Special_Senses__Ch_8__S2015
... Sensory receptors are specialized to detect certain types of stimuli. Can be modified dendrites of sensory neurons or specialized cells that release neurotransmitters that stimulate nearby sensory neuron. – Exteroceptors detect stimuli outside the body. Taste, smell, vision. Indirectly linked to ...
... Sensory receptors are specialized to detect certain types of stimuli. Can be modified dendrites of sensory neurons or specialized cells that release neurotransmitters that stimulate nearby sensory neuron. – Exteroceptors detect stimuli outside the body. Taste, smell, vision. Indirectly linked to ...
No Slide Title
... glycoproteins; penetrate through membrane For protein & charged hormones (peptides or neurotransmitters) What are the main types of receptors? ...
... glycoproteins; penetrate through membrane For protein & charged hormones (peptides or neurotransmitters) What are the main types of receptors? ...
Lesson 10: Innate Immunity/ Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
... • Responses of the innate system are activated by protein receptors (Toll-like receptors) on the plasma membrane of defensive cells • Toll-like receptors (TLRs) recognize various components found on/in pathogens (pathogenassociated molecular patterns) • Examples of PAMPs ...
... • Responses of the innate system are activated by protein receptors (Toll-like receptors) on the plasma membrane of defensive cells • Toll-like receptors (TLRs) recognize various components found on/in pathogens (pathogenassociated molecular patterns) • Examples of PAMPs ...
Cell Test Review - Okemos Public Schools
... 18. Skin contains fat tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue. What level of organization is skin? 19. A slide containing muscle tissue would contain what type of cells? 20. Trace the path of a protein from its making to it’s exit out of a cell. ...
... 18. Skin contains fat tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue. What level of organization is skin? 19. A slide containing muscle tissue would contain what type of cells? 20. Trace the path of a protein from its making to it’s exit out of a cell. ...
4 How substances get in and out of cells
... (b) Eventually, the gas will be evenly distributed between the two containers so each one will contain 0.5g per litre. 2 The salt molecules will move by diffusion till they are evenly distributed. ...
... (b) Eventually, the gas will be evenly distributed between the two containers so each one will contain 0.5g per litre. 2 The salt molecules will move by diffusion till they are evenly distributed. ...
The Cell in Action
... The Cell Cycle • Cell cycle is the life cycle of a cell. • DNA is made up of chromosomes. • Chromosomes are copied which ensures that the new cells have the exact DNA as the parent cells. • Prokaryotic cells are less complicated and may split by binary fission. The cell splits into two and each new ...
... The Cell Cycle • Cell cycle is the life cycle of a cell. • DNA is made up of chromosomes. • Chromosomes are copied which ensures that the new cells have the exact DNA as the parent cells. • Prokaryotic cells are less complicated and may split by binary fission. The cell splits into two and each new ...
M6697 - Sigma
... apoptosis, can be a regulated and programmed mechanism.1 One specific form of programmed necrosis that depends on the serine/threonine kinase activity of RIP kinase proteins was termed necroptosis.2 RIP3 has been identified as a key protein in TNF-induced necroptosis and MLKL (mixed lineage kinase d ...
... apoptosis, can be a regulated and programmed mechanism.1 One specific form of programmed necrosis that depends on the serine/threonine kinase activity of RIP kinase proteins was termed necroptosis.2 RIP3 has been identified as a key protein in TNF-induced necroptosis and MLKL (mixed lineage kinase d ...
Common Characteristics of cells
... Ribosomes are the proteins involve in conversion of genetic information into protein. Two types of ribosomes exist within the cell: free ribosome (located in the cytosol and bound ribosome (attached to endoplasmic reticulum). ...
... Ribosomes are the proteins involve in conversion of genetic information into protein. Two types of ribosomes exist within the cell: free ribosome (located in the cytosol and bound ribosome (attached to endoplasmic reticulum). ...
Chemistry Comes Alive: Part B Classes of Compounds • Inorganic
... • Contain C, H, O, N, and sometimes S and P Structural Levels of Proteins Fibrous and Globular Proteins • Fibrous (structural) proteins • Strandlike, water insoluble, and stable • Examples: keratin, elastin, collagen, and certain contractile fibers ...
... • Contain C, H, O, N, and sometimes S and P Structural Levels of Proteins Fibrous and Globular Proteins • Fibrous (structural) proteins • Strandlike, water insoluble, and stable • Examples: keratin, elastin, collagen, and certain contractile fibers ...
Chemical biology beyond binary codes
... interaction is between one of the `effector' loops (necessary for binding to the FK506^FKBP12 target calcineurin) and the FK506 binding site [1]. The FKBP-Met36 mutant could be used in an alternative, negative dimerization system, complementary to the FK1012 induced dimerizer FKBP12. So for instance ...
... interaction is between one of the `effector' loops (necessary for binding to the FK506^FKBP12 target calcineurin) and the FK506 binding site [1]. The FKBP-Met36 mutant could be used in an alternative, negative dimerization system, complementary to the FK1012 induced dimerizer FKBP12. So for instance ...
Internal Structure: Bacteria have a very simple internal structure, and
... - Capsule – Protective layer of polysaccharides (and sometimes proteins) around the cell. It is often associated with pathogenic bacteria because it serves as a barrier against phagocytosis by leukocytes (white blood cells). - Outer membrane – This lipid bilayer is found in Gram negative bacteria & ...
... - Capsule – Protective layer of polysaccharides (and sometimes proteins) around the cell. It is often associated with pathogenic bacteria because it serves as a barrier against phagocytosis by leukocytes (white blood cells). - Outer membrane – This lipid bilayer is found in Gram negative bacteria & ...
No Slide Title
... disposal system contain enzymes that break apart nearly all cell molecules. digest worn out cell parts If the lysosome breaks, it can destroy the cell! ...
... disposal system contain enzymes that break apart nearly all cell molecules. digest worn out cell parts If the lysosome breaks, it can destroy the cell! ...
Nerve Hormone WebQuest 2015
... 41. What happens to the cortex, hippocampus and ventricles when a person suffers from Alzheimer’s ...
... 41. What happens to the cortex, hippocampus and ventricles when a person suffers from Alzheimer’s ...
Chapter_Twenty_1_
... 2. Unlike most amino acids, thyroxine is nonpolar and can cross the cell membrane. Iodine deficiency results in goiter and cretinism. – Thyroxine, is one of two iodine-containing hormones produced by the thyroid gland. ...
... 2. Unlike most amino acids, thyroxine is nonpolar and can cross the cell membrane. Iodine deficiency results in goiter and cretinism. – Thyroxine, is one of two iodine-containing hormones produced by the thyroid gland. ...
File
... 10. Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products 11. Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists 12. Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 13. Packages proteins for transport out of the cell 14. Produces lipids ...
... 10. Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products 11. Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists 12. Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 13. Packages proteins for transport out of the cell 14. Produces lipids ...
Cellular Transport PowerPoint
... decrease in turgor pressure will occur; so it is plasmolyzed. › Turgor pressure = internal pressure of a ...
... decrease in turgor pressure will occur; so it is plasmolyzed. › Turgor pressure = internal pressure of a ...
PDF
... Precise orchestration of palate formation involves the complex interaction of signalling cascades and transcriptional networks in the developing craniofacial region. Pax9 and Osr2 have previously been implicated in palate formation, but little is known about how these molecular components interact w ...
... Precise orchestration of palate formation involves the complex interaction of signalling cascades and transcriptional networks in the developing craniofacial region. Pax9 and Osr2 have previously been implicated in palate formation, but little is known about how these molecular components interact w ...
Biology 155 Practice Exam 1
... 36. Which organelle has a double membrane structure? a. chloroplast b. ribosome c. centiole d. endoplasmic reticulum 37. Which does NOT have microtubules as an important part of its structure? a. lysosome b. cytoskeleton c. centrioles d. basal body 38. Cells of the small intestine synthesize and sec ...
... 36. Which organelle has a double membrane structure? a. chloroplast b. ribosome c. centiole d. endoplasmic reticulum 37. Which does NOT have microtubules as an important part of its structure? a. lysosome b. cytoskeleton c. centrioles d. basal body 38. Cells of the small intestine synthesize and sec ...
Cells Questions - misslongscience
... Contain chlorophyll which absorbs light to make food by photosynthesis 11. What is a specialised cell? Cells that are adapted to carry out specific jobs 12. What is the job of a sperm cell and how is it adapted to do it? To fertilise an egg. Adaptations: tail to swim; full of mitochondria which prov ...
... Contain chlorophyll which absorbs light to make food by photosynthesis 11. What is a specialised cell? Cells that are adapted to carry out specific jobs 12. What is the job of a sperm cell and how is it adapted to do it? To fertilise an egg. Adaptations: tail to swim; full of mitochondria which prov ...
Chapter 7 Review List
... Define, describe, state the function, be able to identify, know the structure. ...
... Define, describe, state the function, be able to identify, know the structure. ...
File
... Do Now 1. Plant cells are usually rectangular while animal cells can be round or any other shape 2. The “brain” of the cell that tells it what to do 3. Organisms made of animal cells get their food (& energy) by consuming other organisms. Organisms made of plant cells perform photosynthesis to turn ...
... Do Now 1. Plant cells are usually rectangular while animal cells can be round or any other shape 2. The “brain” of the cell that tells it what to do 3. Organisms made of animal cells get their food (& energy) by consuming other organisms. Organisms made of plant cells perform photosynthesis to turn ...
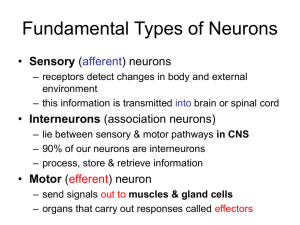
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.