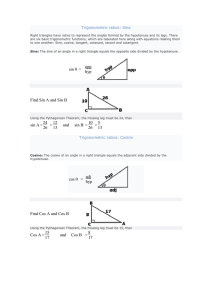
sin θ = opp hyp Find Sin A and Sin B sin A = 24 26 = 12 13 and sin B
... Important note: There is a big difference between sec θ and cos-1x. The first one means "1/cos θ". The second one involves finding an angle whose cosine is x. So on your calculator, don't use your cos-1 button to find sec θ. ...
... Important note: There is a big difference between sec θ and cos-1x. The first one means "1/cos θ". The second one involves finding an angle whose cosine is x. So on your calculator, don't use your cos-1 button to find sec θ. ...
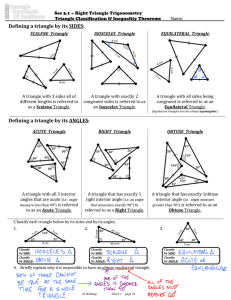
Day 3 Lesson 1 Classifying Triangles
... List the given triangles that would fall into this category. 3. Possible answer: 3 ! !s ; C, E, H ...
... List the given triangles that would fall into this category. 3. Possible answer: 3 ! !s ; C, E, H ...
Maths SoW - Thinking Skills @ Townley
... Algebra Cards – find value of each card when x = 30, which ones are the same value when x = 20, what does 2x mean, put in order from smallest to largest when x = 12 (or which one would be in the middle), which three could be the angles in a triangle when x = 38. Non-algebraic linking activity such ...
... Algebra Cards – find value of each card when x = 30, which ones are the same value when x = 20, what does 2x mean, put in order from smallest to largest when x = 12 (or which one would be in the middle), which three could be the angles in a triangle when x = 38. Non-algebraic linking activity such ...
Geometry Assessment Blueprint
... Use ratios of similar 3-dimensional figures to determine unknown values, such as angles, side lengths, perimeter or circumference of a face, area of a face, and volume. Models and Perspective (4.3) Create a model of a 3-dimensional figure from a 2-dimensional drawing and make a 2-dimensional represe ...
... Use ratios of similar 3-dimensional figures to determine unknown values, such as angles, side lengths, perimeter or circumference of a face, area of a face, and volume. Models and Perspective (4.3) Create a model of a 3-dimensional figure from a 2-dimensional drawing and make a 2-dimensional represe ...
Ch 6
... ∆ABC is not a right triangle. Determine the area of ∆ABC given that mA 78 , AB = 8 mm and AC = 17 mm. Hint: First draw a perpendicular segment from angle B to segment AC to find the triangle’s height (altitude). ...
... ∆ABC is not a right triangle. Determine the area of ∆ABC given that mA 78 , AB = 8 mm and AC = 17 mm. Hint: First draw a perpendicular segment from angle B to segment AC to find the triangle’s height (altitude). ...