THINK ABOUT IT
... • Stains or dyes help scientists see the structures within the cells. • Electron microscope-use beams of electrons that are focused by magnetic fields. • Offers a much higher resolution and allows scientists to view much smaller things. – Transmission electron microscope-make it possible to explore ...
... • Stains or dyes help scientists see the structures within the cells. • Electron microscope-use beams of electrons that are focused by magnetic fields. • Offers a much higher resolution and allows scientists to view much smaller things. – Transmission electron microscope-make it possible to explore ...
File
... These are embryonic stem cells Scientists would like to harvest these to do research because they can turn into any type of cell ...
... These are embryonic stem cells Scientists would like to harvest these to do research because they can turn into any type of cell ...
cell review
... 32. How is the nucleus the same as the cell membrane and how is it defferent 33. What makes up the cell membrane? 34. What is the process that allows movement in and out of the cell by following a concentration gradient? 35. Filtration and osmosis is a type of what membrane transport? 36. How is pri ...
... 32. How is the nucleus the same as the cell membrane and how is it defferent 33. What makes up the cell membrane? 34. What is the process that allows movement in and out of the cell by following a concentration gradient? 35. Filtration and osmosis is a type of what membrane transport? 36. How is pri ...
There are two types of cells
... Plague, also called Black Death. This bacteria was spread through fleas and rodents. ...
... Plague, also called Black Death. This bacteria was spread through fleas and rodents. ...
1-1 Intro to Cells - Mr. Doc`s Online Lab
... The Basics of a Cell (Cont.) ! The size of a cell also plays a role in its function. ! A cell’s size is limited by the relationship between the cell’s outer surface area and its volume (surface area-to-volume ratio.) ! This is important because it limits how much “stuff” a cell can take in and p ...
... The Basics of a Cell (Cont.) ! The size of a cell also plays a role in its function. ! A cell’s size is limited by the relationship between the cell’s outer surface area and its volume (surface area-to-volume ratio.) ! This is important because it limits how much “stuff” a cell can take in and p ...
Notes: Cells
... magnify objects in steps (this is what we use in class) Magnification- the ability to make objects appear larger ...
... magnify objects in steps (this is what we use in class) Magnification- the ability to make objects appear larger ...
IB Biology Topic 2 - Cells Revision Sheet What is understood by the
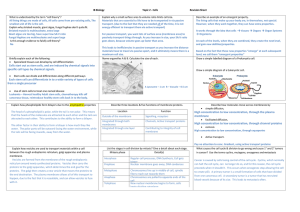
... goes down, because volume goes up faster than area. This leads to inefficiencies in passive transport as you increase the distance materials have to travel via passive xport, and it ultimately means there is a maximum cell size. Name organelles A & B. Calculate the size of each. ...
... goes down, because volume goes up faster than area. This leads to inefficiencies in passive transport as you increase the distance materials have to travel via passive xport, and it ultimately means there is a maximum cell size. Name organelles A & B. Calculate the size of each. ...
Cells and Heredity Ch. 1
... mitochondria to change sugars into energy, because they both need energy to survive. ...
... mitochondria to change sugars into energy, because they both need energy to survive. ...
CHAPTER 3 CELLS unit of life
... Protein channels are openings in the cell membrane to allow transport of chemicals through the membrane. Cell receptors are proteins that attach to chemical messengers from other cells. These are important for cell to communicate with each other; eg. hormones Glycocalyx is a term for the several che ...
... Protein channels are openings in the cell membrane to allow transport of chemicals through the membrane. Cell receptors are proteins that attach to chemical messengers from other cells. These are important for cell to communicate with each other; eg. hormones Glycocalyx is a term for the several che ...
Cell Organelles
... Much like a crossing guard, the cell membrane controls traffic. It functions by accepting and releasing materials into and out of the cell. The materials move across the cell membrane using diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport, using flagella or cilia. Flagella has only one or two ...
... Much like a crossing guard, the cell membrane controls traffic. It functions by accepting and releasing materials into and out of the cell. The materials move across the cell membrane using diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport, using flagella or cilia. Flagella has only one or two ...
Cell Notes
... ii. Described “little boxes” when he looked at cork. iii. Also looked at living plants and saw that some cells were filled with “juice” iv. What do you think the “juice” was? ...
... ii. Described “little boxes” when he looked at cork. iii. Also looked at living plants and saw that some cells were filled with “juice” iv. What do you think the “juice” was? ...
Cells- Osmosis and Diffusion
... made up of one or more cells. •2) Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things. •3) All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... made up of one or more cells. •2) Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things. •3) All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
Domain - Cells preassessment quesitons
... • A Water leaves the tubules of the kidney in response to the hypertonic fluid surrounding the tubules. • B Digestive enzymes are excreted into the small intestine. • C White blood cells consume pathogens and cell debris at the site of an infection. • D Calcium is pumped inside a muscle cell after t ...
... • A Water leaves the tubules of the kidney in response to the hypertonic fluid surrounding the tubules. • B Digestive enzymes are excreted into the small intestine. • C White blood cells consume pathogens and cell debris at the site of an infection. • D Calcium is pumped inside a muscle cell after t ...
HOMEOSTASIS AND CELL TRANSPORT NOTES SOLUTIONS
... Membranes are made of special lipid molecules called _________________________ arranged in two layers called a ______________. ...
... Membranes are made of special lipid molecules called _________________________ arranged in two layers called a ______________. ...
Type of Cell Diversity
... Skeletal Muscle – elongated shape which allow cells to shorten (contract) moving our skeleton. They contain long protein fibers. Smooth Muscle – elongated shape too which allow our internal organs to change size ...
... Skeletal Muscle – elongated shape which allow cells to shorten (contract) moving our skeleton. They contain long protein fibers. Smooth Muscle – elongated shape too which allow our internal organs to change size ...
10.4 Guided Notes (Cell Differentiation and Stem Cells)
... _____________________________________________ abnormal development • New _____________________________________________ for safety in humans • Cell-based regenerative therapies – stem cells induced to differentiate into specific cell types to repair damaged cells • ____________ demand for organs & ...
... _____________________________________________ abnormal development • New _____________________________________________ for safety in humans • Cell-based regenerative therapies – stem cells induced to differentiate into specific cell types to repair damaged cells • ____________ demand for organs & ...
cells
... A. In 1600s, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch lens grinder, built a microscope and was the 1st to observe tiny living ...
... A. In 1600s, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch lens grinder, built a microscope and was the 1st to observe tiny living ...
Answers to Cell Lab
... Elodea have that the onion does not? Why might this be so? The Elodea has chloroplasts and the onion cells did not. The onion cells that we were looking at are found below ground where the sun doesn’t shine; therefore, chloroplasts are of no use to them. If I had given you the leafy part of the onio ...
... Elodea have that the onion does not? Why might this be so? The Elodea has chloroplasts and the onion cells did not. The onion cells that we were looking at are found below ground where the sun doesn’t shine; therefore, chloroplasts are of no use to them. If I had given you the leafy part of the onio ...
Origins of Heredity
... •It is hypothesized that this RNA started to evolve inside cell-like structures made of proteins, amino acids, and lipids •Then the RNA started to direct the cell ...
... •It is hypothesized that this RNA started to evolve inside cell-like structures made of proteins, amino acids, and lipids •Then the RNA started to direct the cell ...
Method for producing autonomously contracting cardiac muscle
... Method for producing autonomously contracting cardiac muscle cells from adult stem cells, in particular human adult stem cells Key words: pharmacology, drug development, organotypic model system Heart failure is one of the main causes of death in industrialised countries and is a result of the inabi ...
... Method for producing autonomously contracting cardiac muscle cells from adult stem cells, in particular human adult stem cells Key words: pharmacology, drug development, organotypic model system Heart failure is one of the main causes of death in industrialised countries and is a result of the inabi ...
Functions of Cell Structures
... Cut and paste these functions for the correct cell structure on the Functions of Cell Structures page. Contains chlorophyll that changes sunlight into food Collects and stores food, water, and waste Produces the cells energy – “power plant” Directs materials inside the cell where to go Stiff wall th ...
... Cut and paste these functions for the correct cell structure on the Functions of Cell Structures page. Contains chlorophyll that changes sunlight into food Collects and stores food, water, and waste Produces the cells energy – “power plant” Directs materials inside the cell where to go Stiff wall th ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.