Ch7-2CellStructure - Saint Joseph High School
... • Made up of dozens of proteins and RNA • Cells make proteins on ribosomes • Some are suspended in the cytosol. These are “free” ribosomes. “Free” ribosomes make proteins that remain in the cell. • Proteins that leave the cell are made on ribosomes on the surface of the ...
... • Made up of dozens of proteins and RNA • Cells make proteins on ribosomes • Some are suspended in the cytosol. These are “free” ribosomes. “Free” ribosomes make proteins that remain in the cell. • Proteins that leave the cell are made on ribosomes on the surface of the ...
1 - The main principle of cell theory are 2
... 1 - The main principle of cell theory are • All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells • All cells arise from pre existing cells through the process of cell division • The body of living organisms is made up of one or more cells . Protoplasm : The protoplasm is a semi fluid mat ...
... 1 - The main principle of cell theory are • All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells • All cells arise from pre existing cells through the process of cell division • The body of living organisms is made up of one or more cells . Protoplasm : The protoplasm is a semi fluid mat ...
BIO 6.3 Carbon - Steinbach Science
... determine the kind of protein Proteins are the building blocks of many structural components of organisms, as well as are important in contracting of muscle tissue, transporting oxygen in the bloodstream, ...
... determine the kind of protein Proteins are the building blocks of many structural components of organisms, as well as are important in contracting of muscle tissue, transporting oxygen in the bloodstream, ...
Passive Transport
... The fluid outside the cell has the same free water concentration than the cytosol, then the outside fluid is isotonic and water moves into and out of the cell at equal rates. ...
... The fluid outside the cell has the same free water concentration than the cytosol, then the outside fluid is isotonic and water moves into and out of the cell at equal rates. ...
Ch. 8 Honors PP
... - At this point the cell is TURGID or firm, a healthy state for most plant cells - If plant cells are in an isotonic solution, water will not enter and cells become FLACCID (limp) and the plant wilts - If plant cells are in a hypertonic environment water will leave the cell and PLASMOLYSIS occurs; ...
... - At this point the cell is TURGID or firm, a healthy state for most plant cells - If plant cells are in an isotonic solution, water will not enter and cells become FLACCID (limp) and the plant wilts - If plant cells are in a hypertonic environment water will leave the cell and PLASMOLYSIS occurs; ...
“Guided Reading and Study” Student Notes Chapter 2.4, “Looking
... Use the answer key below to cross-reference the notes you took on ‘Looking Inside the Cell’ for this “Guided Reading and Study” lesson. As you are cross-referencing your notes with the answer-key notes below, ALSO be sure to self-evaluate your original responses by doing the following: a. Place a ‘c ...
... Use the answer key below to cross-reference the notes you took on ‘Looking Inside the Cell’ for this “Guided Reading and Study” lesson. As you are cross-referencing your notes with the answer-key notes below, ALSO be sure to self-evaluate your original responses by doing the following: a. Place a ‘c ...
Study Guide
... 2. State the three parts of the cell theory 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotic cells 4. Compare and contrast plant and animal cells 5. Label and describe the functions of the organelles found in eukaryotic cells 6. Explain how the organelles work together to manufacture cellular prod ...
... 2. State the three parts of the cell theory 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotic cells 4. Compare and contrast plant and animal cells 5. Label and describe the functions of the organelles found in eukaryotic cells 6. Explain how the organelles work together to manufacture cellular prod ...
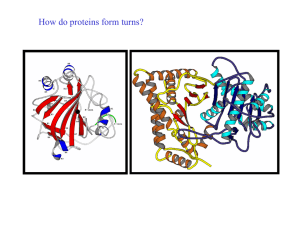
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... A reverse turn is region of the polypeptide having a hydrogen bond from one main chain carbonyl oxygen to the main chain N-H group 3 residues along the chain (i.e. O(i) to N(i+3)) Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and g ...
... A reverse turn is region of the polypeptide having a hydrogen bond from one main chain carbonyl oxygen to the main chain N-H group 3 residues along the chain (i.e. O(i) to N(i+3)) Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and g ...
Transport by Carriers
... Method of transport (use of channel or carrier protein) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Concentration gradient Type / size of molecule transported ...
... Method of transport (use of channel or carrier protein) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Concentration gradient Type / size of molecule transported ...
Topic 2: Cells Page 1 (1) human (3) stomach (4) chloroplast 1. The
... variety of life functions. In a single-celled organism, these functions are performed by (1) tissues ...
... variety of life functions. In a single-celled organism, these functions are performed by (1) tissues ...
The!cell!
... molecules!to!simpler!compounds.!E.g.!converting!the!chemical!energy!stored!in! glucose!molecules!into!ATP!for!use!in!cellular!processes!and!activities.! Other!pathways!consume!energy!to!build!complex!molecules!from!simpler!ones! (anabolism).!E.g.!synthesis!of!a!protein!from!amino!acids.! ...
... molecules!to!simpler!compounds.!E.g.!converting!the!chemical!energy!stored!in! glucose!molecules!into!ATP!for!use!in!cellular!processes!and!activities.! Other!pathways!consume!energy!to!build!complex!molecules!from!simpler!ones! (anabolism).!E.g.!synthesis!of!a!protein!from!amino!acids.! ...
Midterm Review
... into compounds that are more convenient for the cells to use enclosed by two membranes ...
... into compounds that are more convenient for the cells to use enclosed by two membranes ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Role of the Membrane Proteins • Integral (transmembrane) – Inserted completely through the membrane – Function as channel or carrier proteins • Transport substances through the membrane that cannot normally pass through freely (large substances) ...
... Role of the Membrane Proteins • Integral (transmembrane) – Inserted completely through the membrane – Function as channel or carrier proteins • Transport substances through the membrane that cannot normally pass through freely (large substances) ...
Cell Anatomy: Structures and Functions
... 1. Explain cell theory. 2. Describe the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells and prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3. Be able to identify and know the function of each of the following organelles: a. cell wall l. microtubule b. cell (plasma) membrane m. microfilament c. riboso ...
... 1. Explain cell theory. 2. Describe the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells and prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3. Be able to identify and know the function of each of the following organelles: a. cell wall l. microtubule b. cell (plasma) membrane m. microfilament c. riboso ...
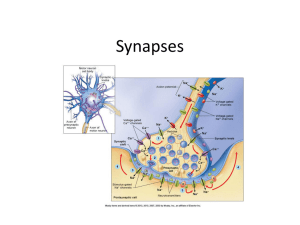
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... • 1. synaptic knob—bulge at end of one axon terminal of presynaptic neuron • 2. synaptic cleft-tiny (25 nm) gap between two neurons • 3. plasma membrane of post synaptic neuron– usually at the dendrite or cell body- contains protein receptors ...
... • 1. synaptic knob—bulge at end of one axon terminal of presynaptic neuron • 2. synaptic cleft-tiny (25 nm) gap between two neurons • 3. plasma membrane of post synaptic neuron– usually at the dendrite or cell body- contains protein receptors ...
The cell theory states that: All living things are
... The Endoplasmic Reticulum is the cells DELIVERY SYSTEM. •Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Delivers proteins. •A tubular system connecting the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane. ...
... The Endoplasmic Reticulum is the cells DELIVERY SYSTEM. •Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Delivers proteins. •A tubular system connecting the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane. ...
plasma-membrane
... • Water concentration around the cell is the same as the water concentration inside the cell • No net movement of water occurs • Cell remains the same size – The type of dissolved particles does not have to be the same, but the total concentration of all dissolved particles is ...
... • Water concentration around the cell is the same as the water concentration inside the cell • No net movement of water occurs • Cell remains the same size – The type of dissolved particles does not have to be the same, but the total concentration of all dissolved particles is ...
You Light Up My Life
... • Interior is able to open to both sides • Change shape when they interact with solute • Play roles in active and passive transport ...
... • Interior is able to open to both sides • Change shape when they interact with solute • Play roles in active and passive transport ...
Day 2 EOCT Station Review Answer Sheet
... d) Organelle found in plants and protists that photosynthesizes; has a ...
... d) Organelle found in plants and protists that photosynthesizes; has a ...
Cells in Their Environment
... Diffusion and Cells Diffusion is one of the ways that substances move into and out of cells. The concentration of a substance that a cell uses up, such as oxygen, is low inside the cell. Outside the cell, the concentration of the substance is higher. The molecules of the substance diffuse across the ...
... Diffusion and Cells Diffusion is one of the ways that substances move into and out of cells. The concentration of a substance that a cell uses up, such as oxygen, is low inside the cell. Outside the cell, the concentration of the substance is higher. The molecules of the substance diffuse across the ...
1.7 Cells in Their Environment
... Diffusion and Cells Diffusion is one of the ways that substances move into and out of cells. The concentration of a substance that a cell uses up, such as oxygen, is low inside the cell. Outside the cell, the concentration of the substance is higher. The molecules of the substance diffuse across the ...
... Diffusion and Cells Diffusion is one of the ways that substances move into and out of cells. The concentration of a substance that a cell uses up, such as oxygen, is low inside the cell. Outside the cell, the concentration of the substance is higher. The molecules of the substance diffuse across the ...
Notes
... • Causes cell membrane to enlarge – process occurs during growth. • Molecules released become part of cell membrane, part of matrix surrounding cell, or nourish nearby cells. ...
... • Causes cell membrane to enlarge – process occurs during growth. • Molecules released become part of cell membrane, part of matrix surrounding cell, or nourish nearby cells. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.