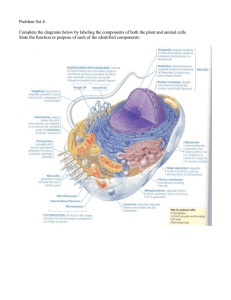
Name
... Organelle means “__________ __________.” a. Vacuoles: ___________ areas located in the __________. Some of these vacuoles store _______ for future use. Some store __________. Others store ___________ until they can be removed from the cell. In animal cells they resemble _______ _______ _______ ...
... Organelle means “__________ __________.” a. Vacuoles: ___________ areas located in the __________. Some of these vacuoles store _______ for future use. Some store __________. Others store ___________ until they can be removed from the cell. In animal cells they resemble _______ _______ _______ ...
Cells and Life Key Concept Builder LESSON 1 Key Concept
... Cells and Life Key Concept How did scientists’ understanding of cells develop? Directions: Put a check mark on the line before each item that helped scientists develop the cell theory. ...
... Cells and Life Key Concept How did scientists’ understanding of cells develop? Directions: Put a check mark on the line before each item that helped scientists develop the cell theory. ...
Biology Test 1 Study Guide – Things to know
... 9. What is the chemical formula for water and what does that mean? 10. What happens between atoms during a covalent bond? 11. What is the most abundant compound in living things? 12. Water is a polar molecule. Which end is slightly negative and which end is slightly positive? 13. If a substance has ...
... 9. What is the chemical formula for water and what does that mean? 10. What happens between atoms during a covalent bond? 11. What is the most abundant compound in living things? 12. Water is a polar molecule. Which end is slightly negative and which end is slightly positive? 13. If a substance has ...
Living Systems
... Chloroplast- makes food Vacuole- holds water Cell membrane- lets thing in and out of the cell ...
... Chloroplast- makes food Vacuole- holds water Cell membrane- lets thing in and out of the cell ...
MICROSCOPE - Use the cards to help identify the parts of the
... of transport goes down the concentration gradient. Types includes diffusion (the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration), osmosis (the movement of water from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration), and facilitated diffusion (diffusion of ...
... of transport goes down the concentration gradient. Types includes diffusion (the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration), osmosis (the movement of water from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration), and facilitated diffusion (diffusion of ...
Explore HW
... If a red blood cell is placed into a test tube of salt water, what will happen to the cell? Is this solution hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic? ...
... If a red blood cell is placed into a test tube of salt water, what will happen to the cell? Is this solution hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic? ...
Problem Set 4:
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
2.3: EUKARYOTIC CELLS
... • Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell • Annotate the diagram with the functions of each named structure. • Identify named structures in an electron micrograph of liver cells. • Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ...
... • Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell • Annotate the diagram with the functions of each named structure. • Identify named structures in an electron micrograph of liver cells. • Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ...
Learning Objectives/ Study Guide File
... 1. Understand the cell cycle. Be able to recognize and explain the phases & steps, their relationship to each other, their outcomes, and the rat at which they occur. 2. Be able to contrast prokaryotic & eukaryotic cell division and plant & animal cytokinesis. 3. Understand the various regulatory mec ...
... 1. Understand the cell cycle. Be able to recognize and explain the phases & steps, their relationship to each other, their outcomes, and the rat at which they occur. 2. Be able to contrast prokaryotic & eukaryotic cell division and plant & animal cytokinesis. 3. Understand the various regulatory mec ...
Unit 3 - Cells
... • B. cells are the basic unit of structure & function of all living things • C. new cells are produced from existing cells ...
... • B. cells are the basic unit of structure & function of all living things • C. new cells are produced from existing cells ...
Introduction to Cells and the Microscope
... TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM) • Shows internal workings of the cell • Can magnify up to 100,000x • Shoots electrons THROUGH the sample to create a “map” of the insides • Good for viewing organelles and cell ...
... TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM) • Shows internal workings of the cell • Can magnify up to 100,000x • Shoots electrons THROUGH the sample to create a “map” of the insides • Good for viewing organelles and cell ...
DNMT3B controls fates in human pluripotent and nullipotent stem cells
... in embryonic stem (ES) and embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells. To determine DNMT3B function in human ES and EC cells, we have established inducible DNMT3B knockdown of human ES cells, and of both human pluripotent and nullipotent EC cells. We find that DNMT3B does not inhibit differentiation and apoptos ...
... in embryonic stem (ES) and embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells. To determine DNMT3B function in human ES and EC cells, we have established inducible DNMT3B knockdown of human ES cells, and of both human pluripotent and nullipotent EC cells. We find that DNMT3B does not inhibit differentiation and apoptos ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Cells are the basic units of all life. • All organisms are made of one or more cells • All cells come from pre-existing cells ...
... • Cells are the basic units of all life. • All organisms are made of one or more cells • All cells come from pre-existing cells ...
Cells
... • Regulates movement of substances in and out of cell • Molecules that are part of the membrane receive information from outside and transmit it inward in a process called signal transduction • Also, helps adhere to other cells (important in forming tissues) • It is selectively permeable because it ...
... • Regulates movement of substances in and out of cell • Molecules that are part of the membrane receive information from outside and transmit it inward in a process called signal transduction • Also, helps adhere to other cells (important in forming tissues) • It is selectively permeable because it ...
NOTES: 7.3-7.4 - Cell Transport
... 1) PASSIVE TRANSPORT (types): DIFFUSION: ● movement of a substance from where it is conc. to where it is less conc. (“ ...
... 1) PASSIVE TRANSPORT (types): DIFFUSION: ● movement of a substance from where it is conc. to where it is less conc. (“ ...
Ch 6 Organelles
... f. __________________Thickest fiber of cytoskeleton g. __________________Thinnest fiber of cytoskeleton h. __________________ Connects the cytoplasm of one plant cell to another i. __________________Packages proteins for transport out of the cell j. __________________The site of cellular respiration ...
... f. __________________Thickest fiber of cytoskeleton g. __________________Thinnest fiber of cytoskeleton h. __________________ Connects the cytoplasm of one plant cell to another i. __________________Packages proteins for transport out of the cell j. __________________The site of cellular respiration ...
Cells Structures and Functions 6 Grade
... that plant and animal cells have in common. State the structure and function of these organelles. ...
... that plant and animal cells have in common. State the structure and function of these organelles. ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.