Cell Section 1
... Diversity of Cells (Differences between cells) -not all cells are the same- their structure is based on their FUNCTION -nerve cells – long- transmit info white blood cells- change shape to fight invaders, skin- flat cells like plates for protection -they come in various shapes, sizes, and organizat ...
... Diversity of Cells (Differences between cells) -not all cells are the same- their structure is based on their FUNCTION -nerve cells – long- transmit info white blood cells- change shape to fight invaders, skin- flat cells like plates for protection -they come in various shapes, sizes, and organizat ...
CHAPTER 1: THE CELL 1.1 (p. 15) 1. Name four characteristics of
... Photosynthetic plant leaf cells generate glucose which is transported by xylem and phloem tissue along with water for use throughout the tree. 4. In what way does a specialized cell in a multicellular organism differ from the cell of a unicellular organism? In unicellular organism, one cell must do ...
... Photosynthetic plant leaf cells generate glucose which is transported by xylem and phloem tissue along with water for use throughout the tree. 4. In what way does a specialized cell in a multicellular organism differ from the cell of a unicellular organism? In unicellular organism, one cell must do ...
Cells AP Bio Test Review ANSWERS
... 28. Processes, sorts, & packages cellular secretions (lipids, enzymes, proteins) for export from the cell. ...
... 28. Processes, sorts, & packages cellular secretions (lipids, enzymes, proteins) for export from the cell. ...
Plant cells - Sackville School
... Cell structure and function • Cells are the ‘building blocks’ of living organisms. • Cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them. • All cells have the same overall structure (cell membrane, cytoplasm and a nucleus) that allow them to carry out the basic life processes - but some are c ...
... Cell structure and function • Cells are the ‘building blocks’ of living organisms. • Cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them. • All cells have the same overall structure (cell membrane, cytoplasm and a nucleus) that allow them to carry out the basic life processes - but some are c ...
Cell Analogy Sheet
... Cell Analogy Sheet Purpose: To show mastery of each organelles function and role within a cell. Directions: Students will make their own unified analogy for the functions and roles of cell organelles. 1. Cell wall is: a plant cells outermost organelle. It is in charge of protecting the cell, as well ...
... Cell Analogy Sheet Purpose: To show mastery of each organelles function and role within a cell. Directions: Students will make their own unified analogy for the functions and roles of cell organelles. 1. Cell wall is: a plant cells outermost organelle. It is in charge of protecting the cell, as well ...
Endosymbiosis Questions KEY Endosymbiosis Questions KEY
... MAKE THEMSELVES). 2. Give at least two examples that show the amoeba and the x-bacteria were still considered separate organisms. (ANY 2 OF THESE) ...
... MAKE THEMSELVES). 2. Give at least two examples that show the amoeba and the x-bacteria were still considered separate organisms. (ANY 2 OF THESE) ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Notes
... • Cells in our world come in two basic types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. ...
... • Cells in our world come in two basic types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. ...
prokaryotes, eukaryotes
... gametangia produce ______________sporangia produce haploid spores that can be dispersed ...
... gametangia produce ______________sporangia produce haploid spores that can be dispersed ...
Cell Organelles
... does this mean??) • Found in all types of cells – prokaryotes and eukaryotes! ...
... does this mean??) • Found in all types of cells – prokaryotes and eukaryotes! ...
UNIT 2 : Cells - Loudoun County Public Schools
... 1. Explain why cells are called the basic units of life. a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are very small to make it easy for nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to exit the cell. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (h ...
... 1. Explain why cells are called the basic units of life. a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are very small to make it easy for nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to exit the cell. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (h ...
organ system - Scholieren.com
... Plants and animals are made up of small parts: cells. These are tiny building blocks. You can’t see them with the naked eye so you need a microscope. When you look at the cells through a microscope the cells seem to be flat, but in reality they are a kind of boxes because something is in it. There a ...
... Plants and animals are made up of small parts: cells. These are tiny building blocks. You can’t see them with the naked eye so you need a microscope. When you look at the cells through a microscope the cells seem to be flat, but in reality they are a kind of boxes because something is in it. There a ...
Mitosis Matching Worksheet
... _______ 8. Periods of intense growth ‐ cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles. _______ 9. “In‐between” DIVISIONS ‐ A period of growth. _______ 10. Some cells can spend almost their entire life cycle in this phase (even 60 YEARS). _______ 11. The centromeres that joins the ...
... _______ 8. Periods of intense growth ‐ cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles. _______ 9. “In‐between” DIVISIONS ‐ A period of growth. _______ 10. Some cells can spend almost their entire life cycle in this phase (even 60 YEARS). _______ 11. The centromeres that joins the ...
Document
... Explain the two main basic types of cells Distinguish among the scientists Describe organelles of the cell Relate the difference between plant and animal cells ...
... Explain the two main basic types of cells Distinguish among the scientists Describe organelles of the cell Relate the difference between plant and animal cells ...
Extraction and Purification
... • Usually select tissue that has large amounts of the materials necessary for the study. • Tissues are acquired in a fashion that provides for protection of the system to be studied. – Use fresh tissue or immediately placed in ice cold solution – Bacterial cells are centrifuged at 16,000g and separa ...
... • Usually select tissue that has large amounts of the materials necessary for the study. • Tissues are acquired in a fashion that provides for protection of the system to be studied. – Use fresh tissue or immediately placed in ice cold solution – Bacterial cells are centrifuged at 16,000g and separa ...
organelles - GEOCITIES.ws
... Some animal cells have many small ones Store food, water and wastes ...
... Some animal cells have many small ones Store food, water and wastes ...
osmosis cells
... leaves the cells • Turgor pressure is lost – Cells wilt QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... leaves the cells • Turgor pressure is lost – Cells wilt QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
common formative assessment planning template
... 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells; each cell carries on life-sustaining functions. Multi-cellular organisms need specialized structures and systems to perform basic life functions. 2. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and ...
... 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells; each cell carries on life-sustaining functions. Multi-cellular organisms need specialized structures and systems to perform basic life functions. 2. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and ...
Cell Structure Lab
... of living things, the basic building units of all life have much in common. In this investigation, you will see what some cells look like and compare the structure and organization of cells from different organisms. ...
... of living things, the basic building units of all life have much in common. In this investigation, you will see what some cells look like and compare the structure and organization of cells from different organisms. ...
What Part of the Cell am I?
... I’m a series of tubes found throughout the cell, I transport proteins and other things as well. What am I? ...
... I’m a series of tubes found throughout the cell, I transport proteins and other things as well. What am I? ...
PowerPoint- Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
... viruses: 1) Are viruses living? Support your answer. 2) Are viruses smaller or larger than bacterial cells? 3) How are viruses and bacteria similar? 4) What instrument is needed to see a virus? ...
... viruses: 1) Are viruses living? Support your answer. 2) Are viruses smaller or larger than bacterial cells? 3) How are viruses and bacteria similar? 4) What instrument is needed to see a virus? ...
Slide ()
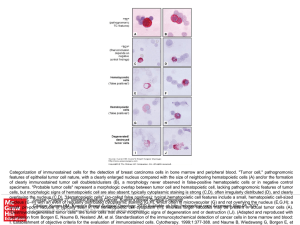
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
Q2_Proj_Teacher-Guide_Microscopy
... PA 3.1.12.A.: Assess and apply patterns in science and technology; compare and contrast structure and function relationships as they relate to patterns. PA 3.3.12.A.: Explain the relationship between structure and function at all levels of organization; explain and analyze the relationship between s ...
... PA 3.1.12.A.: Assess and apply patterns in science and technology; compare and contrast structure and function relationships as they relate to patterns. PA 3.3.12.A.: Explain the relationship between structure and function at all levels of organization; explain and analyze the relationship between s ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.