cell membrane
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
Cellular respiration produces: ______ + ______ +
... Folded sacs that package and distribute material in the cell and also send materials outside the cell: ____________ 8. Three structures found only in plant cells: ____________, ____________, _____________ 9. Production of food in plant cells uses what material? _______________ 10. Production of food ...
... Folded sacs that package and distribute material in the cell and also send materials outside the cell: ____________ 8. Three structures found only in plant cells: ____________, ____________, _____________ 9. Production of food in plant cells uses what material? _______________ 10. Production of food ...
Vocabulary Flip Chart - Effingham County Schools
... symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed ...
... symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed ...
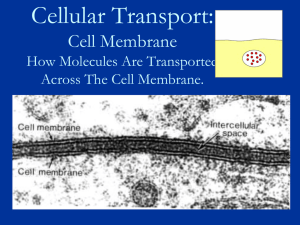
Cell Membrane Structure
... • 2 layers of Phospholipids turned tail to tail • Semipermeable (selectively permeable) – Picky about what can move across the membrane – Only allows certain things through ...
... • 2 layers of Phospholipids turned tail to tail • Semipermeable (selectively permeable) – Picky about what can move across the membrane – Only allows certain things through ...
Major components of cells
... Peripheral membrane proteins • They are proteins that dissociate from the membrane following treatments with polar reagents (solutions of extreme pH or high salt concentration) that do not disrupt the phospholipid bilayer. • Once dissociated, they are soluble in aqueous buffers. • They are indirect ...
... Peripheral membrane proteins • They are proteins that dissociate from the membrane following treatments with polar reagents (solutions of extreme pH or high salt concentration) that do not disrupt the phospholipid bilayer. • Once dissociated, they are soluble in aqueous buffers. • They are indirect ...
Cells: Organelles - Biology Courses Server
... – Finishes, sorts, and then ships cell products to other organelles OR to the plasma membrane for secretion ...
... – Finishes, sorts, and then ships cell products to other organelles OR to the plasma membrane for secretion ...
Organelle Chart
... cellular substances to cell membrane to be released outside the cell Store water, waste, food and other cellular materials Break down large food molecules, waste and worn out parts ...
... cellular substances to cell membrane to be released outside the cell Store water, waste, food and other cellular materials Break down large food molecules, waste and worn out parts ...
10.Life is cellular
... 13. Most cells get energy in one of two ways ---- from ________________________ or from the ___________. 14. ___________________________ are organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. 15. ______________________________ are ...
... 13. Most cells get energy in one of two ways ---- from ________________________ or from the ___________. 14. ___________________________ are organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. 15. ______________________________ are ...
Organic Compounds
... • Organic compounds are composed of hundreds to thousands of individual molecules. – The single molecules in a polymer are called monomers. ...
... • Organic compounds are composed of hundreds to thousands of individual molecules. – The single molecules in a polymer are called monomers. ...
Cell Organelles
... • Fluid-filled sacs used for the storage of materials used by cells. – This may include water, food molecules, inorganic ions (not carbon), and enzymes. – Animal cells contain small vacuoles while plants have large central vacuoles. ...
... • Fluid-filled sacs used for the storage of materials used by cells. – This may include water, food molecules, inorganic ions (not carbon), and enzymes. – Animal cells contain small vacuoles while plants have large central vacuoles. ...
Cell Processes Study Guide OL Answer Key
... Diffusion Movement of particles from high to low concentration. This is a type of passive transport. Moves particles into and out of cells through cell membrane. ...
... Diffusion Movement of particles from high to low concentration. This is a type of passive transport. Moves particles into and out of cells through cell membrane. ...
Type of Cell Diversity
... receive and transmits messages to other body parts. Long plasma membrane and a lot of rough ER to make proteins needed for the membrane. ...
... receive and transmits messages to other body parts. Long plasma membrane and a lot of rough ER to make proteins needed for the membrane. ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... UNDERSTANDING CELLS: How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be able to put them in to order from least to most complex and explain each one. CELL PARTS: Be able ...
... UNDERSTANDING CELLS: How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be able to put them in to order from least to most complex and explain each one. CELL PARTS: Be able ...
Chapter 3 Review
... __allows some particles to pass and other particles not to pass__________________________ 22. During periods of strenuous activity, muscle cells run low on ___Oxygen_____. 23. Circle the molecule and draw a box around the element. ( H2O ) Mg 24. A type of protein that regulates nearly all chemical r ...
... __allows some particles to pass and other particles not to pass__________________________ 22. During periods of strenuous activity, muscle cells run low on ___Oxygen_____. 23. Circle the molecule and draw a box around the element. ( H2O ) Mg 24. A type of protein that regulates nearly all chemical r ...
Chapter 4 The Cell and it`s Environment
... • Many particles needed by cells must have some help getting across the cell membrane. • Facilitated diffusion - the use of transport proteins to aid the passage of materials across the plasma membrane ...
... • Many particles needed by cells must have some help getting across the cell membrane. • Facilitated diffusion - the use of transport proteins to aid the passage of materials across the plasma membrane ...
Slide ()
... Mechanism of thyroid hormone receptor action. The thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) form heterodimers that bind specifically to thyroid hormone response elements (TRE) in the promoter regions of target genes. In the absence of hormone, TR binds co-repressor (CoR) proteins t ...
... Mechanism of thyroid hormone receptor action. The thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) form heterodimers that bind specifically to thyroid hormone response elements (TRE) in the promoter regions of target genes. In the absence of hormone, TR binds co-repressor (CoR) proteins t ...
Chapter 7.1 - sprenklescience
... 1. Chloroplasts – photosynthesizing organelles found in plants & protists. ...
... 1. Chloroplasts – photosynthesizing organelles found in plants & protists. ...
File
... products of specific plant disease resistance (R) genes • An R protein recognizes a corresponding molecule made by the pathogen’s Avr gene • R proteins activate plant defenses by triggering signal transduction pathways • These defenses include the hypersensitive response and systemic acquired resist ...
... products of specific plant disease resistance (R) genes • An R protein recognizes a corresponding molecule made by the pathogen’s Avr gene • R proteins activate plant defenses by triggering signal transduction pathways • These defenses include the hypersensitive response and systemic acquired resist ...
Cell Structure (Organelles)
... 2. molecule – two or more elements or atoms combined a. may or may not be the same element b. example – Oxygen (O2), Salt (NaCl) 3. compound – two or more different elements combined a. all compounds are molecules, not all molecules are compounds b. example – Carbon dioxide (CO2), Water (H2O) 4. ato ...
... 2. molecule – two or more elements or atoms combined a. may or may not be the same element b. example – Oxygen (O2), Salt (NaCl) 3. compound – two or more different elements combined a. all compounds are molecules, not all molecules are compounds b. example – Carbon dioxide (CO2), Water (H2O) 4. ato ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... bind to specific substrates to speed up chemical reactions. c. Protein signals move from one cell to another and bind to the membrane of the receiving cell ...
... bind to specific substrates to speed up chemical reactions. c. Protein signals move from one cell to another and bind to the membrane of the receiving cell ...
doc
... 2. also contains proteins a. integral protein penetrate all the way through b. peripheral proteins attach to surface c. proteins act as markers, channels, enzymes, structural support, receptors d. if proteins have a sugar molecule attached they are called glycoproteins 3. plasma membrane also contai ...
... 2. also contains proteins a. integral protein penetrate all the way through b. peripheral proteins attach to surface c. proteins act as markers, channels, enzymes, structural support, receptors d. if proteins have a sugar molecule attached they are called glycoproteins 3. plasma membrane also contai ...
Two proteins compete for one port on a growth factor
... Quantifying the relative concentration of these two proteins in a patient's tumor, Ladbury said, might be developed into reliable markers for gauging the likelihood that the cancer will spread and guide Such is the case with two proteins identified by scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderso ...
... Quantifying the relative concentration of these two proteins in a patient's tumor, Ladbury said, might be developed into reliable markers for gauging the likelihood that the cancer will spread and guide Such is the case with two proteins identified by scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderso ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.