EDEXECL topics HIGHER
... Distinguish between acute, obtuse, reflex and right angles Use angle properties on a line and at a point to calculate unknown angles Use angle properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to calculate unknown angles Use parallel lines to identify alternate and corresponding angles Calculate interior a ...
... Distinguish between acute, obtuse, reflex and right angles Use angle properties on a line and at a point to calculate unknown angles Use angle properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to calculate unknown angles Use parallel lines to identify alternate and corresponding angles Calculate interior a ...
Answer - ClassZone
... 9. Sample answer: Lines AC and BC both contain C and are perpendicular to j, so by the Perpendicular Postulate they are the same line. Points A and B can each be described as the intersection of this line and line j, so they must be the same point, but this contradicts the given information. (Recall ...
... 9. Sample answer: Lines AC and BC both contain C and are perpendicular to j, so by the Perpendicular Postulate they are the same line. Points A and B can each be described as the intersection of this line and line j, so they must be the same point, but this contradicts the given information. (Recall ...
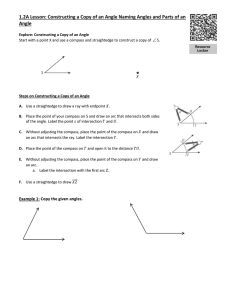
Answer Key 1 5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles
... 2. Create two circles with the same radius centered at each endpoint. The line connecting the intersection points of the circles is the perpendicular bisector. 3. The midpoint is the point where the line segment and perpendicular bisector intersect. 4. A bisector cuts a line segment in half while a ...
... 2. Create two circles with the same radius centered at each endpoint. The line connecting the intersection points of the circles is the perpendicular bisector. 3. The midpoint is the point where the line segment and perpendicular bisector intersect. 4. A bisector cuts a line segment in half while a ...