Cell processes to maintain Homeostasis
... A. Homeostasis is the ability to maintain or regulate ones internal environment for survival. B. Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells C. Some substances can cross the cell membrane without any input of energy by the cell, known as ...
... A. Homeostasis is the ability to maintain or regulate ones internal environment for survival. B. Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells C. Some substances can cross the cell membrane without any input of energy by the cell, known as ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... FIGURE 22-5: Schematic illustration of the mechanisms by which the activity of adenylyl cyclases may be regulated. Whereas all forms of adenylyl cyclase are activated by Gαs (αs) and forskolin, different types of the enzyme can be distinguished by their regulation by Ca 2+ and by other G protein su ...
... FIGURE 22-5: Schematic illustration of the mechanisms by which the activity of adenylyl cyclases may be regulated. Whereas all forms of adenylyl cyclase are activated by Gαs (αs) and forskolin, different types of the enzyme can be distinguished by their regulation by Ca 2+ and by other G protein su ...
Ecological Principals Unit Plan * 7th Grade
... b) are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things, c) come from pre-existing cells after life originated, and d) are different from viruses. 2. Compare the structure, function and interrelatedness of cell organelles in eukaryotic cells (e.g., nucleus, chromosome, mitochondria, cel ...
... b) are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things, c) come from pre-existing cells after life originated, and d) are different from viruses. 2. Compare the structure, function and interrelatedness of cell organelles in eukaryotic cells (e.g., nucleus, chromosome, mitochondria, cel ...
Asexual Reprodction
... to days, to a lifetime Eukaryotic Cells are more complex, so process of cell division is more complicated ...
... to days, to a lifetime Eukaryotic Cells are more complex, so process of cell division is more complicated ...
Parts of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells
... Proteins attached to surface (inside or outside)= PERIPHERAL PROTEINS Proteins stuck into membrane = INTEGRAL PROTEINS (can go part way in or all the way through) ...
... Proteins attached to surface (inside or outside)= PERIPHERAL PROTEINS Proteins stuck into membrane = INTEGRAL PROTEINS (can go part way in or all the way through) ...
2.-1
... Generalized Cell Structures • Plasma membrane = cell membrane • Nucleus = genetic material of cell • Cytoplasm = everything between the membrane and the nucleus – cytosol = intracellular fluid – organelles = subcellular structures with specific functions ...
... Generalized Cell Structures • Plasma membrane = cell membrane • Nucleus = genetic material of cell • Cytoplasm = everything between the membrane and the nucleus – cytosol = intracellular fluid – organelles = subcellular structures with specific functions ...
The Plasma Membrane
... It is fluid because the phospholipid molecules move within the membrane. Proteins in the membrane that move among the phospholipids create the mosaic pattern. ...
... It is fluid because the phospholipid molecules move within the membrane. Proteins in the membrane that move among the phospholipids create the mosaic pattern. ...
•(High- Low) • (Low - High) 3 Types of Passive Transport
... collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them from over-expanding. • Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do not dehydrate. • Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by remove excess salt and water. 8 Prepared by: Mr. Louie B. Dasas ST ...
... collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them from over-expanding. • Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do not dehydrate. • Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by remove excess salt and water. 8 Prepared by: Mr. Louie B. Dasas ST ...
Name - Humble ISD
... All living things are made of _cells____ and all cells can be divided into two groups A. Prokaryotic – “_Before nucleus__” Prokaryotic cells lack a true _nucleus___ and other _membrane__- bound internal structures. Prokaryotic cells do contain _DNA_____, usually concentrated in a particular region o ...
... All living things are made of _cells____ and all cells can be divided into two groups A. Prokaryotic – “_Before nucleus__” Prokaryotic cells lack a true _nucleus___ and other _membrane__- bound internal structures. Prokaryotic cells do contain _DNA_____, usually concentrated in a particular region o ...
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS Toll-like receptors & Host
... Ancient immune defence system based on the Toll signalling In insect, IL-1 receptor and the Toll protein are only similar in the segments within the cell They searched for human proteins that totally resemble to Toll ...
... Ancient immune defence system based on the Toll signalling In insect, IL-1 receptor and the Toll protein are only similar in the segments within the cell They searched for human proteins that totally resemble to Toll ...
Molecules of Life Worksheet
... 12. What are the monomers of proteins called? How many are there? Name the 4 things bonded to the center carbon of this monomer. 13. The main difference among amino acids is their ____ group. What is the R-group on glycine? on alanine? 14. Differences in R-groups give different proteins different __ ...
... 12. What are the monomers of proteins called? How many are there? Name the 4 things bonded to the center carbon of this monomer. 13. The main difference among amino acids is their ____ group. What is the R-group on glycine? on alanine? 14. Differences in R-groups give different proteins different __ ...
Biochemical screen for potential membrane fission catalysts
... of transport carriers that sort and distribute membrane lipids and proteins across these compartments, and in some cases contribute to their biogenesis. Membrane fission is a thermodynamically unfavorable event, which according to previous literature is catalyzed by specific proteins that hydrolyze ...
... of transport carriers that sort and distribute membrane lipids and proteins across these compartments, and in some cases contribute to their biogenesis. Membrane fission is a thermodynamically unfavorable event, which according to previous literature is catalyzed by specific proteins that hydrolyze ...
CELL MEMBRANE
... • Each cell is a separate unit of life, therefore, it has a boundary – the plasma membrane (a.k.a., cell membrane). • The cell membrane separates the inner contents of a cell from its external environment - it maintains a constant internal environment despite changes to its outside world. • It forms ...
... • Each cell is a separate unit of life, therefore, it has a boundary – the plasma membrane (a.k.a., cell membrane). • The cell membrane separates the inner contents of a cell from its external environment - it maintains a constant internal environment despite changes to its outside world. • It forms ...
Gene Section KLRK1 (killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily K, member 1)
... a minor subset of CD4+ T cells. It associates noncovalently with the DAP10 signaling protein and provides activating or costimulatory signals to NK cells and T cells. NKG2D binds to a family of glycoproteins, in humans the MICA, MICB, and ULBP1-6 membrane proteins, which are frequently expressed on ...
... a minor subset of CD4+ T cells. It associates noncovalently with the DAP10 signaling protein and provides activating or costimulatory signals to NK cells and T cells. NKG2D binds to a family of glycoproteins, in humans the MICA, MICB, and ULBP1-6 membrane proteins, which are frequently expressed on ...
Class: 11 Subject: Biology Topic: Cell
... bottomrespectively. In this, proteins are of two categories- peripheral (extrinsic) & integral (intrinsic). The integral proteins are tightly held in place by strong hydrophilic or hydrophobic interactions or both and are difficult to remove from the membranes. Two peripheral proteins are superficia ...
... bottomrespectively. In this, proteins are of two categories- peripheral (extrinsic) & integral (intrinsic). The integral proteins are tightly held in place by strong hydrophilic or hydrophobic interactions or both and are difficult to remove from the membranes. Two peripheral proteins are superficia ...
BIO 311C Introductory Biology Student Learning Outcomes
... 7. Cell Communication: Cells communicate with each other and can convert environmental signals to complex integrated responses within a cell. ...
... 7. Cell Communication: Cells communicate with each other and can convert environmental signals to complex integrated responses within a cell. ...
Osmosis and diffusion webquest
... Now click on “Add salt” and observe what happens. After salt (in reality there would be many Na+ and Cl- ions) is added, how do the water molecules move across the membrane? Is there an overall direction of movement (where do most of the molecules end up?) ...
... Now click on “Add salt” and observe what happens. After salt (in reality there would be many Na+ and Cl- ions) is added, how do the water molecules move across the membrane? Is there an overall direction of movement (where do most of the molecules end up?) ...
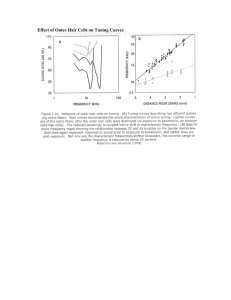
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... potentials in neurons of the spiral ganglion. The patterns of evoked neural activity convey information to the central nervous system (top). In a deafened ear, hair cells have died or no longer function, depriving the spiral ganglion cells of their normal input (bottom). Without regular use, the neu ...
... potentials in neurons of the spiral ganglion. The patterns of evoked neural activity convey information to the central nervous system (top). In a deafened ear, hair cells have died or no longer function, depriving the spiral ganglion cells of their normal input (bottom). Without regular use, the neu ...
Lh6Ch11aMembranes
... – Dynamics of membranes – Structure and function of membrane proteins – Transport across biological membranes ...
... – Dynamics of membranes – Structure and function of membrane proteins – Transport across biological membranes ...
Honors Biology Unit 3 Ch.4,5 Cells & Membranes THINKING AHEAD:
... c. I can describe the functions of organelles that make energy for cell metabolism: mitochondria and chloroplasts. d. I can describe the functions of organelles that store products in a cell: vacuoles and lysosomes. e. I can describe the functions of the organelles that give the cell shape and struc ...
... c. I can describe the functions of organelles that make energy for cell metabolism: mitochondria and chloroplasts. d. I can describe the functions of organelles that store products in a cell: vacuoles and lysosomes. e. I can describe the functions of the organelles that give the cell shape and struc ...
What is an inference
... ...the cell membrane allows some ...extensions of the cytoplasm substances and not others to pass surround and engulf large through particles ...
... ...the cell membrane allows some ...extensions of the cytoplasm substances and not others to pass surround and engulf large through particles ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.