Horror and Modernity
... amount of money, power and knowledge is transferred between nods in the global web. Two basic contradictions bound this world: the first is what Castells calls the contradiction between 'Net and Self', or that the capital and information circulating at the global level continuously runs up against i ...
... amount of money, power and knowledge is transferred between nods in the global web. Two basic contradictions bound this world: the first is what Castells calls the contradiction between 'Net and Self', or that the capital and information circulating at the global level continuously runs up against i ...
Download Syllabus (PDF, 70 KB) (PDF, 68 KB)
... models. The larger part of the course will be devoted to the longitudinal case. Here, stochastic actor-‐based models for network evolution will stand central. The basic model allows analysing global network ...
... models. The larger part of the course will be devoted to the longitudinal case. Here, stochastic actor-‐based models for network evolution will stand central. The basic model allows analysing global network ...
Mobile-ized, Glocalized Interaction in a Time of Networked
... groupware – online-only applications that assumed coworkers spent all their time focused in a solidary group. I didn’t think it was accurate then (Wellman, 1997). It has even less empirical warrant now. Fifteen years of research – by NetLab and others – has shown us that the new normal is the intert ...
... groupware – online-only applications that assumed coworkers spent all their time focused in a solidary group. I didn’t think it was accurate then (Wellman, 1997). It has even less empirical warrant now. Fifteen years of research – by NetLab and others – has shown us that the new normal is the intert ...
Sociology - mrsvanderley
... 7. Theoretical perspective that follows the tradition of Karl Marx: ...
... 7. Theoretical perspective that follows the tradition of Karl Marx: ...
American Sociologists Albion SMALL (1854
... Man Physical and economic needs Woman Expressive needs Other institutions (welfare, school, social services, etc.) are meant to assist the family meet its needs ...
... Man Physical and economic needs Woman Expressive needs Other institutions (welfare, school, social services, etc.) are meant to assist the family meet its needs ...
Ch - HCC Learning Web
... networking and multitasking are of particular interests to sociologists. Digital divide- differential access to technological advances IV. ...
... networking and multitasking are of particular interests to sociologists. Digital divide- differential access to technological advances IV. ...
Society and Groups - U
... shared values and other social bonds. Social Structure refers to the recurring patterns of behavior in society which people create through their interactions and relationships. ...
... shared values and other social bonds. Social Structure refers to the recurring patterns of behavior in society which people create through their interactions and relationships. ...
Social network analysis and semantic web
... Social network analysis helps understanding and exploiting the key features of social networks in order to manage their assets, their life cycle and predict their ...
... Social network analysis helps understanding and exploiting the key features of social networks in order to manage their assets, their life cycle and predict their ...
This is a Powerpoint
... interconnecting network using IP, and not all networks that use IP are part of the internet. Thus IPTV networks such as AT&T’s U-Verse service are isolated from the Internet, and are therefore not covered by network neutrality agreements. ...
... interconnecting network using IP, and not all networks that use IP are part of the internet. Thus IPTV networks such as AT&T’s U-Verse service are isolated from the Internet, and are therefore not covered by network neutrality agreements. ...
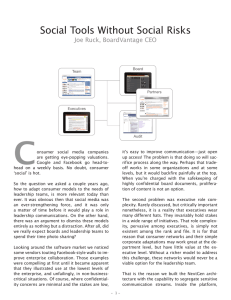
Social Tools Without Social Risks
... ring-fenced TeamSpaces. This allows direct and open communication within a ...
... ring-fenced TeamSpaces. This allows direct and open communication within a ...
Durkheim`s Methodology and Theory
... • Natural Sciences (biology, physics) had to use QUANTATATIVE research, because their subject was not accessible, so they used statistical means to generate conclusions about the structure of natural societies, or Laws of Nature ...
... • Natural Sciences (biology, physics) had to use QUANTATATIVE research, because their subject was not accessible, so they used statistical means to generate conclusions about the structure of natural societies, or Laws of Nature ...
An Introduction to Sociology
... Sociology is a young science. Its origins date back to the early 1800s industrial revolution when Western society underwent tremendous change. Urbanization, specifically, gave rise to social issues that hadn’t existed in the same capacity previously. For example, pollution, poverty, malnutrition, un ...
... Sociology is a young science. Its origins date back to the early 1800s industrial revolution when Western society underwent tremendous change. Urbanization, specifically, gave rise to social issues that hadn’t existed in the same capacity previously. For example, pollution, poverty, malnutrition, un ...
GROUPS AND ORGANIZATIONS
... • Groups are essence of life in society. • They stand between the individual and the larger society. • Society is the largest and most complex group that sociologists study. ...
... • Groups are essence of life in society. • They stand between the individual and the larger society. • Society is the largest and most complex group that sociologists study. ...
FuncBasics
... The shared culture is transmitted through socialisation into common norms and values ...
... The shared culture is transmitted through socialisation into common norms and values ...
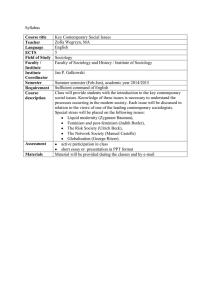
Syllabus Course title Key Contemporary Social Issues Teacher Zofia
... Faculty of Sociology and History / Institute of Sociology Jan P. Galkowski Summer semester (Feb-Jun), academic year 2014/2015 Sufficient command of English Class will provide students with the introduction to the key contemporary social issues. Knowledge of these issues is necessary to understand th ...
... Faculty of Sociology and History / Institute of Sociology Jan P. Galkowski Summer semester (Feb-Jun), academic year 2014/2015 Sufficient command of English Class will provide students with the introduction to the key contemporary social issues. Knowledge of these issues is necessary to understand th ...
Sociology Mid -Term Exam
... 14. By adopting a ____, you can look beyond commonly held beliefs to the hidden meanings behind human actions. 15. People who view society as a set of interrelated parts that work together to produce a stable social system are said to employ the 16. The physical objects that people create and use fo ...
... 14. By adopting a ____, you can look beyond commonly held beliefs to the hidden meanings behind human actions. 15. People who view society as a set of interrelated parts that work together to produce a stable social system are said to employ the 16. The physical objects that people create and use fo ...
SOC 8311 Basic Social Statistics
... applied analytic rigor to concept of “social network.” He saw “the whole of social life” as “a set of points some of which are joined by lines” to form a “total network” of relations. The informal sphere of interpersonal relations was a “partial network” within this total network (Barnes 1954:43). I ...
... applied analytic rigor to concept of “social network.” He saw “the whole of social life” as “a set of points some of which are joined by lines” to form a “total network” of relations. The informal sphere of interpersonal relations was a “partial network” within this total network (Barnes 1954:43). I ...
Sociology Lecture Notes -- 1-2
... Class conflict Bourgeoisie naturally exploits workers; workers will rise up and overthrow Bourgeoisie Society will eventually move to being classless (communism) Planned revolution could speed up change (ex: Russian Revolution) ...
... Class conflict Bourgeoisie naturally exploits workers; workers will rise up and overthrow Bourgeoisie Society will eventually move to being classless (communism) Planned revolution could speed up change (ex: Russian Revolution) ...
Ch. 1 Sec. 2 notes File - Oakland Schools Moodle
... Herbert Spencer Society is like a body--parts working together to promote well being and survival Social darwinism: natural social selection would ensure survival of fittest in society ...
... Herbert Spencer Society is like a body--parts working together to promote well being and survival Social darwinism: natural social selection would ensure survival of fittest in society ...
Computers Networks
... currently use is a paragon of engineering, rather than a snapshot of our understanding at the time. We build great myths of spin about how what we have done is the only way to do it, to the point that our universities now teach the flaws to students (and professors and textbook authors) who don’t kn ...
... currently use is a paragon of engineering, rather than a snapshot of our understanding at the time. We build great myths of spin about how what we have done is the only way to do it, to the point that our universities now teach the flaws to students (and professors and textbook authors) who don’t kn ...
structual functionalism - BCI
... • He pioneered the modern method of statistical analysis and he set the precedent for other sociologists to follow as they research controversial issues. ...
... • He pioneered the modern method of statistical analysis and he set the precedent for other sociologists to follow as they research controversial issues. ...
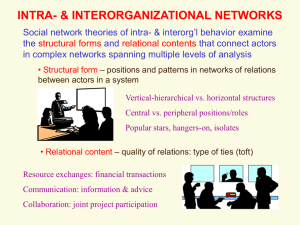
Making Invisible Work Visible: Using Social Network Analysis to
... • A variety of factors can cause these informal networks to break-down, such as formal network structures, work processes, geographic dispersion, human resource management, leadership style, and culture. ...
... • A variety of factors can cause these informal networks to break-down, such as formal network structures, work processes, geographic dispersion, human resource management, leadership style, and culture. ...