Chapter 7 Test Review Guide
... 11. Describe the fluid mosaic model. 12. Give some reasons for why cells need to transport materials into and out of cells. 13. List what kind of substances can and cannot cross easily through the lipid bilayer. 14. Explain the difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. 15. List ...
... 11. Describe the fluid mosaic model. 12. Give some reasons for why cells need to transport materials into and out of cells. 13. List what kind of substances can and cannot cross easily through the lipid bilayer. 14. Explain the difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. 15. List ...
Review For Chapter 3 – Cell Structure and Function There are
... Review For Chapter 3 – Cell Structure and Function There are approximately 40-45 questions on the test: multiple choice, short answer, completion, and essay. You need to know all of the chapter vocabulary, cell theory, the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and the major differences betw ...
... Review For Chapter 3 – Cell Structure and Function There are approximately 40-45 questions on the test: multiple choice, short answer, completion, and essay. You need to know all of the chapter vocabulary, cell theory, the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and the major differences betw ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Guiding Questions: What are the
... _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Cells - Cloudfront.net
... living things were 2. Cells are the basic units made up of cells. of structure and This discovery function in living brought about the ...
... living things were 2. Cells are the basic units made up of cells. of structure and This discovery function in living brought about the ...
Cell story book project
... Cell Story Book Project due January 14, 2010 Imagine that you work for the Shaps Book Company. Your editor wants you to develop a children’s book about cells and their parts. The book should be something that a 2nd-4th grader would be able to understand. The editor gives you a list of the book requi ...
... Cell Story Book Project due January 14, 2010 Imagine that you work for the Shaps Book Company. Your editor wants you to develop a children’s book about cells and their parts. The book should be something that a 2nd-4th grader would be able to understand. The editor gives you a list of the book requi ...
Notes on Unit 7A Cells
... Cytoplasm – liquid part of the cell. It is where the chemical reactions happen. Nucleus – control centre of the cell. It controls the reactions and cell reproduction Cell membrane – outer skin of the cell, controls what gets into and out of the cell. ...
... Cytoplasm – liquid part of the cell. It is where the chemical reactions happen. Nucleus – control centre of the cell. It controls the reactions and cell reproduction Cell membrane – outer skin of the cell, controls what gets into and out of the cell. ...
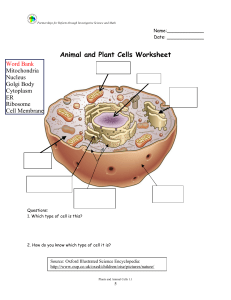
Animal and Plant Cells Worksheet
... 1. Controls what enters and leaves a cell 4. Stores water and nutrients for the cell 5. Sends materials made by the ribosomes to where they need to go 7. Found only in plant cells, give the cell a rigid shape 9. A think substance that fills the cell and contains the ...
... 1. Controls what enters and leaves a cell 4. Stores water and nutrients for the cell 5. Sends materials made by the ribosomes to where they need to go 7. Found only in plant cells, give the cell a rigid shape 9. A think substance that fills the cell and contains the ...
Cells, Tissues, & Organs
... enzymes. Break down old cell parts • Cytoskeleton - The “skeleton” of the cell. Consists of microtubules and microfilaments • Vacuoles - Large membranous bubbles which store substances inside the cell ...
... enzymes. Break down old cell parts • Cytoskeleton - The “skeleton” of the cell. Consists of microtubules and microfilaments • Vacuoles - Large membranous bubbles which store substances inside the cell ...
The Cell Cycle, Rate and Control
... This part takes approximately 90% of the time: interphase The three stages within this part are: G1, S, G2 each stage means o G1 = growth before DNA replication o S = DNA replication o G2 = growth after DNA replication The shortest time involves these phases prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophas ...
... This part takes approximately 90% of the time: interphase The three stages within this part are: G1, S, G2 each stage means o G1 = growth before DNA replication o S = DNA replication o G2 = growth after DNA replication The shortest time involves these phases prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophas ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... The Cell Theory states: 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells Cell Size Most are too small to be seen without a microscope. Organisms that lay eggs are the only large cells. ...
... The Cell Theory states: 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells Cell Size Most are too small to be seen without a microscope. Organisms that lay eggs are the only large cells. ...
The Cell
... ________________________ c) Hooke’s work inspired other scientists to search for cells elsewhere. ...
... ________________________ c) Hooke’s work inspired other scientists to search for cells elsewhere. ...
NAME DIABETES Energy our body needs comes from
... If a lump/tumor isn’t doing any harm, we call it a _________ ___________; meaning it’s ______________. If an abnormal cell grows like crazy and starts to infiltrate other tissue, and mutate more frequently, this group of cells are _______________ ______________. ...
... If a lump/tumor isn’t doing any harm, we call it a _________ ___________; meaning it’s ______________. If an abnormal cell grows like crazy and starts to infiltrate other tissue, and mutate more frequently, this group of cells are _______________ ______________. ...
Document
... Chromosomes-provides direction for cell to follow Endoplasmic Reticulum-transportation ...
... Chromosomes-provides direction for cell to follow Endoplasmic Reticulum-transportation ...
MUSINGU HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY DECEMBER 2013 HOLIDAY
... FORM ONE 1. Define the term species. 2. The diagram below represents a cell organelle. ...
... FORM ONE 1. Define the term species. 2. The diagram below represents a cell organelle. ...
EOC Review Part 3
... What happens during anaerobic cellular respiration? Fermentation is when cells convert sugar to ATP in the absence of oxygen Describe the structure and function of enzymes, and explain their importance in biological systems. Folded protein fits like a “lock and key” to substrate. Speeds up chemical ...
... What happens during anaerobic cellular respiration? Fermentation is when cells convert sugar to ATP in the absence of oxygen Describe the structure and function of enzymes, and explain their importance in biological systems. Folded protein fits like a “lock and key” to substrate. Speeds up chemical ...
Patti`ss Cellular Structures (5th)
... Background: You have been learning about living things. Living things are made of cells. Cells carry out all life processes. New cells come from existing cells. Cells are too small to be seen with the eye alone. You can look and study cells using a microscope. Plant cells and animal cells are simila ...
... Background: You have been learning about living things. Living things are made of cells. Cells carry out all life processes. New cells come from existing cells. Cells are too small to be seen with the eye alone. You can look and study cells using a microscope. Plant cells and animal cells are simila ...
cells\resources\worksheet prokaryotes info and qs
... The cell surface membrane provides a site for the regulation of the passage of nutrients into the cell: it is selectively permeable with carrier mechanisms for molecules. It also provides a location for the enzymes concerned with metabolic activities. Most of the enzymes concerned with respiration a ...
... The cell surface membrane provides a site for the regulation of the passage of nutrients into the cell: it is selectively permeable with carrier mechanisms for molecules. It also provides a location for the enzymes concerned with metabolic activities. Most of the enzymes concerned with respiration a ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.