nuclear region
... • Food, contractile and central vacuoles • Certain plants have vacuoles that act as disposal sites for “toxic” metabolic byproducts • Others hold pigments that determine the petal color of flowers • Defense mechanism to make plant unpalatable to animals ...
... • Food, contractile and central vacuoles • Certain plants have vacuoles that act as disposal sites for “toxic” metabolic byproducts • Others hold pigments that determine the petal color of flowers • Defense mechanism to make plant unpalatable to animals ...
Topic 3
... In this segregation series, cells that aggregate more towards the interior have a greater surface tension score (dyne/cm) than do the cells in the outer later. These differences in surface tension suggest one mechanism by which differentiation may proceed. ...
... In this segregation series, cells that aggregate more towards the interior have a greater surface tension score (dyne/cm) than do the cells in the outer later. These differences in surface tension suggest one mechanism by which differentiation may proceed. ...
(1-4) D-glucose, a
... ZP3 glycoprotein in extracellular coat of ovulated eggs a-linked galactose at the non-reducing end Binding triggers release of sperm enzymes, dissolves zona pellucida to allow sperm to enter ...
... ZP3 glycoprotein in extracellular coat of ovulated eggs a-linked galactose at the non-reducing end Binding triggers release of sperm enzymes, dissolves zona pellucida to allow sperm to enter ...
H/Ws 1 to 4
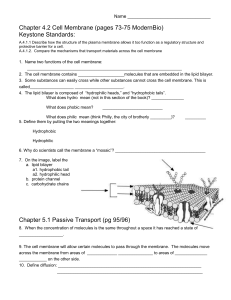
... A: This arrangement allows for a stable boundary between two aqueous compartments (water inside and outside of the cell). Q: Where do the proteins fit in the membrane? A: The difference in adherence of the cell membrane (CM), to water is due to the hydrophilic proteins in the membrane. Only the hydr ...
... A: This arrangement allows for a stable boundary between two aqueous compartments (water inside and outside of the cell). Q: Where do the proteins fit in the membrane? A: The difference in adherence of the cell membrane (CM), to water is due to the hydrophilic proteins in the membrane. Only the hydr ...
Cell Organelles - Smyth County Virginia Public Schools
... • Food vacuoles form when cell engulfs material from outside cell (phagocytosis) • Plant cell vacuoles surrounded by membrane called tonoplast – Used as storage for cell wastes, water – Get larger by merging with smaller vacuoles – Occupy most of volume of plant cell, cytosol is thin region between ...
... • Food vacuoles form when cell engulfs material from outside cell (phagocytosis) • Plant cell vacuoles surrounded by membrane called tonoplast – Used as storage for cell wastes, water – Get larger by merging with smaller vacuoles – Occupy most of volume of plant cell, cytosol is thin region between ...
CELLS
... Composed of a phospholipid bilayer that has proteins embedded in it Cholesterol is also an important component of cell membranes since it keeps the membrane intact yet fluid The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and leave the cell ...
... Composed of a phospholipid bilayer that has proteins embedded in it Cholesterol is also an important component of cell membranes since it keeps the membrane intact yet fluid The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and leave the cell ...
MCAS BIOLOGY REVIEW Cell Biology
... jelly-like material around organelles finish & ship proteins make ATP in cellular respiration cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals ...
... jelly-like material around organelles finish & ship proteins make ATP in cellular respiration cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals ...
Syllabus
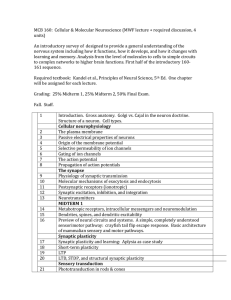
... An introductory survey of designed to provide a general understanding of the nervous system including how it functions, how it develops, and how it changes with learning and memory. Analysis from the ...
... An introductory survey of designed to provide a general understanding of the nervous system including how it functions, how it develops, and how it changes with learning and memory. Analysis from the ...
biology – ecology
... Map (Pg#221, Fig 8.4) Identify the role of the Mitochondria in Animal & Plant Cells (Pg#228, fig 8.11) Compare & Contrast Anaerobic Respiration with Aerobic, including the number of ATP’s that are produced in each using a Double Bubble Map (Pg#228-30) ...
... Map (Pg#221, Fig 8.4) Identify the role of the Mitochondria in Animal & Plant Cells (Pg#228, fig 8.11) Compare & Contrast Anaerobic Respiration with Aerobic, including the number of ATP’s that are produced in each using a Double Bubble Map (Pg#228-30) ...
Name
... 14. Isotonic means _____________________________ Hypertonic means ___________________________ Hypotonic means ____________________________ 15. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water (the water would be considered hypotonic), water will move ___________ of the cell. If that happens, ...
... 14. Isotonic means _____________________________ Hypertonic means ___________________________ Hypotonic means ____________________________ 15. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water (the water would be considered hypotonic), water will move ___________ of the cell. If that happens, ...
Cell Facts - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... organelles with membranes, complex ex: plants, protists, fungi, animals Cell Organelle ...
... organelles with membranes, complex ex: plants, protists, fungi, animals Cell Organelle ...
MP2 QUARTERLY EXAM STUDY GUIDE
... inside the cell is greater than outside the cell; water moves out & the cell shrinks ...
... inside the cell is greater than outside the cell; water moves out & the cell shrinks ...
Quiz 2 Review Sheet
... the four variables. Sample questions are in the PowerPoint. 9. Explain what happens to the size of the FOV under high power as compared to low power. Why does this happen? Why can one not use a ruler under high power to measure the FOV? 10. Explain the orientation of an object as viewed through a mi ...
... the four variables. Sample questions are in the PowerPoint. 9. Explain what happens to the size of the FOV under high power as compared to low power. Why does this happen? Why can one not use a ruler under high power to measure the FOV? 10. Explain the orientation of an object as viewed through a mi ...
Unit C Line Master 15
... 8.What happens as a cell increases in size? a. The surface area decreases. b. The volume of the cell decreases. c. The distance from the surface to the centre decreases. d. More molecules need to be transported across the cell surface. B. Written Response (6 marks) 9. Soft drinks may contain various ...
... 8.What happens as a cell increases in size? a. The surface area decreases. b. The volume of the cell decreases. c. The distance from the surface to the centre decreases. d. More molecules need to be transported across the cell surface. B. Written Response (6 marks) 9. Soft drinks may contain various ...
Gametogenesis, Fertilization and Blastula Formation
... For each cell that enters meiosis, 4 sperm cells are produced It is continuous for the reproductive life of a male and occurs in an uninterrupted sequence Sperm structure Head: contains the haploid nucleus and an acrosome—vesicle containing enzymes Middle piece: contains a long, spiral shaped mi ...
... For each cell that enters meiosis, 4 sperm cells are produced It is continuous for the reproductive life of a male and occurs in an uninterrupted sequence Sperm structure Head: contains the haploid nucleus and an acrosome—vesicle containing enzymes Middle piece: contains a long, spiral shaped mi ...
Dr. Begay`s Notes from Pharm I
... PHARMACODYNAMICS The study of the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs and their mechanism of action ...
... PHARMACODYNAMICS The study of the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs and their mechanism of action ...
Plasma Membrane and Cell Wall
... Location: membrane Found in together; the between the phosphate phospholipids heads are not in the bilayer. attached to each other ...
... Location: membrane Found in together; the between the phosphate phospholipids heads are not in the bilayer. attached to each other ...
Mech133-RvwMolecBasisNeoplasia
... A. the binding of a growth factor to its specific receptor on the cell membrane B. TRANSIENT and LIMITED activation of the growth factor receptor activates several signal transducing proteins on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane C. Transmission of the transduced signal across the cytosol to ...
... A. the binding of a growth factor to its specific receptor on the cell membrane B. TRANSIENT and LIMITED activation of the growth factor receptor activates several signal transducing proteins on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane C. Transmission of the transduced signal across the cytosol to ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... anvil, hammer and stirrup) that amplify the vibrations generated by the eardrum and transmit them to another membrane, the oval window. The inner ear, located within the ...
... anvil, hammer and stirrup) that amplify the vibrations generated by the eardrum and transmit them to another membrane, the oval window. The inner ear, located within the ...
Lesson 3.3 Glossary - Home of Joplin FFA
... Genes – The simplest unit of inheritance. Physically, each gene is apparently a nucleic acid with a unique structure. It influences certain traits. Golgi apparatus – A system of membranes in eukaryotic cells that modifies proteins for export by the cell. Guanine – One of the four bases of DNA; it pa ...
... Genes – The simplest unit of inheritance. Physically, each gene is apparently a nucleic acid with a unique structure. It influences certain traits. Golgi apparatus – A system of membranes in eukaryotic cells that modifies proteins for export by the cell. Guanine – One of the four bases of DNA; it pa ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.