Word - University at Albany
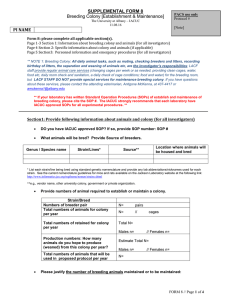
... Provide a scientific justification for establishing and maintaining a breeding colony of animals. Include how the colony contributes to the overall objectives of your research and why animals from commercial vendor sources are not appropriate. Also please include issues with fertility, litter size, ...
... Provide a scientific justification for establishing and maintaining a breeding colony of animals. Include how the colony contributes to the overall objectives of your research and why animals from commercial vendor sources are not appropriate. Also please include issues with fertility, litter size, ...
Predicting family dynamics in social vertebrates
... As the benefits of large group size wane; As ecological opportunities for independent breeding increase or decrease; As breeder deaths and replacements, as well as immigrations alter family composition; As the social dominance of individual changes with age and experience. ...
... As the benefits of large group size wane; As ecological opportunities for independent breeding increase or decrease; As breeder deaths and replacements, as well as immigrations alter family composition; As the social dominance of individual changes with age and experience. ...
Descent with Modification and Population Evolution
... Modifications resulting over time as descendants inhabit differing environments Metaphor depiction of history of life—“Tree” Tips are contemporary Branch points represent ancestors or evolutionary lines Most branch points are dead ...
... Modifications resulting over time as descendants inhabit differing environments Metaphor depiction of history of life—“Tree” Tips are contemporary Branch points represent ancestors or evolutionary lines Most branch points are dead ...
05 Evolution 2009
... ***Are most mutations beneficial? Are most mutations dominant? What happens to harmful mutations? • Most mutations are harmful and recessive; natural selection weeds out most deleterious alleles, leaving those that best suit organisms to their environments. • Some mutations are neutral. They may be ...
... ***Are most mutations beneficial? Are most mutations dominant? What happens to harmful mutations? • Most mutations are harmful and recessive; natural selection weeds out most deleterious alleles, leaving those that best suit organisms to their environments. • Some mutations are neutral. They may be ...
evolution
... The random loss of rare alleles, without respect to the survival or reproductive value, reduces the genetic diversity of a population. ...
... The random loss of rare alleles, without respect to the survival or reproductive value, reduces the genetic diversity of a population. ...
Bowles, S. and Gintis, H.: A cooperative species—human reciprocity
... unfair proposal, the rejection rate is smaller than when responding impulsively. It very much depends on circumstances how reciprocal we are. Couldn’t it be that we have developed a very flexible behavioral repertoire of which “cooperativeness” is only one option? Social preferences in the narrower ...
... unfair proposal, the rejection rate is smaller than when responding impulsively. It very much depends on circumstances how reciprocal we are. Couldn’t it be that we have developed a very flexible behavioral repertoire of which “cooperativeness” is only one option? Social preferences in the narrower ...
Inheritance notes - Shawlands Academy
... The gene for tall is labelled ‘T’ because the dominant gene is tall. We use ‘t’ to represent small. The gametes only have one copy of the gene because when two gametes meet during fertilisation the new organism will have the correct number of chromosomes. The F1 can no longer be called true breeding ...
... The gene for tall is labelled ‘T’ because the dominant gene is tall. We use ‘t’ to represent small. The gametes only have one copy of the gene because when two gametes meet during fertilisation the new organism will have the correct number of chromosomes. The F1 can no longer be called true breeding ...
Dr. Langerhans` answers to questions
... vary in how many offspring they have per brood. Individuals having only a few offspring tend to leave no descendants behind because they all die after a few generations (because everyone has a high probability of dying). Individuals having lots of offspring per brood tend to leave more descendants b ...
... vary in how many offspring they have per brood. Individuals having only a few offspring tend to leave no descendants behind because they all die after a few generations (because everyone has a high probability of dying). Individuals having lots of offspring per brood tend to leave more descendants b ...
Chapter 24 Presentation
... groups of individuals. Rivers may split land that was formerly as one. ...
... groups of individuals. Rivers may split land that was formerly as one. ...
Notes Chapter 16 The Evolution of Populations and Species
... k. Natural selection alters the proportions of alleles within populations 2) Allele Frequency and the Gene Pool a. Gene Pool – total amount of genetic information available in a population b. Allele frequency – determined by dividing the number of a certain allele by the total number of alleles in t ...
... k. Natural selection alters the proportions of alleles within populations 2) Allele Frequency and the Gene Pool a. Gene Pool – total amount of genetic information available in a population b. Allele frequency – determined by dividing the number of a certain allele by the total number of alleles in t ...
population
... This left him unable to explain two things: a. source of variation b. how inheritable traits pass from one generation to the next ...
... This left him unable to explain two things: a. source of variation b. how inheritable traits pass from one generation to the next ...
Chapter 16: Evolution of Populations
... This left him unable to explain two things: a. source of variation b. how inheritable traits pass from one generation to the next ...
... This left him unable to explain two things: a. source of variation b. how inheritable traits pass from one generation to the next ...
Speciation - Mr. Croft
... • Morphological Species Concept: the idea that organisms can be classified by differences in their appearance – Using this concept, scientists can readily communicate about the characteristics, behavior, and relationships of organisms. – The morphological concept of species is limited because it doe ...
... • Morphological Species Concept: the idea that organisms can be classified by differences in their appearance – Using this concept, scientists can readily communicate about the characteristics, behavior, and relationships of organisms. – The morphological concept of species is limited because it doe ...
Selection_and_Speciation
... • Gene mutations occur at a constant and low rate, some are beneficial and result in increasing the organisms reproductive success. This mutation will therefore be passed on. • An accumulation of mutations can occur, which could mean that if the population was reintroduced to the original population ...
... • Gene mutations occur at a constant and low rate, some are beneficial and result in increasing the organisms reproductive success. This mutation will therefore be passed on. • An accumulation of mutations can occur, which could mean that if the population was reintroduced to the original population ...
Why Genetic Programming?
... – a new subtree is grown there using the same random growth process that was used to generate the initial population. ...
... – a new subtree is grown there using the same random growth process that was used to generate the initial population. ...
direct selection
... Problems with the genetic explanation. In most eusocial colonies, the primary reproductive ("queens") mates more than once, reducing the degree of relatedness between her daughters. Therefore, the effects of haplodiploidy in kin selection are reduced. Also, the termites, the only completely eusocial ...
... Problems with the genetic explanation. In most eusocial colonies, the primary reproductive ("queens") mates more than once, reducing the degree of relatedness between her daughters. Therefore, the effects of haplodiploidy in kin selection are reduced. Also, the termites, the only completely eusocial ...
Chapter 7 Social Relations
... health of an individual organism. ability of an organism to adapt to new environmental situations. quality of offspring produced. number of genes contributed by an individual to the next generation. all of the above ...
... health of an individual organism. ability of an organism to adapt to new environmental situations. quality of offspring produced. number of genes contributed by an individual to the next generation. all of the above ...
Oct 30 - University of San Diego
... Allele frequencies in small populations may reflect genotypes of founding individuals Common in isolated populations Ex: Finns descended from small group of people ~4000 years ago; genetically distinct from other ...
... Allele frequencies in small populations may reflect genotypes of founding individuals Common in isolated populations Ex: Finns descended from small group of people ~4000 years ago; genetically distinct from other ...
Outline of Achievements - The Japan Prize Foundation
... Application of DNA markers leads to realization of efficient selective breeding Throughout the 1990s to 2000s, Dr. Tanksley continues to lead the field of selective breeding and plant genetics. One of his research themes was to elucidate which genes of wild plant species mankind had taken advantage ...
... Application of DNA markers leads to realization of efficient selective breeding Throughout the 1990s to 2000s, Dr. Tanksley continues to lead the field of selective breeding and plant genetics. One of his research themes was to elucidate which genes of wild plant species mankind had taken advantage ...
biological species concept
... natural selection sexual selection genetic drift can lead to speciation ...
... natural selection sexual selection genetic drift can lead to speciation ...
Speciation
... • Morphological Species Concept: the idea that organisms can be classified by differences in their appearance – Using this concept, scientists can readily communicate about the characteristics, behavior, and relationships of organisms. – The morphological concept of species is limited because it doe ...
... • Morphological Species Concept: the idea that organisms can be classified by differences in their appearance – Using this concept, scientists can readily communicate about the characteristics, behavior, and relationships of organisms. – The morphological concept of species is limited because it doe ...
EXAM 3-A
... steadily increasing over 100 years. This increase has been explained as the result of better nutrition and less disease. Has the average height in these populations evolved? a) Yes b) No 29. A small number of marine isopods (Idotea montereyensis) distributed along the California coast, disperse to t ...
... steadily increasing over 100 years. This increase has been explained as the result of better nutrition and less disease. Has the average height in these populations evolved? a) Yes b) No 29. A small number of marine isopods (Idotea montereyensis) distributed along the California coast, disperse to t ...
Molecular breeding: Challenges and perspectives
... markers are used as a substitute for phenotypic selection and to accelerate the release of improved cultivars. Marker-assisted selection (MAS). Selection of individuals with specific alleles for traits controlled by a limited number of loci (up to 6-8). Marker-assisted backcrossing (MABC). Transfer ...
... markers are used as a substitute for phenotypic selection and to accelerate the release of improved cultivars. Marker-assisted selection (MAS). Selection of individuals with specific alleles for traits controlled by a limited number of loci (up to 6-8). Marker-assisted backcrossing (MABC). Transfer ...
Crop Improvement and Management Research Program
... productivity have also seemed to plateau in the last decade. The conflation of these factors in 2007 saw rises in global food prices caused by supply shortages. This crisis impacted most heavily on the poor, who have the least amount of flexibility to cater for price rises of staple foods. For broad ...
... productivity have also seemed to plateau in the last decade. The conflation of these factors in 2007 saw rises in global food prices caused by supply shortages. This crisis impacted most heavily on the poor, who have the least amount of flexibility to cater for price rises of staple foods. For broad ...
Genetic Drift
... In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration) is the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another. Migration into or out of a population may be responsible for a marked change in allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). ...
... In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration) is the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another. Migration into or out of a population may be responsible for a marked change in allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). ...























