Chapter 2: Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Both plant and animal cells are bound by a cell membrane. This organelle acts like a barrier between this internal cell and the outside environment. The cell membrane also permits / denies the entrance and exit of many molecules, nutrients and waste materials. Cell Wall ...
... Both plant and animal cells are bound by a cell membrane. This organelle acts like a barrier between this internal cell and the outside environment. The cell membrane also permits / denies the entrance and exit of many molecules, nutrients and waste materials. Cell Wall ...
Anatomy_of_Cells - Northwest ISD Moodle
... other regulatory chemicals and trigger metabolic changes in the cell Marker Proteins: (glycoproteins) allows cells to recognize each other for immune or developmental purposes Transport Proteins: either channel or transport needed chemicals through the membrane that can not otherwise pass through th ...
... other regulatory chemicals and trigger metabolic changes in the cell Marker Proteins: (glycoproteins) allows cells to recognize each other for immune or developmental purposes Transport Proteins: either channel or transport needed chemicals through the membrane that can not otherwise pass through th ...
10-2 Cell Division lecture notes
... 2 phases of cell division: Mitosis is the division of the ___________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Cytokinesis: _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... 2 phases of cell division: Mitosis is the division of the ___________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Cytokinesis: _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Recitation 1 Solutions
... Classify each of the above organisms as unicellular or multi-cellular. Bacterial and yeast cells are unicellular whereas flies, mice and rabbits are multi-cellular. 2. You are given three different cell types, each stained with a dye that specifically binds to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). You observ ...
... Classify each of the above organisms as unicellular or multi-cellular. Bacterial and yeast cells are unicellular whereas flies, mice and rabbits are multi-cellular. 2. You are given three different cell types, each stained with a dye that specifically binds to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). You observ ...
Cell Theory and Cell Structure
... • There are two parts outside the cell: - Cell Wall: hard outside covering (not in animal cells) - Cell Membrane: cell ‘skin’ that controls transport in and out ...
... • There are two parts outside the cell: - Cell Wall: hard outside covering (not in animal cells) - Cell Membrane: cell ‘skin’ that controls transport in and out ...
Key Points on Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... i. Cell division forms new cells. Cells also increase in size before dividing. ii. An organism gets larger as the number of its cells increases. f. Must be able to reproduce. i. Reproduction is not essential for the survival of individual organisms, but must occur for a species to survive. g. Must c ...
... i. Cell division forms new cells. Cells also increase in size before dividing. ii. An organism gets larger as the number of its cells increases. f. Must be able to reproduce. i. Reproduction is not essential for the survival of individual organisms, but must occur for a species to survive. g. Must c ...
The Cell Theory - Broken Arrow Public Schools
... It is amazing to think that the cells that make up our bodies are just as alive as we are. Humans are just an intricately designed community of cells, which must work together to survive. ...
... It is amazing to think that the cells that make up our bodies are just as alive as we are. Humans are just an intricately designed community of cells, which must work together to survive. ...
Fall 2009 Lecture 1 - Department of Chemistry -
... - Vitamins: organic compounds necessary for proper growth and development - Heme: Organometallic compound containing iron; important for transporting oxygen in your blood stream. Building blocks are used to create macromolecules: polymer of several, hundreds, to sometimes millions of building blocks ...
... - Vitamins: organic compounds necessary for proper growth and development - Heme: Organometallic compound containing iron; important for transporting oxygen in your blood stream. Building blocks are used to create macromolecules: polymer of several, hundreds, to sometimes millions of building blocks ...
Cell Features
... Can Exist in a broad range of environments Enzymes and Ribosomes are free to move around in the cytoplasm. No internal structures to divide the cell Single circular molecule of DNA Have a cell wall that provides structure and support and made of polysaccharides Cell wall can be surrounded by a capsu ...
... Can Exist in a broad range of environments Enzymes and Ribosomes are free to move around in the cytoplasm. No internal structures to divide the cell Single circular molecule of DNA Have a cell wall that provides structure and support and made of polysaccharides Cell wall can be surrounded by a capsu ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 20. Demonstrate and describe proper microscope technique and handling. ...
... 20. Demonstrate and describe proper microscope technique and handling. ...
Cells Study Guide - Little Miami Schools
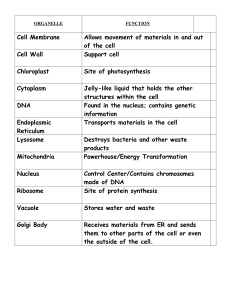
... How cells got their name and the scientists who first viewed cells (Hooke vs. VonLeeuwenhoek) 3 parts of the cell theory The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell Organelles of a cell: be able to label a diagram of a cell with the parts Be able to describe the function of the ...
... How cells got their name and the scientists who first viewed cells (Hooke vs. VonLeeuwenhoek) 3 parts of the cell theory The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell Organelles of a cell: be able to label a diagram of a cell with the parts Be able to describe the function of the ...
cell theory
... membranes allow a large amount of work to be done in a small amount of space • Transportation unit for the cell • Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) – Ribosomes attached – Protein synthesis ...
... membranes allow a large amount of work to be done in a small amount of space • Transportation unit for the cell • Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) – Ribosomes attached – Protein synthesis ...
SUPER DUPER CELL EXPLORATION WEBQUEST
... Every living thing is composed of at least one cell. Bacteria, amoebae, and paramecia are made of one cell and are capable of the activities of life. Organisms made of one cell are unicellular. Most living things are made of more than one cell and are called multicellular. Cells of these organisms f ...
... Every living thing is composed of at least one cell. Bacteria, amoebae, and paramecia are made of one cell and are capable of the activities of life. Organisms made of one cell are unicellular. Most living things are made of more than one cell and are called multicellular. Cells of these organisms f ...
LAB- Plant vs. Animal Cell Directions
... Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundreds of years of observations by many biologists, the cell theory was developed. The cell theory states that the cell is the structural and functional unit ...
... Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundreds of years of observations by many biologists, the cell theory was developed. The cell theory states that the cell is the structural and functional unit ...
Week-At-A-Glance - Harrison High School
... Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. ...
... Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. ...
Cell theory states: living things are composed of one or
... By the late 1830s, botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory. The unified cell theory states that: all living things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing ce ...
... By the late 1830s, botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory. The unified cell theory states that: all living things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing ce ...
There are two types of cells
... Plague, also called Black Death. This bacteria was spread through fleas and rodents. ...
... Plague, also called Black Death. This bacteria was spread through fleas and rodents. ...
Two types of cells
... Plague, also called Black Death. This bacteria was spread through fleas and rodents. ...
... Plague, also called Black Death. This bacteria was spread through fleas and rodents. ...
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... There are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. A prokaryotic cell does not have a true nucleus. Although the genetic material is usually contained in a central location, a membrane does not surround it. Furthermore, prokaryotic cells have no membrane bound organelles. Bacteria are p ...
... There are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. A prokaryotic cell does not have a true nucleus. Although the genetic material is usually contained in a central location, a membrane does not surround it. Furthermore, prokaryotic cells have no membrane bound organelles. Bacteria are p ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.