Cell Organelles Graphic Organizer
... - Found in plant cells - Contains green chlorophyll Cell Wall Function: Photosynthesis uses sunlight to make sugar for plant ...
... - Found in plant cells - Contains green chlorophyll Cell Wall Function: Photosynthesis uses sunlight to make sugar for plant ...
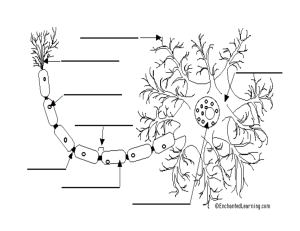
axon diagram
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
File
... Click on the prokaryotic cell model and answer the following questions: 2. Label the prokaryotic bacterial cell below. 3. What substance is located in the nucleoid region of this cell? ...
... Click on the prokaryotic cell model and answer the following questions: 2. Label the prokaryotic bacterial cell below. 3. What substance is located in the nucleoid region of this cell? ...
Structure and Function of Cells
... outside the cell membrane; can be made of cellulose Outermost living layer of the cell; elastic and flexible; contains pores Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane; consists of a jellylike substance that contains many organelles Large, oval structure in the center of the cell; bounded by t ...
... outside the cell membrane; can be made of cellulose Outermost living layer of the cell; elastic and flexible; contains pores Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane; consists of a jellylike substance that contains many organelles Large, oval structure in the center of the cell; bounded by t ...
Cell Growth
... 1. What is cell growth? (**getting bigger, gaining mass) 2. What's the difference btwn growth and division?(**getting bigger, reproduction) 3. Are our cells the same size as an infants? (**yes) Then, why is a baby smaller?(**they have less cells) 4. How do we grow? (**cells increase in size and numb ...
... 1. What is cell growth? (**getting bigger, gaining mass) 2. What's the difference btwn growth and division?(**getting bigger, reproduction) 3. Are our cells the same size as an infants? (**yes) Then, why is a baby smaller?(**they have less cells) 4. How do we grow? (**cells increase in size and numb ...
Ch.4 Cell Notes - Milan Area Schools
... Puts finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER Packages finished material for shipment to ...
... Puts finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER Packages finished material for shipment to ...
True or False. The cells in your body are Eukaryotic. Explain. A: True
... A: Vacuoles are large storehouses for water in a plant cell. 17. This cell structure controls what passes in and out of the cell. A: Cell membranes are porous and allow various gasses, water, waster, food to pass into and out of the cell. 18. One way plant cells are different from animal cells is th ...
... A: Vacuoles are large storehouses for water in a plant cell. 17. This cell structure controls what passes in and out of the cell. A: Cell membranes are porous and allow various gasses, water, waster, food to pass into and out of the cell. 18. One way plant cells are different from animal cells is th ...
Lesson 6 Plant vs. Animal Cells
... There are many subtle differences between plant and animal cells. The different modes of nutrition is where the biggest differences occur. ...
... There are many subtle differences between plant and animal cells. The different modes of nutrition is where the biggest differences occur. ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Division Name Class Date
... Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Division In order to reproduce, a cell must be able to duplicate its DNA and pass along identical copies to each new daughter cell. This is true for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, the two types of cells do not go about DNA replication in the same way. ...
... Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Division In order to reproduce, a cell must be able to duplicate its DNA and pass along identical copies to each new daughter cell. This is true for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, the two types of cells do not go about DNA replication in the same way. ...
Name: Period: ______ Date: October 16, 2015 Warm
... ______ 2. Plant cells and animal cells are classified as eukaryotic, rather than prokaryotic, due to their unique features. All eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are classified as either plant or animal cells, dependent upon which specific organelles ...
... ______ 2. Plant cells and animal cells are classified as eukaryotic, rather than prokaryotic, due to their unique features. All eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are classified as either plant or animal cells, dependent upon which specific organelles ...
cell wall - WordPress.com
... cells are the basic unit of structure and function. Similar cells are organized into tissues. Different tissues working together to perform a specific job form organs. Groups of organs working together form organ systems. Organ systems work together to form an organism which is anything that can liv ...
... cells are the basic unit of structure and function. Similar cells are organized into tissues. Different tissues working together to perform a specific job form organs. Groups of organs working together form organ systems. Organ systems work together to form an organism which is anything that can liv ...
Eukaryotic Cell
... Giant DNA molecules become visible in the form of chromosomes as the cell compacts the molecules to prepare for cellular division Controls cell activities ...
... Giant DNA molecules become visible in the form of chromosomes as the cell compacts the molecules to prepare for cellular division Controls cell activities ...
Cell Organelles
... Flagella may extend to the rear of a cell and push it forward by snakelike wriggling, or stick out in front and draw it along. Each sperm cell is propelled by a trailing flagellum that accelerates the little torpedo forward in its quest to ...
... Flagella may extend to the rear of a cell and push it forward by snakelike wriggling, or stick out in front and draw it along. Each sperm cell is propelled by a trailing flagellum that accelerates the little torpedo forward in its quest to ...
What are cells? Your body is divided into tiny sections called cells
... • There are cells that are organisms, such as microscopic amoeba and bacteria cells. • There are cells that only function when they are part of a larger organism, such as the cells that make up your body. ...
... • There are cells that are organisms, such as microscopic amoeba and bacteria cells. • There are cells that only function when they are part of a larger organism, such as the cells that make up your body. ...
Bio102 Problems
... 3. Which one of the following is NEVER found in a prokaryotic cell? A. DNA B. Ribosome C. Cell Membrane D. Mitochondria E. Flagella 4. Which structure is “semi-autonomous”? A. Ribosome B. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum C. Nucleus D. Chloroplast E. Cell wall 5. The Endosymbiont Theory is supported by a ...
... 3. Which one of the following is NEVER found in a prokaryotic cell? A. DNA B. Ribosome C. Cell Membrane D. Mitochondria E. Flagella 4. Which structure is “semi-autonomous”? A. Ribosome B. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum C. Nucleus D. Chloroplast E. Cell wall 5. The Endosymbiont Theory is supported by a ...
Summary Peroxisome is a structure present in the all eukaryotic
... containing a fluid with dissolved molecules. In plant cells, the vacuole takes up a large amount of space, at times, it occupies more than 90% of the plant cell space. It is said that vacuoles are usually formed by the fusion of many membrane vesicles. Due to this reason, a vacuole does not have any ...
... containing a fluid with dissolved molecules. In plant cells, the vacuole takes up a large amount of space, at times, it occupies more than 90% of the plant cell space. It is said that vacuoles are usually formed by the fusion of many membrane vesicles. Due to this reason, a vacuole does not have any ...
Mitosis/Cancer Lecture Notes
... • If the cell does not receive the go-ahead signal, it will exit the cycle, switching into a non-dividing state called the G0 phase ...
... • If the cell does not receive the go-ahead signal, it will exit the cycle, switching into a non-dividing state called the G0 phase ...
PowerPoint: Lab-Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
... 1. What structures or organelles were not visible in any of the cells you observed? 2. The potato and onion cells are both plant cells, why were their no chloroplasts observed in either cells? 3. What are three cellular or structure differences between plant cells and animal cells? 4. Why did we not ...
... 1. What structures or organelles were not visible in any of the cells you observed? 2. The potato and onion cells are both plant cells, why were their no chloroplasts observed in either cells? 3. What are three cellular or structure differences between plant cells and animal cells? 4. Why did we not ...
Cells
... Chloroplasts capture energy from the sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. A vacuole is a water filled sac used as a storage area for cells. The cell’s clean up crew are the lysosome. They are small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials in the cell. ...
... Chloroplasts capture energy from the sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. A vacuole is a water filled sac used as a storage area for cells. The cell’s clean up crew are the lysosome. They are small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials in the cell. ...
4-1: What are cells
... o 2. Cells are the basic structure in living things and carry on all life processes. o 3. Cells come only from other living cells. Check: 1. A theory is an idea that explains something and is supported by data. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure in living things. 3. Robert Hooke was the fi ...
... o 2. Cells are the basic structure in living things and carry on all life processes. o 3. Cells come only from other living cells. Check: 1. A theory is an idea that explains something and is supported by data. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure in living things. 3. Robert Hooke was the fi ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.