Cell Transport and Division
... from phase to phase during the cell cycle • Some enzymes work to replicate DNA, some begin cell division, and others control the rest of the cell cycle ...
... from phase to phase during the cell cycle • Some enzymes work to replicate DNA, some begin cell division, and others control the rest of the cell cycle ...
Cell Transport (Diffusion and Osmosis)
... Two Kinds of Transport: • 1. Passive (Diffusion): materials move from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration, without energy expenditure by the cell. • 2. Active: movement of substances against concentration gradients (from low to high), requiring the expenditure of energ ...
... Two Kinds of Transport: • 1. Passive (Diffusion): materials move from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration, without energy expenditure by the cell. • 2. Active: movement of substances against concentration gradients (from low to high), requiring the expenditure of energ ...
Chapter 4 (part 3)
... • Allosteric interaction occur when specific molecules bind a protein and modulates activity • Allosteric modulators or allosteric effectors • Bind reversibly to site separate from functional binding or active site • Modulation of activity occurs through change in protein conformation • 2,3 bisphosp ...
... • Allosteric interaction occur when specific molecules bind a protein and modulates activity • Allosteric modulators or allosteric effectors • Bind reversibly to site separate from functional binding or active site • Modulation of activity occurs through change in protein conformation • 2,3 bisphosp ...
Cells
... Known as E.R., they are found in both plant and animal cells. These are passageways from the nucleus that transport proteins through the cell. Rough E.R. has ribosomes attached. Smooth E.R. does not have ribosomes attached. The ER is like a system of conveyors moving materials from one place to anot ...
... Known as E.R., they are found in both plant and animal cells. These are passageways from the nucleus that transport proteins through the cell. Rough E.R. has ribosomes attached. Smooth E.R. does not have ribosomes attached. The ER is like a system of conveyors moving materials from one place to anot ...
BIOLOGY ONE
... 69. What molecule is found in mitochondria & chloroplasts, & what does that allow them to do? 70. Contrast cilia & flagella. 71. What part of the cell is selectively permeable? What does that mean? 72. What is maintained due to selective permeability? 73. What are the 3 main components of the cell m ...
... 69. What molecule is found in mitochondria & chloroplasts, & what does that allow them to do? 70. Contrast cilia & flagella. 71. What part of the cell is selectively permeable? What does that mean? 72. What is maintained due to selective permeability? 73. What are the 3 main components of the cell m ...
Membrane Structure, Function and Transport Across Membranes
... excess water and then squirt it out. ...
... excess water and then squirt it out. ...
Genetik des Riechens und die Riech
... deorphanization of ORs concerning the activated ligands and by the small number of antibodies available. In contrast to the olfactory sensory neurons which are believed to express all 350 functional OR genes (only one OR type per cell), cells in nonolfactory tissues tend to express more than one ind ...
... deorphanization of ORs concerning the activated ligands and by the small number of antibodies available. In contrast to the olfactory sensory neurons which are believed to express all 350 functional OR genes (only one OR type per cell), cells in nonolfactory tissues tend to express more than one ind ...
Biology
... are made of very long double helix molecules called ______________________ and protein. When a cell divides these structures coil up tightly and become visible especially if they have been stained. When a cell is not dividing, the DNA is loosely coiled and appear as dense granular patches called chr ...
... are made of very long double helix molecules called ______________________ and protein. When a cell divides these structures coil up tightly and become visible especially if they have been stained. When a cell is not dividing, the DNA is loosely coiled and appear as dense granular patches called chr ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Na+ Channels Close, K+ Channels Open & K+ Diffuses Out of Neuron Results In Repolarization (+ outside/- inside) Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Na+ Channels Close, K+ Channels Open & K+ Diffuses Out of Neuron Results In Repolarization (+ outside/- inside) Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Na+ Channels Close, K+ Channels Open & K+ Diffuses Out of Neuron Results In Repolarization (+ outside/- inside) Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Na+ Channels Close, K+ Channels Open & K+ Diffuses Out of Neuron Results In Repolarization (+ outside/- inside) Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
Cell Biology - This area is password protected
... Fills the interior of the cell. It consists of a liquid (called the _________ that contains water, proteins and dissolved ions) and cell organelles. It is used to transport substances throughout the cell and create internal pressure and is where most chemical _______________ occur. Nucleus contains ...
... Fills the interior of the cell. It consists of a liquid (called the _________ that contains water, proteins and dissolved ions) and cell organelles. It is used to transport substances throughout the cell and create internal pressure and is where most chemical _______________ occur. Nucleus contains ...
Pathology - U
... lymphocytes, granulocytes, eosinophils, or macrophages, wherein the Fc receptor reacts with the Fc portion of the antibody molecule. c. Antibody-Mediated Cellular Dysfunction. Antibodies bind to antigen and impair function without evoking secondary reactions. (ex. Grave’s disease) 6) Understand comp ...
... lymphocytes, granulocytes, eosinophils, or macrophages, wherein the Fc receptor reacts with the Fc portion of the antibody molecule. c. Antibody-Mediated Cellular Dysfunction. Antibodies bind to antigen and impair function without evoking secondary reactions. (ex. Grave’s disease) 6) Understand comp ...
Option A Cerebral Cortex and Senses
... Sensory Receptors, cont. • Chemoreceptors- respond to chemical substances – Taste and smell – In Blood vessels- detect pH changes – Damaged tissue- pain receptors respond to chemicals secreted by damaged tissue – Olfactory receptors- smell ...
... Sensory Receptors, cont. • Chemoreceptors- respond to chemical substances – Taste and smell – In Blood vessels- detect pH changes – Damaged tissue- pain receptors respond to chemicals secreted by damaged tissue – Olfactory receptors- smell ...
Endocrine System PPT
... Different Types of Hormones • The two major types of hormones found in living organisms are steroid hormones and peptide hormones. These work differently when targeting cells. 1. Steroid (lipid-based) hormones – steroid hormones are lipidbased, so they can easily pass through the phospholipid bilay ...
... Different Types of Hormones • The two major types of hormones found in living organisms are steroid hormones and peptide hormones. These work differently when targeting cells. 1. Steroid (lipid-based) hormones – steroid hormones are lipidbased, so they can easily pass through the phospholipid bilay ...
lecture notes-molecular biology-web
... Cell level-role of cell receptors in metabolism and cellular differentiation - Almost all cells have receptors (protein) on their surfaces providing a cell with information about its environment. - Surface receptor can bind a chemical in the extracellular space which control the direction of cell mo ...
... Cell level-role of cell receptors in metabolism and cellular differentiation - Almost all cells have receptors (protein) on their surfaces providing a cell with information about its environment. - Surface receptor can bind a chemical in the extracellular space which control the direction of cell mo ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Golgi vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane. Lipids and proteins of a vesicle’s membrane fuse with the plasma membrane, and the vesicle’s contents are released to the exterior of the cell. ...
... Golgi vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane. Lipids and proteins of a vesicle’s membrane fuse with the plasma membrane, and the vesicle’s contents are released to the exterior of the cell. ...
Credit: Duane Froese, ScienceDaily Aug. 28, 2007
... http://www.aber.ac.uk/gwydd-cym/graffeg/biolgell/cludiant/collenchyma.jpg ...
... http://www.aber.ac.uk/gwydd-cym/graffeg/biolgell/cludiant/collenchyma.jpg ...
Animal Cell Culture
... • Has cytoskeleton or system of protein filaments (actin filaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules)-provide cell mechanical strength, control shape and guide cell movement. • Some animal cells contain cilia- used to transport substrate across the cell surface. ...
... • Has cytoskeleton or system of protein filaments (actin filaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules)-provide cell mechanical strength, control shape and guide cell movement. • Some animal cells contain cilia- used to transport substrate across the cell surface. ...
Access Slides - Science Signaling
... trisphosphate, which mobilizes Ca2+, and diacylglycerol (DAG), which activates protein kinase C (PKC). PAR1 can activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by transactivation of the EGF receptor, through activation of PKC, phosphatidylinositol 3kinase (PI3K), Pyk2, and other mechanisms. G ...
... trisphosphate, which mobilizes Ca2+, and diacylglycerol (DAG), which activates protein kinase C (PKC). PAR1 can activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by transactivation of the EGF receptor, through activation of PKC, phosphatidylinositol 3kinase (PI3K), Pyk2, and other mechanisms. G ...
Peripheral nervous system
... • tau protein - internal protein that normally maintain transport microtubules could cause tangles when mutated ...
... • tau protein - internal protein that normally maintain transport microtubules could cause tangles when mutated ...
Calcium is a universal second messenger, and changes in
... concentration ([Ca2+]i) triggers a wide spectrum of cellular responses including a long-lasting modification of synaptic transmission and changes in cellular excitability and gene expression that may lead to changes in the transmission of nociceptive stimuli. The intracellular calcium stores, such a ...
... concentration ([Ca2+]i) triggers a wide spectrum of cellular responses including a long-lasting modification of synaptic transmission and changes in cellular excitability and gene expression that may lead to changes in the transmission of nociceptive stimuli. The intracellular calcium stores, such a ...
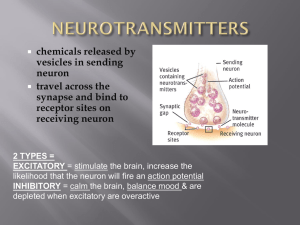
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.