Cell Specialization notes FIB
... What does this mean exactly? And how does it happen? Actually, a cell’s location within the embryo helps determine how it will differentiate. First, it is decided which genetic information will be expressed, thereby indicating the type of cell that is to be formed. Then, through cell different ...
... What does this mean exactly? And how does it happen? Actually, a cell’s location within the embryo helps determine how it will differentiate. First, it is decided which genetic information will be expressed, thereby indicating the type of cell that is to be formed. Then, through cell different ...
document
... closely is correlated with tumour progression and amount of perivascular tryptasepositive MCs . ...
... closely is correlated with tumour progression and amount of perivascular tryptasepositive MCs . ...
Nerve tissue
... • Cerebellar layers: • Molecular layer • mostly neuronal fibers • Purkynje layer • large multipolar neurons • Granule cell layer • small integrator neurons ...
... • Cerebellar layers: • Molecular layer • mostly neuronal fibers • Purkynje layer • large multipolar neurons • Granule cell layer • small integrator neurons ...
How are plant cells different?
... • receive proteins and other compounds from the ER. • package these materials & distribute them to other parts of the cell • release materials outside the cell ...
... • receive proteins and other compounds from the ER. • package these materials & distribute them to other parts of the cell • release materials outside the cell ...
Plant Cells and Tissues, Part 2
... Phloem is involved in the transport of organic solutes in the plant. The main conducting elements are aligned to form tubes called sieve tubes. The sieve-tube elements at maturity are living cells, interconnected by perforations in their end walls formed from enlarged and modified plasmodesmata (sie ...
... Phloem is involved in the transport of organic solutes in the plant. The main conducting elements are aligned to form tubes called sieve tubes. The sieve-tube elements at maturity are living cells, interconnected by perforations in their end walls formed from enlarged and modified plasmodesmata (sie ...
Evaluating the Feasibility of Small Molecule Phenamil as a Novel
... Growth factors for bone regenerative engineering technology have been extensively investigated in the field because of their inherent osteoinductive potential. Traditionally, growth factors are large recombinant proteins that have been shown to be osteoinductive. For instance, bone morphogenetic pro ...
... Growth factors for bone regenerative engineering technology have been extensively investigated in the field because of their inherent osteoinductive potential. Traditionally, growth factors are large recombinant proteins that have been shown to be osteoinductive. For instance, bone morphogenetic pro ...
Different Stem Cell Types used in Treating Orthopedic
... fluid or membrane that surrounds a fetus. ...
... fluid or membrane that surrounds a fetus. ...
Chapter 5 Summary
... complex active and reproducing units of life. The concept that cells are the basic unit of life is known as the cell theory. There are two basic groups of cells. They include karyotic (bacteria) and eukaryotic (the vast majority of all living things). The Microscope and Cell Discovery and Descriptio ...
... complex active and reproducing units of life. The concept that cells are the basic unit of life is known as the cell theory. There are two basic groups of cells. They include karyotic (bacteria) and eukaryotic (the vast majority of all living things). The Microscope and Cell Discovery and Descriptio ...
CELLS, CELLS, & More CELLS!
... • All living creatures are made up of cells • Cells come from pre-existing cell The adult human body is made up of about 60-90 trillion cells. (if you lined up all the cells in a human body end-to-end, you could actually circle the earth 4.5 times.) ...
... • All living creatures are made up of cells • Cells come from pre-existing cell The adult human body is made up of about 60-90 trillion cells. (if you lined up all the cells in a human body end-to-end, you could actually circle the earth 4.5 times.) ...
Plant and Animal Cell Lab 1. List the 3 parts of the Cell Theory 2
... 1. Put a drop of methylene blue on a slide. Caution: methylene blue will stain clothes and skin. 2. Gently scrape the inside of your cheek with the flat side of a toothpick. Scrape lightly. 3. Stir the end of the toothpick in the stain and throw the toothpick away. 4. Place a coverslip onto the slid ...
... 1. Put a drop of methylene blue on a slide. Caution: methylene blue will stain clothes and skin. 2. Gently scrape the inside of your cheek with the flat side of a toothpick. Scrape lightly. 3. Stir the end of the toothpick in the stain and throw the toothpick away. 4. Place a coverslip onto the slid ...
cell cycle - Explore Biology
... __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 12. What is the G1 checkpoint and where does it fit into the cycle? __________________________________________________________________________ _______ ...
... __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 12. What is the G1 checkpoint and where does it fit into the cycle? __________________________________________________________________________ _______ ...
new biotechnology PowerPoint
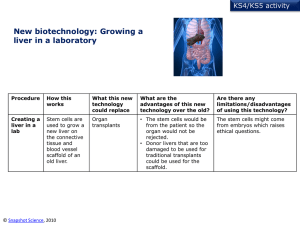
... (so could not be used in vaccinations for example). • Could the liver cope with removing the antibodies from the body? ...
... (so could not be used in vaccinations for example). • Could the liver cope with removing the antibodies from the body? ...
There are two types of cells
... 1. They do not have a nucleus, and their genetic material is not stored in the nucleus. ...
... 1. They do not have a nucleus, and their genetic material is not stored in the nucleus. ...
HW 2.1 Organelles Homework Name: Date: ___ In the Venn
... b) Endoplasmic Reticulum c) Golgi Body d) Mitochondria ...
... b) Endoplasmic Reticulum c) Golgi Body d) Mitochondria ...
講義下載
... the cell membrane – Lost cell wall – Cytoskeleton under the plasma membrane – Increase ability to EAT! ...
... the cell membrane – Lost cell wall – Cytoskeleton under the plasma membrane – Increase ability to EAT! ...
4 Multicellular Organisms
... has wings for flying and webbed feet for swimming. Different parts are made up of different specialized cells. In complex multicellular organisms, cells are organized into groups that work together to perform specific jobs. When cells work together to perform one specific function, they are generall ...
... has wings for flying and webbed feet for swimming. Different parts are made up of different specialized cells. In complex multicellular organisms, cells are organized into groups that work together to perform specific jobs. When cells work together to perform one specific function, they are generall ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Growth of an organism • How do living things grow? • Organisms grow by adding (making) more cells, not by increasing the size of their cells ...
... Growth of an organism • How do living things grow? • Organisms grow by adding (making) more cells, not by increasing the size of their cells ...
Mammalian cell culture
... • Derived from a primary cell culture. • Isolated by selection or cloning. • Becoming a more homogeneous cell population that is contains a specific cell type. • Finite life span in vitro. ...
... • Derived from a primary cell culture. • Isolated by selection or cloning. • Becoming a more homogeneous cell population that is contains a specific cell type. • Finite life span in vitro. ...
EPC (Skin, Fish)
... This cell line known as Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) was originally reported to be from Carp (Cyprinus carpio) epidermal herpes virus-induced hyperplastic lesions. More recently EPC was found to be derived from Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas) see Winton et al., 2010. This has been confir ...
... This cell line known as Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) was originally reported to be from Carp (Cyprinus carpio) epidermal herpes virus-induced hyperplastic lesions. More recently EPC was found to be derived from Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas) see Winton et al., 2010. This has been confir ...
CELLS
... Plant and animal cells share many characteristics Both types of cells are eukaryotic and have many of the same organelles They both have cell membranes There are, however, 3 structures found in plant cells that are not in animal cells ...
... Plant and animal cells share many characteristics Both types of cells are eukaryotic and have many of the same organelles They both have cell membranes There are, however, 3 structures found in plant cells that are not in animal cells ...
7-2 - Cloudfront.net
... made in ER • This is the “touch-up” shop in the factory – Proteins are touched up then shipped ...
... made in ER • This is the “touch-up” shop in the factory – Proteins are touched up then shipped ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.