A1979HZ27200001
... Tumor Institute in Houston in an attempt to demonstrate just where the tissues of inbred maize and their heterotic hybrids showed differences in the nature or number of ...
... Tumor Institute in Houston in an attempt to demonstrate just where the tissues of inbred maize and their heterotic hybrids showed differences in the nature or number of ...
Mr - socesbio.c…
... CB1d: the main idea (Central Dogma) of molecular biology shows how information moves from DNA to RNA during Transcription, and Translates into proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. CB1e: how endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies (apparatus) help move proteins. CB1f: sunlight (energy) and carbon d ...
... CB1d: the main idea (Central Dogma) of molecular biology shows how information moves from DNA to RNA during Transcription, and Translates into proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. CB1e: how endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies (apparatus) help move proteins. CB1f: sunlight (energy) and carbon d ...
Biological Membranes
... Uses energy in the form of ATP Pumps two K+ ions into the cell for every three Na+ ions it pumps out This causes an electrical as well as chemical gradient across the cell membrane – an electrochemical gradient This gradient stores energy for the cell and can be used to help drive other tran ...
... Uses energy in the form of ATP Pumps two K+ ions into the cell for every three Na+ ions it pumps out This causes an electrical as well as chemical gradient across the cell membrane – an electrochemical gradient This gradient stores energy for the cell and can be used to help drive other tran ...
The Cell
... secretions from salt that gets trapped inside cells that draws moisture inside. Movement through the Cell Membrane Diffusion – movement from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (example – oxygen/carbon dioxide) Facilitated Diffusion – Special carrier molecule moves substanc ...
... secretions from salt that gets trapped inside cells that draws moisture inside. Movement through the Cell Membrane Diffusion – movement from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (example – oxygen/carbon dioxide) Facilitated Diffusion – Special carrier molecule moves substanc ...
RG Transport Review 0910
... materials can pass through by diffusion, without a problem. The graph below shows the size of some molecules that need to move across the lipid bilayer. Size of Molecules ...
... materials can pass through by diffusion, without a problem. The graph below shows the size of some molecules that need to move across the lipid bilayer. Size of Molecules ...
Cell Membrane
... 1. All living things are made up of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division Principles of Cell Theory: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Smallest living unit of structure and function of all organisms ...
... 1. All living things are made up of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division Principles of Cell Theory: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Smallest living unit of structure and function of all organisms ...
The Cell Cycle
... • The cell membrane pinches to off to form 2 new cells. • 2 identical cells are formed ...
... • The cell membrane pinches to off to form 2 new cells. • 2 identical cells are formed ...
The Parts of the Cell - St. Pius X High School
... TAY SACHS DISEASE --missing an enzyme in lysosomes that breaks down a fatty substance --fat builds up in the brain and nervous tissue, smothering cells --results in degeneration and death ...
... TAY SACHS DISEASE --missing an enzyme in lysosomes that breaks down a fatty substance --fat builds up in the brain and nervous tissue, smothering cells --results in degeneration and death ...
cell
... Peripheral membrane proteins - do not penetrate the hydrophobic core of the membrane; can be easily removed without destroying the membrane structure. Integral membrane proteins - fully incorporated into the membrane and are in contact with both the inside and the outside of the cell; some act as c ...
... Peripheral membrane proteins - do not penetrate the hydrophobic core of the membrane; can be easily removed without destroying the membrane structure. Integral membrane proteins - fully incorporated into the membrane and are in contact with both the inside and the outside of the cell; some act as c ...
Mitosis
... The life of a cell is divided into three stages known as the cell cycle: 1. Interphase: cell carries out normal functions and prepares to divide 2. Mitosis: nucleus divides splits into two 3. Cytokinesis: cell and contents divide into two daughter cells. ...
... The life of a cell is divided into three stages known as the cell cycle: 1. Interphase: cell carries out normal functions and prepares to divide 2. Mitosis: nucleus divides splits into two 3. Cytokinesis: cell and contents divide into two daughter cells. ...
lessonuploads/Chapter 1 Section 2 vocab chart HO
... Thin strands floating around in the nucleus ...
... Thin strands floating around in the nucleus ...
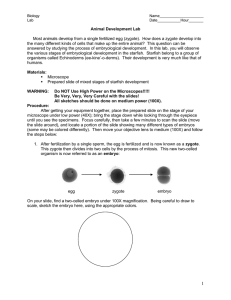
LabStarfishDevelopment
... The outer layer of the gastrula is called the ectoderm (ecto=outside), and develops into the skin and nervous system of the animal. The inner layer of this form is called the endoderm (endo=inside or within), and develops into the lining of the digestive tract and organs that are part of the digesti ...
... The outer layer of the gastrula is called the ectoderm (ecto=outside), and develops into the skin and nervous system of the animal. The inner layer of this form is called the endoderm (endo=inside or within), and develops into the lining of the digestive tract and organs that are part of the digesti ...
Effects of Pathogens On Plant Physiology
... – Rusts, Mildews and Apple Scab Destroy Considerable Portion of Cuticle and Epidermis – Loss of Turgor and Wilting of Leaves – Suction Forces may Lead to Collapse or Dysfunction of Underlying Vessels ...
... – Rusts, Mildews and Apple Scab Destroy Considerable Portion of Cuticle and Epidermis – Loss of Turgor and Wilting of Leaves – Suction Forces may Lead to Collapse or Dysfunction of Underlying Vessels ...
Basic Structure of a Cell
... 86. What 3 things make up the Endomembrane transport system in a cell? 87. Ribosomes are made of _____________ and __________ and function as ______________ factories. 88. Ribosomes join _________________ to make proteins though a process called ________________________. 89. Where are free ribosomes ...
... 86. What 3 things make up the Endomembrane transport system in a cell? 87. Ribosomes are made of _____________ and __________ and function as ______________ factories. 88. Ribosomes join _________________ to make proteins though a process called ________________________. 89. Where are free ribosomes ...
Chapter 5: Cell Transport
... Cell Transport *A cell must exchange materials with its surroundings, a process controlled by the cell membrane *Cell membranes are selectively permeable, regulating what enters/leaves the cell ...
... Cell Transport *A cell must exchange materials with its surroundings, a process controlled by the cell membrane *Cell membranes are selectively permeable, regulating what enters/leaves the cell ...
Slide ()
... Contact mode AFM images (15×15μm) of untreated HAECs (A), (C), (D) and after 45min treatment with 4μM cytochalasin B (B). Superposed on each image is a gray scale map of the pointwise elastic modulus extracted at an indentation depth of 200nm obtained from an array of 64 force curves as described in ...
... Contact mode AFM images (15×15μm) of untreated HAECs (A), (C), (D) and after 45min treatment with 4μM cytochalasin B (B). Superposed on each image is a gray scale map of the pointwise elastic modulus extracted at an indentation depth of 200nm obtained from an array of 64 force curves as described in ...
Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport
... Equilibrium • When the concentration of molecules of a substance is the same throughout a space • Even at equilibrium the random motions of molecules still occur • Random motions on one direction balance out those of the other direction ...
... Equilibrium • When the concentration of molecules of a substance is the same throughout a space • Even at equilibrium the random motions of molecules still occur • Random motions on one direction balance out those of the other direction ...
NC-3000™ DNA Fragmentation Assay
... system and cellular fluorescence is quantified and apoptotic cells with fragmented DNA are seen as a sub-G1 peak in a DNA content histogram displayed on PC screen. Markers in the histogram can be used to demarcate apoptotic cells. ...
... system and cellular fluorescence is quantified and apoptotic cells with fragmented DNA are seen as a sub-G1 peak in a DNA content histogram displayed on PC screen. Markers in the histogram can be used to demarcate apoptotic cells. ...
Biology Midterm Review Sheet
... What are chloroplasts and how are they related to photosynthesis? What are vacuoles? How is the size different in an animal versus a plant cell? Why do you think this is so? What is diffusion? How is concentration of solutions involved? Compare passive to active transport, which one requires energy? ...
... What are chloroplasts and how are they related to photosynthesis? What are vacuoles? How is the size different in an animal versus a plant cell? Why do you think this is so? What is diffusion? How is concentration of solutions involved? Compare passive to active transport, which one requires energy? ...
chapter 1o section 3 notes
... Internal regulators are proteins that respond to events inside a cell. They allow the cell cycle to proceed only once certain processes have happened inside the cell. External regulators are proteins that respond to events outside the cell. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. ...
... Internal regulators are proteins that respond to events inside a cell. They allow the cell cycle to proceed only once certain processes have happened inside the cell. External regulators are proteins that respond to events outside the cell. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. ...
p75 neurotrophin receptor and pro-BDNF promote cell survival and
... or alone, as indicated in figure. B. In parallel, viability was evaluated under identical experimental conditions by using XTT (Roche Ref 11-465-015-001) to validate our results. Results are represented as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Differences were ...
... or alone, as indicated in figure. B. In parallel, viability was evaluated under identical experimental conditions by using XTT (Roche Ref 11-465-015-001) to validate our results. Results are represented as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Differences were ...
Study Guide, Section 2
... Label the diagram of the stages of mitosis using lines 13–16. Use these choices: anaphase ...
... Label the diagram of the stages of mitosis using lines 13–16. Use these choices: anaphase ...
Cell Structure and Function
... organelles and their functions • Warm up: how does cell structure relate to cell function? How can this relationship be seen between different organisms? Hint: Smooth muscle cell of a human Smooth Muscle cell of a cow ...
... organelles and their functions • Warm up: how does cell structure relate to cell function? How can this relationship be seen between different organisms? Hint: Smooth muscle cell of a human Smooth Muscle cell of a cow ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.