7-2 Ratios in Similar Polygons 7-2 Ratios in Similar Polygons
... congruent angles and the pairs of congruent sides. ∠Q ≅ ∠Z; ∠R ≅ ∠Y; ∠S ≅ ∠X; QR ≅ ZY; RS ≅ YX; QS ≅ ZX Solve each proportion. ...
... congruent angles and the pairs of congruent sides. ∠Q ≅ ∠Z; ∠R ≅ ∠Y; ∠S ≅ ∠X; QR ≅ ZY; RS ≅ YX; QS ≅ ZX Solve each proportion. ...
Geometry Standards with Learning Targets
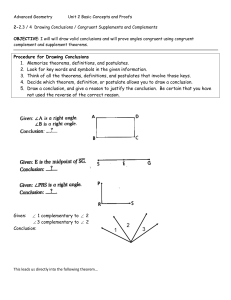
... including complementary and supplementary angles, linear pair (Linear Pair Postulate), and vertical angles (Vertical Angles Theorem) b) Identify and solve problems involving special pairs of angles formed by the intersection of parallel lines and a transversal. c) Determine from the relationships of ...
... including complementary and supplementary angles, linear pair (Linear Pair Postulate), and vertical angles (Vertical Angles Theorem) b) Identify and solve problems involving special pairs of angles formed by the intersection of parallel lines and a transversal. c) Determine from the relationships of ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)