7th grd 1st qtr study guide 0708 NO ans good
... New plants can be created from stem cutting of the same parent plant. Of what it this an example? Humans typically maintain a body temperature of 37°C and a fairly constant level of sugar in the blood. What process are these examples of? The following are know as what? A plant growing toward light; ...
... New plants can be created from stem cutting of the same parent plant. Of what it this an example? Humans typically maintain a body temperature of 37°C and a fairly constant level of sugar in the blood. What process are these examples of? The following are know as what? A plant growing toward light; ...
Cellular Reproduction
... Recall that all cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. All substances moving into or out of the cell must cross the plasma membrane. The surface area of the cell is the area covered by the plasma membrane. The volume of a cell is the space taken by the inner contents. Because cells are small, th ...
... Recall that all cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. All substances moving into or out of the cell must cross the plasma membrane. The surface area of the cell is the area covered by the plasma membrane. The volume of a cell is the space taken by the inner contents. Because cells are small, th ...
Cell structure student notes PreAP 14-15
... Cell Parts and Their Functions: Specialized cell parts called __________________________—“little organs” 1. ___________ _______________________—determines what goes in and out of the cell 2. _________________________—gel-like medium that holds the organelles in position 3. ______________________—co ...
... Cell Parts and Their Functions: Specialized cell parts called __________________________—“little organs” 1. ___________ _______________________—determines what goes in and out of the cell 2. _________________________—gel-like medium that holds the organelles in position 3. ______________________—co ...
2nd 9-WEEKS STUDY GUIDE – PART 2
... 11. What is the difference in Passive Transport and Active Transport? Active Transport requires energy from the cell. Active transport moves molecules against the conc. gradient. (low to high) CELL CYCLE 1. Describe the 4 steps of the cell cycle. Draw a diagram that shows them in order. ...
... 11. What is the difference in Passive Transport and Active Transport? Active Transport requires energy from the cell. Active transport moves molecules against the conc. gradient. (low to high) CELL CYCLE 1. Describe the 4 steps of the cell cycle. Draw a diagram that shows them in order. ...
1st 6 Test Review Notes 2012
... Uses observations/tests results to compare and contrast 2 or more objects with each other Records observations/tests results as data Uses data to form a conclusion by comparing, contrasting, and showing relationships between two or more objects. ...
... Uses observations/tests results to compare and contrast 2 or more objects with each other Records observations/tests results as data Uses data to form a conclusion by comparing, contrasting, and showing relationships between two or more objects. ...
Mitosis Meiosis Study Guide
... Figure 2: The classical and minimal models of cell cycle control Where and when do cyclins act on the cell cycle? (A) Cycling cells undergo three major transitions during their cell cycle. The beginning of S phase is marked by the onset of DNA replication, the start of mitosis (M) is accompanied by ...
... Figure 2: The classical and minimal models of cell cycle control Where and when do cyclins act on the cell cycle? (A) Cycling cells undergo three major transitions during their cell cycle. The beginning of S phase is marked by the onset of DNA replication, the start of mitosis (M) is accompanied by ...
micro intro organelles
... according to genetic instructions • Free ribosomes are suspended in the cytoplasm which make proteins that will function in the cytosol • Bound ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum which make proteins that be included in membranes or transported outside the cell ...
... according to genetic instructions • Free ribosomes are suspended in the cytoplasm which make proteins that will function in the cytosol • Bound ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum which make proteins that be included in membranes or transported outside the cell ...
HRW BIO CRF Ch 04_p01-44
... endocytosis. During endocytosis, the cell membrane forms a pouch around a substance outside the cell. The pouch then closes up and pinches off from the membrane to form a vesicle. Vesicles formed by endocytosis may fuse with lysosomes or other organelles. The movement of a substance by a vesicle to ...
... endocytosis. During endocytosis, the cell membrane forms a pouch around a substance outside the cell. The pouch then closes up and pinches off from the membrane to form a vesicle. Vesicles formed by endocytosis may fuse with lysosomes or other organelles. The movement of a substance by a vesicle to ...
The Cell Theory - Broken Arrow Public Schools
... It is amazing to think that the cells that make up our bodies are just as alive as we are. Humans are just an intricately designed community of cells, which must work together to survive. ...
... It is amazing to think that the cells that make up our bodies are just as alive as we are. Humans are just an intricately designed community of cells, which must work together to survive. ...
The Cell Membrane
... Let’s Discuss the following: • Structure of a phosopholipid bilayer • Evidence for the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane • Properties of proteins embedded in cell membrane and freeze fracture • How does winter wheat avoid cell membrane ...
... Let’s Discuss the following: • Structure of a phosopholipid bilayer • Evidence for the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane • Properties of proteins embedded in cell membrane and freeze fracture • How does winter wheat avoid cell membrane ...
Cell Division Flash Cards - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... The nucleus begins to reappear and cytokinesis begins When the cytoplasm divides ...
... The nucleus begins to reappear and cytokinesis begins When the cytoplasm divides ...
Chapter 6 Cell
... saw, and perhaps, that were ever seen, for I had not met with any Writer or Person, that had made any mention of them before this. . . ...
... saw, and perhaps, that were ever seen, for I had not met with any Writer or Person, that had made any mention of them before this. . . ...
Test Key - Growth and Development of Cells
... Specialized: more distinct form and function Unspecialized: no distinct form, still in development stage, no specific function ...
... Specialized: more distinct form and function Unspecialized: no distinct form, still in development stage, no specific function ...
Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
... Cells are small, but molecules for their chemical reactions are much smaller ...
... Cells are small, but molecules for their chemical reactions are much smaller ...
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide 6: Cells Cell Theory All living things
... 1. Both protect the cell and allow it to interact with its surroundings b. Nucleus i. A large structure that contains the cell’s genetic material and controls cell activities c. Cytoplasm i. Material inside the cell membrane but not the nucleus III. Two Types of Cells a. Prokaryotes i. Do not have n ...
... 1. Both protect the cell and allow it to interact with its surroundings b. Nucleus i. A large structure that contains the cell’s genetic material and controls cell activities c. Cytoplasm i. Material inside the cell membrane but not the nucleus III. Two Types of Cells a. Prokaryotes i. Do not have n ...
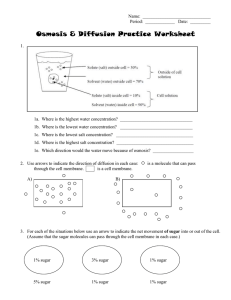
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... 1e. Which direction would the water move because of osmosis? __________________ 2. Use arrows to indicate the direction of diffusion in each case: through the cell membrane. is a cell membrane. A) ...
... 1e. Which direction would the water move because of osmosis? __________________ 2. Use arrows to indicate the direction of diffusion in each case: through the cell membrane. is a cell membrane. A) ...
UNIT DATE RANGE TEACHER GRADE Cells October 31 – Dec 5
... SC.6.L.14.4: Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. SC.7.L.16.1: Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that sp ...
... SC.6.L.14.4: Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. SC.7.L.16.1: Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that sp ...
Cell Membrane - Goshen Community Schools
... Transport Chapter 9 How does stuff get in and out of a cell through the cell membrane? ...
... Transport Chapter 9 How does stuff get in and out of a cell through the cell membrane? ...
Recitation 13 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... “uncommitted” or “undetermined”. These cells become determined or committed, where they have decided their fate, but have not yet assumed it. Subsequently, cells differentiate to assume their final fate. Determination involves activation of a few regulatory genes, which control activation of many ef ...
... “uncommitted” or “undetermined”. These cells become determined or committed, where they have decided their fate, but have not yet assumed it. Subsequently, cells differentiate to assume their final fate. Determination involves activation of a few regulatory genes, which control activation of many ef ...
Click - Lake County Schools
... SC.6.L.14.4: Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. SC.7.L.16.1: Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that sp ...
... SC.6.L.14.4: Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. SC.7.L.16.1: Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that sp ...
Cell vs. Prison Cell
... The centriole is like the prison chains because the centrioles attach to chromosomes as spindle fibers and pull them apart just like the prison chains are used to help keep some of the prisoners apart. ...
... The centriole is like the prison chains because the centrioles attach to chromosomes as spindle fibers and pull them apart just like the prison chains are used to help keep some of the prisoners apart. ...
Stem Cells - California Science Teacher
... Stem Cell Basics • 2 basic types: – Embryonic stem cells – Adult stem cells ...
... Stem Cell Basics • 2 basic types: – Embryonic stem cells – Adult stem cells ...
Cell transport
... • C, H, O also N, S • amino acids in large chains...like letters form words • 2 kinds – fibrous – bind structures, provide strength – globular – antibodies, hormones, enzymes. Globular proteins DO things! • enzymes-catalyst for EVERY chemical reaction in the body, remains unchanged ...
... • C, H, O also N, S • amino acids in large chains...like letters form words • 2 kinds – fibrous – bind structures, provide strength – globular – antibodies, hormones, enzymes. Globular proteins DO things! • enzymes-catalyst for EVERY chemical reaction in the body, remains unchanged ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.