Cell Size Limitations Notes1
... Diffusion limits size • An oxygen molecule follows a path to the mitochondria (Oxygen)… plasma membrane cytoplasm mitochondria ...
... Diffusion limits size • An oxygen molecule follows a path to the mitochondria (Oxygen)… plasma membrane cytoplasm mitochondria ...
Cell Physiology Spring 2016 Name: This test is
... 8) Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 9) Packages proteins for transport out of the cell 10) The membrane surrounding the cell 11) Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells 12) Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell 13) Small hair-like structure ...
... 8) Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 9) Packages proteins for transport out of the cell 10) The membrane surrounding the cell 11) Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells 12) Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell 13) Small hair-like structure ...
Intro to Cell Vocabulary
... cell membrane: delicate inner skin DNA in one big loop ribosomes: for building proteins ...
... cell membrane: delicate inner skin DNA in one big loop ribosomes: for building proteins ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems Gene Expression and Regulation
... 2. The amazing Dr. Johnston, yeast biologist extraordinaire, has discovered a new species of yeast that can grow on high-quality chocolate bars. Dr. Johnston’s new yeast species has three specific enzymes needed to break down lipids found in chocolate. a. Describe a process by which a yeast cell mig ...
... 2. The amazing Dr. Johnston, yeast biologist extraordinaire, has discovered a new species of yeast that can grow on high-quality chocolate bars. Dr. Johnston’s new yeast species has three specific enzymes needed to break down lipids found in chocolate. a. Describe a process by which a yeast cell mig ...
Cell Organelles and Functions
... Freely permeable to water and most solutes Only in Plant cells Maintains cell turgidity Provide mechanical support Protect from mechanical damage ...
... Freely permeable to water and most solutes Only in Plant cells Maintains cell turgidity Provide mechanical support Protect from mechanical damage ...
Active Transport vs. Passive Transport both processes move things
... Exocytosis: moves things out of cells by putting substance into vesicle the vesicle moves to cell membrane, fuses with cell membrane, is released to outside of cell these items are moved by bulk transport because they are too large to get in and out of the cell by diffusion examples are proteins, ho ...
... Exocytosis: moves things out of cells by putting substance into vesicle the vesicle moves to cell membrane, fuses with cell membrane, is released to outside of cell these items are moved by bulk transport because they are too large to get in and out of the cell by diffusion examples are proteins, ho ...
Biological (organic) Molecules
... Examples: starch, glycogen, cellulose Consist of many monomers bonded together Used for energy storage and to build cell structures Broken down through cellular respiration to create energy (ATP) Test for complex sugars: use iodine: turns from brown to black in the presence of starch ...
... Examples: starch, glycogen, cellulose Consist of many monomers bonded together Used for energy storage and to build cell structures Broken down through cellular respiration to create energy (ATP) Test for complex sugars: use iodine: turns from brown to black in the presence of starch ...
Matchgame, Vocabulary Review
... The final process of the basic scientific method by which scientists reveal whether the hypothesis was proven correct. The conclusion is one statement, backed up by data analysis, that supports or refutes the hypothesis. ...
... The final process of the basic scientific method by which scientists reveal whether the hypothesis was proven correct. The conclusion is one statement, backed up by data analysis, that supports or refutes the hypothesis. ...
ABSTRACT Mast cells are critical component of the immune system
... activation at molecular level is important for design of new therapies of allergic diseases. Principal transmembrane receptor of mast cells is the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgE (FcεRI). FcεRI anchors IgE on mast cell surface and upon cross-linking with multivalent antigen it becomes phosphorylat ...
... activation at molecular level is important for design of new therapies of allergic diseases. Principal transmembrane receptor of mast cells is the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgE (FcεRI). FcεRI anchors IgE on mast cell surface and upon cross-linking with multivalent antigen it becomes phosphorylat ...
ap® biology 2015 scoring guidelines
... Smell perception in mammals involves the interactions of airborne odorant molecules from the environment with receptor proteins on the olfactory neurons in the nasal cavity. The binding of odorant molecules to the receptor proteins triggers action potentials in the olfactory neurons and results in t ...
... Smell perception in mammals involves the interactions of airborne odorant molecules from the environment with receptor proteins on the olfactory neurons in the nasal cavity. The binding of odorant molecules to the receptor proteins triggers action potentials in the olfactory neurons and results in t ...
Cell structure part B
... Synthesis of phospholipids and cholesterol Synthesis of steroid hormones Synthesis and storage of triglycerides Synthesis and storage of glycogen Storage of ions ( e.g. Ca++ in muscle) Detoxification and inactivation of drugs ...
... Synthesis of phospholipids and cholesterol Synthesis of steroid hormones Synthesis and storage of triglycerides Synthesis and storage of glycogen Storage of ions ( e.g. Ca++ in muscle) Detoxification and inactivation of drugs ...
handout: 7.2 reading guide
... 17) a) Which organelle captures the energy from sunlight? b) Which organisms contain this organelle? 18) a) Which organelle is responsible for releasing stored chemical energy? b) TRUE or FALSE (circle one). Only animal cells have mitochondria within their cells. 19) Which parent do you inherit all ...
... 17) a) Which organelle captures the energy from sunlight? b) Which organisms contain this organelle? 18) a) Which organelle is responsible for releasing stored chemical energy? b) TRUE or FALSE (circle one). Only animal cells have mitochondria within their cells. 19) Which parent do you inherit all ...
Nerve Cells
... • What is Parkinson's disease, and what is the mechanism for its development? How is parkinsonism treated? • How are neurotransmitters released at the synapse? What proteins are involved? Name the calcium ion sensor • Describe the Otto Loewi experiment and explain its significance. • What is myasthe ...
... • What is Parkinson's disease, and what is the mechanism for its development? How is parkinsonism treated? • How are neurotransmitters released at the synapse? What proteins are involved? Name the calcium ion sensor • Describe the Otto Loewi experiment and explain its significance. • What is myasthe ...
Cells ( Think of the analogy of the factory) Cell parts are called
... Chloroplasts: contain chlorophyll, givers plants green color; photosynthesis occur here. Photosynthesis: process by which green plants manufacture their own food. Plants use the energy from the sun to make glucose. Cell wall: provides structure and support for the cells. Every cell has its own cell ...
... Chloroplasts: contain chlorophyll, givers plants green color; photosynthesis occur here. Photosynthesis: process by which green plants manufacture their own food. Plants use the energy from the sun to make glucose. Cell wall: provides structure and support for the cells. Every cell has its own cell ...
A Level Biology
... Year 12 Course Content 1 Biological Molecules 1.1 Monomers and polymers 1.2 Carbohydrates 1.3 Lipids 1.4 Proteins 1.5 Nucleic Acids 1.6 ATP 1.7 Water 1.8 Inorganic ions 2 Cells 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 All cells arise from other cells 2.3 Transport across cell membranes 2.4 Cell recognition and the i ...
... Year 12 Course Content 1 Biological Molecules 1.1 Monomers and polymers 1.2 Carbohydrates 1.3 Lipids 1.4 Proteins 1.5 Nucleic Acids 1.6 ATP 1.7 Water 1.8 Inorganic ions 2 Cells 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 All cells arise from other cells 2.3 Transport across cell membranes 2.4 Cell recognition and the i ...
Cell Junctions II
... Fibronectin is an extracellular protein that helps cells attach to the matrix ...
... Fibronectin is an extracellular protein that helps cells attach to the matrix ...
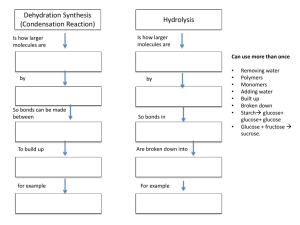
Can use more than once
... Hydrophobic Tails Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Steak ...
... Hydrophobic Tails Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Steak ...
What is a Cell?
... Thought to be more related to animals then plants Most are symbiotic Lacks organs Reproduce sexually or asexually Many are used in everyday human life ...
... Thought to be more related to animals then plants Most are symbiotic Lacks organs Reproduce sexually or asexually Many are used in everyday human life ...
Unit 1 Review
... (b) amino group, carboxyl group 20. All of them— horse hoofs, spider webs, and egg whites— are composed of proteins. 21. (a) The identity of a protein depends on the number and the sequence of amino acids in its structure. W ith 20 different amino acids to choose from, a polypeptide 200 amino acids ...
... (b) amino group, carboxyl group 20. All of them— horse hoofs, spider webs, and egg whites— are composed of proteins. 21. (a) The identity of a protein depends on the number and the sequence of amino acids in its structure. W ith 20 different amino acids to choose from, a polypeptide 200 amino acids ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.