cells
... else until I collect the portfolio. If you lose this sheet, you will need to produce the original work for regrading. 2. Each assignment has a point value based on the amount of time and effort necessary to complete that task. 3. I expect students to be working on this unit at all times while in the ...
... else until I collect the portfolio. If you lose this sheet, you will need to produce the original work for regrading. 2. Each assignment has a point value based on the amount of time and effort necessary to complete that task. 3. I expect students to be working on this unit at all times while in the ...
Cell Division and Mitosis
... All organisms are composed of cells The cell is the basic unit of life All cells have a double-layered plasma membrane Membranes consist largely of phospholipid and protein molecules ...
... All organisms are composed of cells The cell is the basic unit of life All cells have a double-layered plasma membrane Membranes consist largely of phospholipid and protein molecules ...
Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards
... Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards Directions: You will receive 21 notecards and a rubber band or paper clip. On the front of one notecard, write your name and class period and set that card aside. The other 20 notecards will be for your flash cards. Each flash card is worth 5 points and there ar ...
... Cell Parts and Organelles Flash Cards Directions: You will receive 21 notecards and a rubber band or paper clip. On the front of one notecard, write your name and class period and set that card aside. The other 20 notecards will be for your flash cards. Each flash card is worth 5 points and there ar ...
Comparing Bacteria, Archaea and Eucarya
... ! All cells require Energy, and this is universally supplied in the form of ATP. ! All cells are regulated by and respond to External Stimuli. ! All cells Regulate the flow of nutrients and wastes that enter and leave. ! All cells Reproduce and are the result of reproduction. 2. Basic chemical compo ...
... ! All cells require Energy, and this is universally supplied in the form of ATP. ! All cells are regulated by and respond to External Stimuli. ! All cells Regulate the flow of nutrients and wastes that enter and leave. ! All cells Reproduce and are the result of reproduction. 2. Basic chemical compo ...
Intro to Cell Vocabulary
... There are only 2 classes of cells (plant/animal), but there are many kinds of cells in each class. Each kind of cell has a DIFFERENT job to do…it specializes. ...
... There are only 2 classes of cells (plant/animal), but there are many kinds of cells in each class. Each kind of cell has a DIFFERENT job to do…it specializes. ...
Cells Unit Review- Things to know From 4.1 • The five characteristics
... The five characteristics of living things Examples of each of the five characteristics of living things ...
... The five characteristics of living things Examples of each of the five characteristics of living things ...
Cells Alive - Decatur ISD
... Objective: You will look at computer models of cells; learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells Alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will ac ...
... Objective: You will look at computer models of cells; learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells Alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will ac ...
Key Terms Prokaryote Nucleus Organelle Cytoplasm Eukaryote Cell
... prokaryotic cells. Some eukaryotic cells are even large enough to be seen without a microscope! Eukaryotic cells are complex. They have lots of different compartments inside of them called membrane-bound organelles. These are located in the cytoplasm. The most important organelle ...
... prokaryotic cells. Some eukaryotic cells are even large enough to be seen without a microscope! Eukaryotic cells are complex. They have lots of different compartments inside of them called membrane-bound organelles. These are located in the cytoplasm. The most important organelle ...
Transport in plants
... Plant cells need to be turgid (i.e rigid) to support plant tissues. Plant cells become turgid when water moves into the cell by osmosis, and the central vacuole swells and pushes against the cell wall. When plant cells are placed in concentrated sugar solutions they lose water by osmosis and they be ...
... Plant cells need to be turgid (i.e rigid) to support plant tissues. Plant cells become turgid when water moves into the cell by osmosis, and the central vacuole swells and pushes against the cell wall. When plant cells are placed in concentrated sugar solutions they lose water by osmosis and they be ...
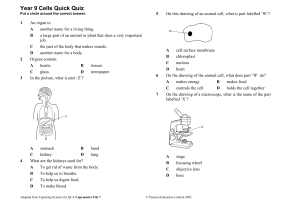
Year 9 Cells Quick Quiz
... A tissue is: A a collection of organs helping each other. B another name for an organ. C a group of cells which are all different, all doing different jobs. D a group of cells which are the same, all doing the same job. A nerve cell has to carry messages around the body quickly. To help it do this i ...
... A tissue is: A a collection of organs helping each other. B another name for an organ. C a group of cells which are all different, all doing different jobs. D a group of cells which are the same, all doing the same job. A nerve cell has to carry messages around the body quickly. To help it do this i ...
Body Cells
... Cells • The basic unit of structure and function of all living things • First discovered by Robert Hook in the 1600s under a crude microscope • Hook looked at cork and reminded him of monk’s roomCELL. • Parts are called Organelles ...
... Cells • The basic unit of structure and function of all living things • First discovered by Robert Hook in the 1600s under a crude microscope • Hook looked at cork and reminded him of monk’s roomCELL. • Parts are called Organelles ...
Cells are the building blocks of life. A group of similar cells working
... A group of similar cells working together. Cells live with other cells like them in groups called tissues. Cytoplasm, cell membrane, organelles, nucleus. Jelly‐like stuff in the cell surrounded by the cell membrane. The cell membrane lets good stuff in and bad stuff out. Structures in the cell ...
... A group of similar cells working together. Cells live with other cells like them in groups called tissues. Cytoplasm, cell membrane, organelles, nucleus. Jelly‐like stuff in the cell surrounded by the cell membrane. The cell membrane lets good stuff in and bad stuff out. Structures in the cell ...
cellular reproduction
... Chromatids: one of the two strands of a chromosome that become visible during meiosis or mitosis Centromeres: region of the chromosome that holds the two sister chromatids together during mitosis ...
... Chromatids: one of the two strands of a chromosome that become visible during meiosis or mitosis Centromeres: region of the chromosome that holds the two sister chromatids together during mitosis ...
Chapter 4 Guided Reading
... 3. What is the difference between the cytoplasm and the cytosol in eukaryotic cells? ...
... 3. What is the difference between the cytoplasm and the cytosol in eukaryotic cells? ...
Vocabulary Inventory
... On our planet Earth, life comes in a variety of forms. We have about 2 million species of animals (such as elephants), 270,000 types of plants (such as sunflowers), 4,000 kinds of bacteria (such as E. coli), 80,000 different protists (such as algae), and 72,000 assorted fungi (such as mushrooms). Wh ...
... On our planet Earth, life comes in a variety of forms. We have about 2 million species of animals (such as elephants), 270,000 types of plants (such as sunflowers), 4,000 kinds of bacteria (such as E. coli), 80,000 different protists (such as algae), and 72,000 assorted fungi (such as mushrooms). Wh ...
Notes Sheet
... 3. Cell Division in Prokaryotes is called ______________________ ________________ Prokaryotic cells are bacteria … small ( ~ ____ micron) unicellular no nucleus or other organelles such as m___________________ v______________________ or c___________________________ 3. Cell Division in Eukaryot ...
... 3. Cell Division in Prokaryotes is called ______________________ ________________ Prokaryotic cells are bacteria … small ( ~ ____ micron) unicellular no nucleus or other organelles such as m___________________ v______________________ or c___________________________ 3. Cell Division in Eukaryot ...
Structures and Functions of Living things
... • New cells are produced from existing cells – Living things begin life as a single cell. This cell divides into two cells. Each new cell also divides into two cells. After a certain point, the cells being to specialize and take on different functions. – Cell division is what causes you or any other ...
... • New cells are produced from existing cells – Living things begin life as a single cell. This cell divides into two cells. Each new cell also divides into two cells. After a certain point, the cells being to specialize and take on different functions. – Cell division is what causes you or any other ...
20.1 viruses wkbk key - OG
... Virus that attacks bacteria *2. What are viruses? Particles of nucleic acid, protein, and lipids that reproduce only by infecting living cells *3. What is a capsid? Protein coat on a virus (for protection) 4. How does a typical virus get inside a cell? Capsid proteins “trick” the cell by binding to ...
... Virus that attacks bacteria *2. What are viruses? Particles of nucleic acid, protein, and lipids that reproduce only by infecting living cells *3. What is a capsid? Protein coat on a virus (for protection) 4. How does a typical virus get inside a cell? Capsid proteins “trick” the cell by binding to ...
3 - Coastalzone
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic living unit of organization for all living things All cells arise from preexisting cells Cells contain all of the hereditary information 3 basic structures of all cell types: 1. plasma membrane - a physical boundary that separate ...
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic living unit of organization for all living things All cells arise from preexisting cells Cells contain all of the hereditary information 3 basic structures of all cell types: 1. plasma membrane - a physical boundary that separate ...
Cell Structure answers
... (organelle means “little organ) that convert energy from one form to another. It is enclosed by two membranes (inner and outer). All of the folds (called cristae) of the inner membrane increase the surface area so the mitochondria can make more ATP (ATP is adenosine triphosphate –a form of cellular ...
... (organelle means “little organ) that convert energy from one form to another. It is enclosed by two membranes (inner and outer). All of the folds (called cristae) of the inner membrane increase the surface area so the mitochondria can make more ATP (ATP is adenosine triphosphate –a form of cellular ...
Cell WEBQUEST: An interactive
... Cells, what are they? What do they do? What are they made of? How do they work? All of the questions you have had in biology. This webquest is designed to review the information you have already learned. Task You will be asked to use the web to research what cells are and what cells are made of. You ...
... Cells, what are they? What do they do? What are they made of? How do they work? All of the questions you have had in biology. This webquest is designed to review the information you have already learned. Task You will be asked to use the web to research what cells are and what cells are made of. You ...
Electrochemical cells
... In secondary cells two reactions can occur, one discharges the cell and another occurs when the cell is recharged ...
... In secondary cells two reactions can occur, one discharges the cell and another occurs when the cell is recharged ...
Chapt 7 review worksheet answers
... separating two solutions. Assume that the water molecules can pass freely through the membrane but salt and starch molecules cannot. When equilibrium is reached, which side will contain the highest fluid level? ...
... separating two solutions. Assume that the water molecules can pass freely through the membrane but salt and starch molecules cannot. When equilibrium is reached, which side will contain the highest fluid level? ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.