral (Sylvian) fissure, calcarine sulcus, central sulcus, parietooccipital sulcus) Major divisions of CNS: myelen ...
Week11_Nov13_2001
... (crania of different sizes are standardized to the same width between the left and right temporomandibular joints; scales differ among taxa); the areas in red represent the approximate extent of the brain endocasts. (III, Right) Measurement of the brain vault size (cranial width at the squamosal-par ...
... (crania of different sizes are standardized to the same width between the left and right temporomandibular joints; scales differ among taxa); the areas in red represent the approximate extent of the brain endocasts. (III, Right) Measurement of the brain vault size (cranial width at the squamosal-par ...
Sheep Brain Dissection
... 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly seen in the brain section. 3. The tiny space within the corpus callosum (which hold cerebrospinal fluid) is called the lateral ventricle. Underneath it, you can find the third ventricle. There are other v ...
... 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly seen in the brain section. 3. The tiny space within the corpus callosum (which hold cerebrospinal fluid) is called the lateral ventricle. Underneath it, you can find the third ventricle. There are other v ...
SKULL BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
... PROJECTING FROM THE INFERIOR ASPECT IS THE PITUITARY GLAND THAT SECRETES HORMONES CONTAINS NUCLEI( GRAY MATTER) IT IS THA MASTER CONTROL CENTER REGULATING THE ACTIVITIES OF THE VISCERAL ORGANS EPTHALAMUS CONSISTS OF NUCLEI AND THE PINEAL BODY UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS IT SECRETS MELATO ...
... PROJECTING FROM THE INFERIOR ASPECT IS THE PITUITARY GLAND THAT SECRETES HORMONES CONTAINS NUCLEI( GRAY MATTER) IT IS THA MASTER CONTROL CENTER REGULATING THE ACTIVITIES OF THE VISCERAL ORGANS EPTHALAMUS CONSISTS OF NUCLEI AND THE PINEAL BODY UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS IT SECRETS MELATO ...
brain) and function of the following: medulla, pons, cerebellum, inf
... Section definitions (midsagittal, parasagittal, coronal, horizontal) Lobes (frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, limbic), regions in each, and dividing sulci (longitudinal fissure, lateral (Sylvian) fissure, calcarine sulcus, central sulcus, parietooccipital sulcus) Major divisions of CNS: myelen ...
... Section definitions (midsagittal, parasagittal, coronal, horizontal) Lobes (frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, limbic), regions in each, and dividing sulci (longitudinal fissure, lateral (Sylvian) fissure, calcarine sulcus, central sulcus, parietooccipital sulcus) Major divisions of CNS: myelen ...
Psychology Study Guide 3
... Death from disease: rare in early adulthood, Cancer is the leading killer of adults under 75, but > 1 in 10,000 in 20-34 (Per 100,000 annual deaths – 15/24=21/25-34=65/35-44=154/ 4554=354/ 55-64=1,053/ 65-74=2,553/ 75-84=5,937/ 85=15,678). Senescence: State of physical decline, in which the body bec ...
... Death from disease: rare in early adulthood, Cancer is the leading killer of adults under 75, but > 1 in 10,000 in 20-34 (Per 100,000 annual deaths – 15/24=21/25-34=65/35-44=154/ 4554=354/ 55-64=1,053/ 65-74=2,553/ 75-84=5,937/ 85=15,678). Senescence: State of physical decline, in which the body bec ...
Brain Paradox
... “It is possible that these atypical aspects of Einstein’s cerebral cortex were related to the difficulty with which he acquired language, his preference for thinking in sensory impressions including visual images rather than words, and his early training on the violin” ...
... “It is possible that these atypical aspects of Einstein’s cerebral cortex were related to the difficulty with which he acquired language, his preference for thinking in sensory impressions including visual images rather than words, and his early training on the violin” ...
Sheep Brain Dissection Analysis
... The sheep brain is quite similar to the human brain except for proportion. The sheep has a smaller cerebrum. Also the sheep brain is oriented anterior to posterior whereas the human brain is superior to inferior. 1. The tough outer covering of the sheep brain is the dura mater, one of three meninges ...
... The sheep brain is quite similar to the human brain except for proportion. The sheep has a smaller cerebrum. Also the sheep brain is oriented anterior to posterior whereas the human brain is superior to inferior. 1. The tough outer covering of the sheep brain is the dura mater, one of three meninges ...
Forebrain cont`d
... behavior can be established and triangulated. • Analogue research with animals establishes a base from which to consider human behavior. • Neuropsychology uses techniques to study the brain such as EEG and scanning techniques (structural imaging-CAT and MRI and *functional imaging PET scans) to give ...
... behavior can be established and triangulated. • Analogue research with animals establishes a base from which to consider human behavior. • Neuropsychology uses techniques to study the brain such as EEG and scanning techniques (structural imaging-CAT and MRI and *functional imaging PET scans) to give ...
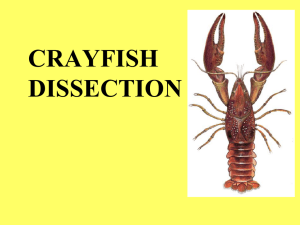
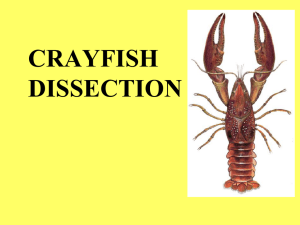
CRAYFISH DISSECTION
... In males – transfer sperm In females – carry eggs/young Create water currents ...
... In males – transfer sperm In females – carry eggs/young Create water currents ...
crayfish dissection - Solon City Schools
... Move water over EGGS, transfer sperm (males) carry young/eggs (females) Propulsion during tailflips ...
... Move water over EGGS, transfer sperm (males) carry young/eggs (females) Propulsion during tailflips ...
Chapter 1
... hindbrain and midbrain to the forebrain, the neural structures become more complex and so do the behaviors they control. • The hemispheres are divided into four lobes – ...
... hindbrain and midbrain to the forebrain, the neural structures become more complex and so do the behaviors they control. • The hemispheres are divided into four lobes – ...
260-2017-01-20-anatomy-I
... Which of the following methods has temporal resolution on the order of seconds? ...
... Which of the following methods has temporal resolution on the order of seconds? ...
SBI4U - sheep brain dissection REVISED
... the meninges covers the surface of the cerebrum. This has been removed for you. However, note the remnants of the meninges. (b) Name the three membranes that make up the meninges. ...
... the meninges covers the surface of the cerebrum. This has been removed for you. However, note the remnants of the meninges. (b) Name the three membranes that make up the meninges. ...
Biological Psychology
... gland in your left hemisphere, remember the pineal gland is a unistructure and in your midsaggital cut you may have left it intact in the other hemisphere. Looking at the most ventral part of the 3rd ventricle, you should be able to appreciate how it extends down into the hollow stalk attaching the ...
... gland in your left hemisphere, remember the pineal gland is a unistructure and in your midsaggital cut you may have left it intact in the other hemisphere. Looking at the most ventral part of the 3rd ventricle, you should be able to appreciate how it extends down into the hollow stalk attaching the ...
Sheep Brain Dissection - Mayfield City Schools
... Intellect and Reason as well as part of emotional control center and home to personality Involved in motor function, problem solving, spontaneity, memory, language, initiation, judgment, impulse control, and social and sexual behavior. There are important ...
... Intellect and Reason as well as part of emotional control center and home to personality Involved in motor function, problem solving, spontaneity, memory, language, initiation, judgment, impulse control, and social and sexual behavior. There are important ...
Bio 12 Brain
... produces hormones, many of which control the release of hormones from other gland in the body the pituitary gland, along with the hypothalamus, form the neuroendocrine control centre (communication between the nervous and endocrine systems) ...
... produces hormones, many of which control the release of hormones from other gland in the body the pituitary gland, along with the hypothalamus, form the neuroendocrine control centre (communication between the nervous and endocrine systems) ...
Sex and the cardiovascular system: the intriguing tale of how women
... and internet files. Much of the human data found in medical texts represent the environment in which the testing was conducted. Medical schools and military institutions located largely in Europe and North America have provided the largest numbers of “healthy” individuals in which to make measures o ...
... and internet files. Much of the human data found in medical texts represent the environment in which the testing was conducted. Medical schools and military institutions located largely in Europe and North America have provided the largest numbers of “healthy” individuals in which to make measures o ...
chapter 14 the brain and cranial nerves
... the brain? a. optic, olfactory, trigeminal, trochlear, ophthalmic b. olfactory, ophthalmic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal c. olfactory, optic, trochlear, trigeminal, facial d. olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal 14. Loss of the sense of smell could result from injury to which cra ...
... the brain? a. optic, olfactory, trigeminal, trochlear, ophthalmic b. olfactory, ophthalmic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal c. olfactory, optic, trochlear, trigeminal, facial d. olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal 14. Loss of the sense of smell could result from injury to which cra ...
Neuroscience of sex differences
Neuroscience of sex differences is the study of the characteristics of the brain that separate the male brain from the female brain. Unlike sexual characteristics, which are the physical qualities that separate the two sexes of an organism, the neurological differences are not visually apparent and therefore hard to study. Psychological sex differences are thought by some to reflect the interaction of genes, hormones and social learning on brain development throughout the lifespan. Some evidence from brain morphology and function studies indicates that male and female brains cannot always be assumed to be identical from either a structural or functional perspective, and some brain structures are sexually dimorphic.