Presentazione di PowerPoint
... lymphocytes that is highly conserved, and well evident in both human and murine species. The term 'NKT cells' was first used to describe a small subset of the T lymphocytes that coexpressed some markers traditionally associated with NK cells. The most prominent of these markers was the NK1.1 ant ...
... lymphocytes that is highly conserved, and well evident in both human and murine species. The term 'NKT cells' was first used to describe a small subset of the T lymphocytes that coexpressed some markers traditionally associated with NK cells. The most prominent of these markers was the NK1.1 ant ...
biochem ch 44B [9-2
... o Individual growth factor may stimulate proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of progenitor cells and may also prevent apoptosis; factors may activate various functions within mature cell; some growth factors act on multiple lineages, whereas others have more limited targets o Leukemias ar ...
... o Individual growth factor may stimulate proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of progenitor cells and may also prevent apoptosis; factors may activate various functions within mature cell; some growth factors act on multiple lineages, whereas others have more limited targets o Leukemias ar ...
Monkemeier / Senko - Madison Public Schools
... - What happens when a cell grows larger and what causes it to divide into two smaller cells rather than growing infinitely larger? - What limits cell size? Objective: Demonstrate that as a cell grows, the cell membrane does not increase in size as fast as the volume of a cell. Vocabulary: Define and ...
... - What happens when a cell grows larger and what causes it to divide into two smaller cells rather than growing infinitely larger? - What limits cell size? Objective: Demonstrate that as a cell grows, the cell membrane does not increase in size as fast as the volume of a cell. Vocabulary: Define and ...
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... diffusion of hydrophobic (lipids) molecules high low concentration gradient ...
... diffusion of hydrophobic (lipids) molecules high low concentration gradient ...
Nervous System Study Guide
... and potassium amount inside and outside of neuron cell. 6. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of sodium amount outside and inside the cell? 7. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of K+ ions inside and outside the neuron cell? 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potentia ...
... and potassium amount inside and outside of neuron cell. 6. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of sodium amount outside and inside the cell? 7. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of K+ ions inside and outside the neuron cell? 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potentia ...
3D Cell Model Project
... I) MODEL – Make a 3 dimensional model of a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell. SHOW all parts listed (see below) and label all parts. You can choose who to work with in your table group. You will briefly present your model to the class. Use common household and/or recyclable materials such as Styrofoam ...
... I) MODEL – Make a 3 dimensional model of a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell. SHOW all parts listed (see below) and label all parts. You can choose who to work with in your table group. You will briefly present your model to the class. Use common household and/or recyclable materials such as Styrofoam ...
Biology Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function
... F. Fluid Mosaic Model 1. Bilayer allows other molecules to “float” in membrane ...
... F. Fluid Mosaic Model 1. Bilayer allows other molecules to “float” in membrane ...
Bacterial physiology
... Most foods naturally contain sufficient moisture to provide bacteria with the water they need in order to grow. Where moisture has been deliberately removed (e.g. in dehydrated foods such as milk powder, soup mixes, etc.), then bacteria will not grow whilst the food remains dry, but once water is ad ...
... Most foods naturally contain sufficient moisture to provide bacteria with the water they need in order to grow. Where moisture has been deliberately removed (e.g. in dehydrated foods such as milk powder, soup mixes, etc.), then bacteria will not grow whilst the food remains dry, but once water is ad ...
Verification of Real Time Systems
... – Phosphorylation (Activation of proteins) – Dephosphorylation (Deactivation of proteins) – Methylation and acetylation (Gene silencing. Plays a role in cell differentiation) – Cleavage (Cutting of genes and proteins. For degradation and apoptosis) – Ubiquitination (Marking of proteins for further ...
... – Phosphorylation (Activation of proteins) – Dephosphorylation (Deactivation of proteins) – Methylation and acetylation (Gene silencing. Plays a role in cell differentiation) – Cleavage (Cutting of genes and proteins. For degradation and apoptosis) – Ubiquitination (Marking of proteins for further ...
E.2 - Perception of Stimuli
... visual cortex through the optic nerve. Some ganglia are sensitive to impulses from the edge of the receptive field, where others are sensitive to impulses from the centre. Edge enhancement (due to lateral inhibition of cells in the retina) results in greater ...
... visual cortex through the optic nerve. Some ganglia are sensitive to impulses from the edge of the receptive field, where others are sensitive to impulses from the centre. Edge enhancement (due to lateral inhibition of cells in the retina) results in greater ...
Cell City Analogy
... 6. The jelly-like area between the nucleus and the cell membrane is called the cytoplasm. It fills the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane. a) What company or place does the cytoplasm resemble in a Cell City? b) Why do you think so? a)______________________________________ b)____________ ...
... 6. The jelly-like area between the nucleus and the cell membrane is called the cytoplasm. It fills the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane. a) What company or place does the cytoplasm resemble in a Cell City? b) Why do you think so? a)______________________________________ b)____________ ...
Most living things are made up of cells. Cells are the building blocks
... Most living things are made up of cells. Cells are the building blocks of organisms in the same way that bricks are the building blocks of houses. Nearly all living cells have three features in common: • A nucleus. This is bounded by a nuclear membrane and contains threadlike chromosomes made of the ...
... Most living things are made up of cells. Cells are the building blocks of organisms in the same way that bricks are the building blocks of houses. Nearly all living cells have three features in common: • A nucleus. This is bounded by a nuclear membrane and contains threadlike chromosomes made of the ...
Cell Organelles
... • Despite our complexity, we begin our lives as single cells. • Questions about life – from ecology to behavior, from evolution to reproduction – must be partly answered at the level of the cell because cells are the basic units of life. ...
... • Despite our complexity, we begin our lives as single cells. • Questions about life – from ecology to behavior, from evolution to reproduction – must be partly answered at the level of the cell because cells are the basic units of life. ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... soluble in lipids can pass through this layer. • O2 and CO2 can pass through easily but water-soluble molecules, such as amino acids, sugars, proteins, nucleic acids, and various ions, cannot pass through. • Cholesterol molecules help to stabilize the membrane. ...
... soluble in lipids can pass through this layer. • O2 and CO2 can pass through easily but water-soluble molecules, such as amino acids, sugars, proteins, nucleic acids, and various ions, cannot pass through. • Cholesterol molecules help to stabilize the membrane. ...
Categories - OISEIntermediateScience
... of ideas and information (e.g., clear expression, logical organization is oral, visual and written forms) ...
... of ideas and information (e.g., clear expression, logical organization is oral, visual and written forms) ...
File
... synapses to make it more efficient During adolescence your brain has a major tidy-up and gets rid of lots of ...
... synapses to make it more efficient During adolescence your brain has a major tidy-up and gets rid of lots of ...
Life Science Cell Structure, Function, Bacteria, Virus Chapter 7
... 17. Ribosomes – The protein factories that make protein for the cell are called ribosomes. They look like tiny dense dots and are found along the endoplasmic reticulum, or simply floating in the cytoplasm. (143) 18. Golgi Bodies – Golgi bodies receive and packages materials like protein from the ER ...
... 17. Ribosomes – The protein factories that make protein for the cell are called ribosomes. They look like tiny dense dots and are found along the endoplasmic reticulum, or simply floating in the cytoplasm. (143) 18. Golgi Bodies – Golgi bodies receive and packages materials like protein from the ER ...
1 - Spokane Public Schools
... 17. Ribosomes – The protein factories that make protein for the cell are called ribosomes. They look like tiny dense dots and are found along the endoplasmic reticulum, or simply floating in the cytoplasm. (143) 18. Golgi Bodies – Golgi bodies receive and packages materials like protein from the ER ...
... 17. Ribosomes – The protein factories that make protein for the cell are called ribosomes. They look like tiny dense dots and are found along the endoplasmic reticulum, or simply floating in the cytoplasm. (143) 18. Golgi Bodies – Golgi bodies receive and packages materials like protein from the ER ...
Proteins and Amino Acids: Function Follows Form
... Proteins in the Body • Amino Acid Pool and Protein Turnover – Cells in your body constantly build and breakdown proteins ______________________________ • ____________________: because we are always recycling our proteins, we need so little protein in our ...
... Proteins in the Body • Amino Acid Pool and Protein Turnover – Cells in your body constantly build and breakdown proteins ______________________________ • ____________________: because we are always recycling our proteins, we need so little protein in our ...
proteins
... Manganese: activator of enzymes Copper: constituent of enzymes, component of haemocyanin Iodine: component of thyroxine, (from sea food, salt) Cobalt: component of vitamin B Zinc: activator of enzymes Fluorine: component of bones & teeth ...
... Manganese: activator of enzymes Copper: constituent of enzymes, component of haemocyanin Iodine: component of thyroxine, (from sea food, salt) Cobalt: component of vitamin B Zinc: activator of enzymes Fluorine: component of bones & teeth ...
Slide
... • Taste system; salt and acids use ionic channels • Other taste receptors use GPCRs • The neural coding for taste system uses a labeled line code ...
... • Taste system; salt and acids use ionic channels • Other taste receptors use GPCRs • The neural coding for taste system uses a labeled line code ...
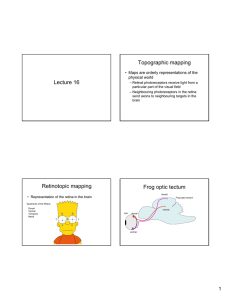
Lecture 16 Topographic mapping Retinotopic mapping Frog optic
... • Retinal neurons with low receptors go to areas of tectum with high ligand • Retinal neurons with high receptors go to areas of tectum with low ligand ...
... • Retinal neurons with low receptors go to areas of tectum with high ligand • Retinal neurons with high receptors go to areas of tectum with low ligand ...
Organic Macromolecules
... different numbers and types of monomers called amino acids A typical protein contains 200–300 amino acids but some are much smaller. the smallest are often called peptides some much larger (the largest to date is titin a protein found in skeletal and cardiac muscle; it contains 26,926 amino acid ...
... different numbers and types of monomers called amino acids A typical protein contains 200–300 amino acids but some are much smaller. the smallest are often called peptides some much larger (the largest to date is titin a protein found in skeletal and cardiac muscle; it contains 26,926 amino acid ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.