Ribosomes and In Vivo Folding
... So successful transit requires the chain not reach native conformation: SecB >>tetramer; binds newly synthesized chain for many proteins; Does not bind correctly folded native state. Chaperonin>>retard folding (Linda Randall) SecB protein rec C. Folding Pathways evolved through biological evolution ...
... So successful transit requires the chain not reach native conformation: SecB >>tetramer; binds newly synthesized chain for many proteins; Does not bind correctly folded native state. Chaperonin>>retard folding (Linda Randall) SecB protein rec C. Folding Pathways evolved through biological evolution ...
Lecture 7: Signal Transduction
... – Ri = the inactivated receptor (cannot be activated) – Rs = the susceptible receptor (can be activated) – Ra = the activated receptor (bound to the ligand) ...
... – Ri = the inactivated receptor (cannot be activated) – Rs = the susceptible receptor (can be activated) – Ra = the activated receptor (bound to the ligand) ...
49_DetailLectOut_jkAR
... The conversion of stimulus energy into a change in membrane potential of a sensory receptor is sensory transduction. The change in membrane potential itself is receptor potential. Receptor potentials are graded potentials; their magnitude varies with the strength of the stimulus. All receptor po ...
... The conversion of stimulus energy into a change in membrane potential of a sensory receptor is sensory transduction. The change in membrane potential itself is receptor potential. Receptor potentials are graded potentials; their magnitude varies with the strength of the stimulus. All receptor po ...
Annexure `CD-01` L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 0 0 0 3
... Student Learning Outcomes: After successfully completing this unit, the student should 1. Be able to apply knowledge of chemistry and biology to solve biochemical problems. 2. .Students will be able to distinguish among carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids with respect to chemical stru ...
... Student Learning Outcomes: After successfully completing this unit, the student should 1. Be able to apply knowledge of chemistry and biology to solve biochemical problems. 2. .Students will be able to distinguish among carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids with respect to chemical stru ...
HveC (nectin-1) is expressed at high levels in sensory neurons, but
... amino acid type I membrane glycoprotein that is widely expressed in cells of epithelial and neuronal origin, and is nearly identical in sequence to nectin-1 (Shukla et al, 2000). The extracellular portion consists of three immunoglobulin-like domains (V-C2C2, from the N-terminal to the membrane prox ...
... amino acid type I membrane glycoprotein that is widely expressed in cells of epithelial and neuronal origin, and is nearly identical in sequence to nectin-1 (Shukla et al, 2000). The extracellular portion consists of three immunoglobulin-like domains (V-C2C2, from the N-terminal to the membrane prox ...
File
... C) peroxisome. D) Golgi apparatus. 36) An immune system cell called the plasma cell produces thousands of antibodies per second for release into the body. What type of intracellular structure would you expect to be very prominent within the cell? A) nucleus B) endoplasmic reticulum C) peroxisome D) ...
... C) peroxisome. D) Golgi apparatus. 36) An immune system cell called the plasma cell produces thousands of antibodies per second for release into the body. What type of intracellular structure would you expect to be very prominent within the cell? A) nucleus B) endoplasmic reticulum C) peroxisome D) ...
7.12D: Plant and Animal Cell Organelles A Framework for Funcčon
... an organelle inside the cell that guides all ac>vity. It is the most important part of the eukaryo>c cell’s existence because the nucleus contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which provides specific instruc>ons for the cell’s purpose and ac>ons. DNA tells the cell how to reproduce new cells and ...
... an organelle inside the cell that guides all ac>vity. It is the most important part of the eukaryo>c cell’s existence because the nucleus contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which provides specific instruc>ons for the cell’s purpose and ac>ons. DNA tells the cell how to reproduce new cells and ...
Lecture 3 – Membrane potential
... An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and the electrical gradient, or difference in charge across ...
... An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and the electrical gradient, or difference in charge across ...
CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CHEMISTRY FOR MICROBIOLOGY
... • The major energy molecule in cells is ATP. • It contains the nitrogenous base adenosine, a ribose sugar, and a chain of three phosphates bonded to the sugar. • The bonds between these phosphates are highenergy bonds that when broken yield energy. ...
... • The major energy molecule in cells is ATP. • It contains the nitrogenous base adenosine, a ribose sugar, and a chain of three phosphates bonded to the sugar. • The bonds between these phosphates are highenergy bonds that when broken yield energy. ...
Bma: Visual Tool for Modeling and Analyzing Biological
... Thus, a QN defines a transition system over Σ. All variables change their value synchronously by following their target functions. We abuse notation and write also T ∶ Σ → Σ as the function that associates with a state s its successor s′ . Each protein in the design corresponds to a variable in the ...
... Thus, a QN defines a transition system over Σ. All variables change their value synchronously by following their target functions. We abuse notation and write also T ∶ Σ → Σ as the function that associates with a state s its successor s′ . Each protein in the design corresponds to a variable in the ...
Resource 2
... Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Cell membranes of both plant and animal cells are made of protein and lipid. ...
... Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Cell membranes of both plant and animal cells are made of protein and lipid. ...
slides
... • All living cells have a cell (plasma) membrane, genetic information is stored in DNA and all are classified either as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. – prokaryotes lack a nucleus and other membraneenclosed structures, all are bacteria (archeobacteria are important ecologically). – eukaryotes have vario ...
... • All living cells have a cell (plasma) membrane, genetic information is stored in DNA and all are classified either as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. – prokaryotes lack a nucleus and other membraneenclosed structures, all are bacteria (archeobacteria are important ecologically). – eukaryotes have vario ...
Chapter 3-Cell Membrane Diffusion Osmosis
... Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell membrane. • Receptors bind with ligands and change shape. • There are two types of receptors. – intracellular receptor – membrane receptor ...
... Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell membrane. • Receptors bind with ligands and change shape. • There are two types of receptors. – intracellular receptor – membrane receptor ...
Additional Science Module B4 – What You Should Know
... I can recall that enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactionsBBC - GCSE Bitesize: Enzymes I can recall that cells make enzymes according to the instructions carried in genes I understand that molecules have to be the correct shape to fit into the active site of I the enzyme (the lock and k ...
... I can recall that enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactionsBBC - GCSE Bitesize: Enzymes I can recall that cells make enzymes according to the instructions carried in genes I understand that molecules have to be the correct shape to fit into the active site of I the enzyme (the lock and k ...
Prokaryotes
... Phylogenetic studies (16S rRNA, 23S rRNA, EF’s and b subunits of ATPase) have identified at least 23 major evolutionary divergences modes of generating cellular energy and nutrition are more superficial than other more basic housekeeping and basic biochemical functions Diversity is described i ...
... Phylogenetic studies (16S rRNA, 23S rRNA, EF’s and b subunits of ATPase) have identified at least 23 major evolutionary divergences modes of generating cellular energy and nutrition are more superficial than other more basic housekeeping and basic biochemical functions Diversity is described i ...
Plant and animal cells
... Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Cell membranes of both plant and animal cells are made of protein and lipid. ...
... Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Cell membranes of both plant and animal cells are made of protein and lipid. ...
Chapter 5.tst - HCC Learning Web
... 9) One of the primary functions of RNA molecules is to A) act as a pattern or blueprint to form DNA. B) transmit genetic information to offspring. C) function in the synthesis of proteins. D) make a copy of itself, thus ensuring genetic continuity. E) form the genes of higher organisms. 10) Which of ...
... 9) One of the primary functions of RNA molecules is to A) act as a pattern or blueprint to form DNA. B) transmit genetic information to offspring. C) function in the synthesis of proteins. D) make a copy of itself, thus ensuring genetic continuity. E) form the genes of higher organisms. 10) Which of ...
EFFECT OF NUTRIENTS ON THE GENE EXPRESSION: Nutri
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
PDF File of Transcript for Dawn Tamarkin`s Case Story
... Now if this is not an onion cell but instead it's a cheek cell, there's no cell wall because animal cells don't have it and students can bend this the right way, and put the nucleus in, maybe even show that they've kind of bend the cell a little sticking out on the slide. And even have some bacteria ...
... Now if this is not an onion cell but instead it's a cheek cell, there's no cell wall because animal cells don't have it and students can bend this the right way, and put the nucleus in, maybe even show that they've kind of bend the cell a little sticking out on the slide. And even have some bacteria ...
I. The Cell Membrane: II. Three Functions of the Cell Membrane
... 3. Isotonic: solution outside of the cell has the same concentration of particles and the same concentration of water ...
... 3. Isotonic: solution outside of the cell has the same concentration of particles and the same concentration of water ...
EOC Practice
... a) The snakes introduced to the region dominated the habitat, forcing the mice to find another place to live. b) The mice became prey to the introduced snakes, allowing the snake population to increase but decreasing the mice population. c) The people in the surrounding area stet traps that killed t ...
... a) The snakes introduced to the region dominated the habitat, forcing the mice to find another place to live. b) The mice became prey to the introduced snakes, allowing the snake population to increase but decreasing the mice population. c) The people in the surrounding area stet traps that killed t ...
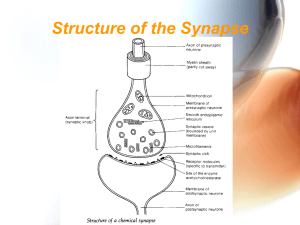
Structure of the Synapse
... threshold is reached then action potential is initated • Inhibitory ion channels - neuroreceptors are Cl- channels. When Cl- channels open, hyperpolarisation occurs, making action potential less likely • Non channel synapses - neuroreceptors are membrane-bound enzymes. When activated, they catalyse ...
... threshold is reached then action potential is initated • Inhibitory ion channels - neuroreceptors are Cl- channels. When Cl- channels open, hyperpolarisation occurs, making action potential less likely • Non channel synapses - neuroreceptors are membrane-bound enzymes. When activated, they catalyse ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.