Stem cell therapy - Irish Heart Foundation
... 1. Gene can disseminate 1. Local gene to whole body therapy 2. Can we get enough where we want it? ...
... 1. Gene can disseminate 1. Local gene to whole body therapy 2. Can we get enough where we want it? ...
Chapter 4
... support to plant tissues. When the turgor pressure of a plant cell increases, does that indicate that the cell is hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic relative to its environment? Explain your answer. ...
... support to plant tissues. When the turgor pressure of a plant cell increases, does that indicate that the cell is hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic relative to its environment? Explain your answer. ...
How do cells move? Mathematical modelling of cytoskeletal
... theoretical modelling and ex-perimental work will be established by the cooperation between the mathematical groups and the group at the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, working in bio-optics and cytoskeleton dynamics. ...
... theoretical modelling and ex-perimental work will be established by the cooperation between the mathematical groups and the group at the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, working in bio-optics and cytoskeleton dynamics. ...
Student Guide to Animal and Plant Cells
... 6. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): produces, processes and transports proteins and lipids. The rough ER has ribosomes on its surface. The smooth ER does not. 7. Mitochondria: breaks down food to make power for a cell. There are many mitochondria in each cell. 8. Chloroplast: catch sunlight and use it to ...
... 6. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): produces, processes and transports proteins and lipids. The rough ER has ribosomes on its surface. The smooth ER does not. 7. Mitochondria: breaks down food to make power for a cell. There are many mitochondria in each cell. 8. Chloroplast: catch sunlight and use it to ...
Chapter 7.3 Guided Reading
... 3. Air has a higher concentration of oxygen molecules than does the cytoplasm of your lung cells. Where in your lungs will there be a net increase of oxygen? A. in the air breathed in C. cells in the air breathed out B. outside of the lung cells D. inside of the lung cells 4. Which of the following ...
... 3. Air has a higher concentration of oxygen molecules than does the cytoplasm of your lung cells. Where in your lungs will there be a net increase of oxygen? A. in the air breathed in C. cells in the air breathed out B. outside of the lung cells D. inside of the lung cells 4. Which of the following ...
Chapter 2
... b. Thicker walls than parenchyma, usually uneven in thickness due to thickening at inner and outer tangential walls c. Located u rneath epidermis d. Function in basic support 3. Sclerenchyma a. Usually dead cells at maturity b. Thick, lignin filled walls c. Two cell types sclereids (stone cells)and ...
... b. Thicker walls than parenchyma, usually uneven in thickness due to thickening at inner and outer tangential walls c. Located u rneath epidermis d. Function in basic support 3. Sclerenchyma a. Usually dead cells at maturity b. Thick, lignin filled walls c. Two cell types sclereids (stone cells)and ...
21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues TEKS 5B, 10B, 10C
... 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues • Ground tissue is found inside a plant. ...
... 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues • Ground tissue is found inside a plant. ...
Pathways of Communication
... 1. Conversion of extracellular signal to intracellular message 2. Amplification of a message many times over ...
... 1. Conversion of extracellular signal to intracellular message 2. Amplification of a message many times over ...
Plant cells and tissues
... 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues • Ground tissue is found inside a plant. ...
... 21.1 Plant Cells and Tissues • Ground tissue is found inside a plant. ...
2nd Nine Weeks Exam Study Guide - Mr. Barger
... 10. _____________ form bonds due to the arrangement of their outer electrons. 11. The outer electrons of an atom are also called ________________ ___________________. 12. There are three types of bonds between atoms. Explain what happens during each bond. 13. Amino acid is to protein as simple sugar ...
... 10. _____________ form bonds due to the arrangement of their outer electrons. 11. The outer electrons of an atom are also called ________________ ___________________. 12. There are three types of bonds between atoms. Explain what happens during each bond. 13. Amino acid is to protein as simple sugar ...
Cells
... 31. What two things make up ribosomes & are ribosomes surrounded by membrane like other organelles? ...
... 31. What two things make up ribosomes & are ribosomes surrounded by membrane like other organelles? ...
tiny bubbles destroy cancer cells
... Tiny bubbles can pack quite a punch - creating nanoscale explosions that destroy cancer cells. Using lasers and nanoparticles, scientists discovered a new technique for singling out individual diseased cells and demolishing them. The scientists used lasers to make "nanobubbles" by zapping gold nanop ...
... Tiny bubbles can pack quite a punch - creating nanoscale explosions that destroy cancer cells. Using lasers and nanoparticles, scientists discovered a new technique for singling out individual diseased cells and demolishing them. The scientists used lasers to make "nanobubbles" by zapping gold nanop ...
Cells Chapter 1 Notes List the objectives for Section 1: Organization
... ● Discovered cells when looking at a slice of cork under a microscope ● thought only plants had cells ...
... ● Discovered cells when looking at a slice of cork under a microscope ● thought only plants had cells ...
Biology 30 Unit 1: The Nervous System
... conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body. The axon carries nerve impulses toward other neurons or to effectors. Most nerves are comprised of many axons held together by connective tissue. ...
... conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body. The axon carries nerve impulses toward other neurons or to effectors. Most nerves are comprised of many axons held together by connective tissue. ...
unit 4: plant tissue - Ms Mohlari and Ms Soji`s life sciences classroom
... The apical meristem are located at or near the tips of stems and roots, where they increase the length of their structures by means of mitosis. This increase in length is called primary growth. Monocots also have an intercalary meristem, this allows them to regrow lost parts. (It is found betw ...
... The apical meristem are located at or near the tips of stems and roots, where they increase the length of their structures by means of mitosis. This increase in length is called primary growth. Monocots also have an intercalary meristem, this allows them to regrow lost parts. (It is found betw ...
Plant Transport - Northwest ISD Moodle
... – transpiration – loss of water from leaves by evaporation How might environmental factors such as temperature effect the water levels in the plant? How would the plant compensate for this change? ...
... – transpiration – loss of water from leaves by evaporation How might environmental factors such as temperature effect the water levels in the plant? How would the plant compensate for this change? ...
Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells
... -‐Be able to label the structures in a prokaryotic cell -‐Be able to identify the 4 structures that ALL prokaryotic cells have -‐Know how prokaryotic cells obtain energy Prokaryotic Cells -‐Be able ...
... -‐Be able to label the structures in a prokaryotic cell -‐Be able to identify the 4 structures that ALL prokaryotic cells have -‐Know how prokaryotic cells obtain energy Prokaryotic Cells -‐Be able ...
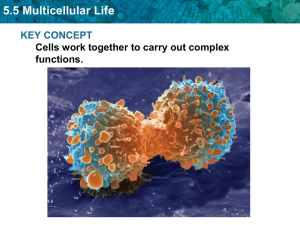
5:5
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
Notes Chapter 10 Lesson 1 The Basics of a Cell
... Cell Single Celled Organism- Living things that are made up of only ONE Cell Multi-celled Organism- Describes organisms that are composed of different kinds of specialized cells ...
... Cell Single Celled Organism- Living things that are made up of only ONE Cell Multi-celled Organism- Describes organisms that are composed of different kinds of specialized cells ...
Connect!
... How do the receptors work? What is a “target” cell? Name some things that cells have receptors for. How do hormones work? Give a specific example of a hormone and its target cell. ...
... How do the receptors work? What is a “target” cell? Name some things that cells have receptors for. How do hormones work? Give a specific example of a hormone and its target cell. ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.