Quantum wave mechanics
... who showed that electrons behave like waves: at some energies the gases like Ar, Kr become transparent to them: the cross section shows a minimum. This is a wave-like effect. In 1931, in Berlin- Reinickendorf, C. Ramsauer and R. Kollath measured angular distribution of scattered electrons, confirmin ...
... who showed that electrons behave like waves: at some energies the gases like Ar, Kr become transparent to them: the cross section shows a minimum. This is a wave-like effect. In 1931, in Berlin- Reinickendorf, C. Ramsauer and R. Kollath measured angular distribution of scattered electrons, confirmin ...
7. DOMAIN OF VALIDITY OF CLASSICAL THEORY I1x I1px h. (7.1
... [The quantity in the brackets in equation (7.8) is the fine structure constant-cf. equation (114.6).] Thus this criterion is approximately equivalent to the condition that the relative speed be nonrelativistic. We have seen that the momentum transfer collision cross section attributes a zero weight ...
... [The quantity in the brackets in equation (7.8) is the fine structure constant-cf. equation (114.6).] Thus this criterion is approximately equivalent to the condition that the relative speed be nonrelativistic. We have seen that the momentum transfer collision cross section attributes a zero weight ...
Lecture 22 - UD Physics
... If we have a beam of incident particles, with uniform intensity (luminosity) number of incident particles per unit area per unit time The member of particles entering ...
... If we have a beam of incident particles, with uniform intensity (luminosity) number of incident particles per unit area per unit time The member of particles entering ...
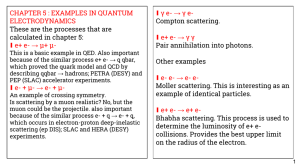
CHAPTER 5 : EXAMPLES IN QUANTUM γ e- → γ e- ∎ ELECTRODYNAMICS
... R = σ ( e e → hadrons ) / σ ( e ebar → μ μbar) . The underlying process in hadron production is e- + e+ → q + qbar. ...
... R = σ ( e e → hadrons ) / σ ( e ebar → μ μbar) . The underlying process in hadron production is e- + e+ → q + qbar. ...
An Introduction to Cross Sections 1. Definition of cross section for
... express the differential cross section in units of fm /sr = 10 cm /sr = 10 mb/sr, the latter using the annoying but traditional unit of 1 barn (1 b) = 10!28 m2 = 10!24 cm2 = 100 fm2 . The above calculations are independent of the relative signs of the two charges. (In the exact calculation, the traj ...
... express the differential cross section in units of fm /sr = 10 cm /sr = 10 mb/sr, the latter using the annoying but traditional unit of 1 barn (1 b) = 10!28 m2 = 10!24 cm2 = 100 fm2 . The above calculations are independent of the relative signs of the two charges. (In the exact calculation, the traj ...
Cross section (physics)
The cross section is an effective area that quantifies the intrinsic likelihood of a scattering event when an incident beam strikes a target object, made of discrete particles. The cross section of a particle is the same as the cross section of a hard object, if the probabilities of hitting them with a ray are the same. It is typically denoted σ and measured in units of area.In scattering experiments, one is often interested in knowing how likely a given event occurs. However, the rate depends strongly on experimental variables such as the density of the target material, the intensity of the beam, or the area of overlap between the beam and the target material. To control for these mundane differences, one can factor out these variables, resulting in an area-like quantity known as the cross section.