Nucleus 1
... growth and reproduction. It controls the cell through protein synthesis. • Protein Synthesis is the process by which amino acids are arranged linearly into proteins through the involvement of ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, messenger RNA, and various enzymes ...
... growth and reproduction. It controls the cell through protein synthesis. • Protein Synthesis is the process by which amino acids are arranged linearly into proteins through the involvement of ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, messenger RNA, and various enzymes ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. ...
... • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. ...
Fuel cells - The Toppers Way
... development, each with its own advantages, limitations, and potential applications. A few of the most promising types include ...
... development, each with its own advantages, limitations, and potential applications. A few of the most promising types include ...
SUMMER HOLIDAYS HOMEWORK (2017-2018)
... 4. What is the general name of (a) rigid form of matter (b) fluid form of matter 5. Why do gases diffuse very fast? 6. Name the process by which a drop of ink spreads in a beaker of water. 7. The boiling point of alcohol is 78 degree celcius. What is this temp. in kelvin scale? 8. The kelvin scale t ...
... 4. What is the general name of (a) rigid form of matter (b) fluid form of matter 5. Why do gases diffuse very fast? 6. Name the process by which a drop of ink spreads in a beaker of water. 7. The boiling point of alcohol is 78 degree celcius. What is this temp. in kelvin scale? 8. The kelvin scale t ...
Plant cells - Cloudfront.net
... that store water, wastes, and sometimes enzymes. - There usually is 1 large vacuole in plant cells. Plants have larger vacuoles because they may not always get water…so they have to store it and slowly use it. ...
... that store water, wastes, and sometimes enzymes. - There usually is 1 large vacuole in plant cells. Plants have larger vacuoles because they may not always get water…so they have to store it and slowly use it. ...
Cells Are Us
... Next, all eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells include everything except bacteria (prokaryotic cells) and viruses (A virus is a small particle that infects cells in biological organisms. can reproduce only by invading and taking over other cells as they lack the cellular machinery for s ...
... Next, all eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells include everything except bacteria (prokaryotic cells) and viruses (A virus is a small particle that infects cells in biological organisms. can reproduce only by invading and taking over other cells as they lack the cellular machinery for s ...
Mrs. Kaplan`s Science Page!
... Name the three organelles that could be seen through the microscope in a cheek cell or onion cell. Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus ...
... Name the three organelles that could be seen through the microscope in a cheek cell or onion cell. Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus ...
Notes - LHSdiffbio
... 2. All cells come from preexisting cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. ...
... 2. All cells come from preexisting cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. ...
What are Cells? - Mona Shores Blogs
... both are made up of organelles (ribosomes, golgi bodies etc….) both cells have a nucleus both combine to make tissues both have cytoplasm many are microscopic ...
... both are made up of organelles (ribosomes, golgi bodies etc….) both cells have a nucleus both combine to make tissues both have cytoplasm many are microscopic ...
Cell Design Studio Highlight Projects - Sigma
... Following confirmation of the genetic modification, cardiomyocytes were generated by directed differentiation of NKX2-5-2A-GFP iPSC0028 cells. Unlike the still-pluripotent modified cells, which showed no expression of GFP, modified cells exhibited robust GFP expression once differentiated to the car ...
... Following confirmation of the genetic modification, cardiomyocytes were generated by directed differentiation of NKX2-5-2A-GFP iPSC0028 cells. Unlike the still-pluripotent modified cells, which showed no expression of GFP, modified cells exhibited robust GFP expression once differentiated to the car ...
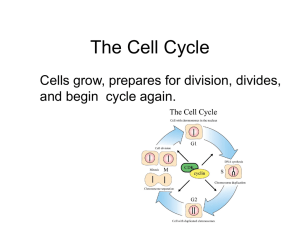
Stages of the cell cycle
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
File
... Shows the evolutionary relationships between organisms, with the oldest organism at one end and each animal being more evolved than the last ...
... Shows the evolutionary relationships between organisms, with the oldest organism at one end and each animal being more evolved than the last ...
The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments A. The Cell: The
... The formation and functions of lysosomes (Step 1) ...
... The formation and functions of lysosomes (Step 1) ...
Animal Tissues PowerPoint for Lab
... together for a particular function. In humans, combinations of different types of tissues make up organs, and groups of organs work together to form organ systems. Four Types of Tissue 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Nervous 4. Muscle ...
... together for a particular function. In humans, combinations of different types of tissues make up organs, and groups of organs work together to form organ systems. Four Types of Tissue 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Nervous 4. Muscle ...
Cell structure is correlated to
... -provides support, limits cell’s volume, and protects against fungi and/or microorganism infection. Cell Walls of Plants ● Plant cell walls may have multiple layers: -Primary cell wall: relatively thin and flexible -Middle lamella: thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells -Secondary cell w ...
... -provides support, limits cell’s volume, and protects against fungi and/or microorganism infection. Cell Walls of Plants ● Plant cell walls may have multiple layers: -Primary cell wall: relatively thin and flexible -Middle lamella: thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells -Secondary cell w ...
CHAPTER 12 THE CELL CYCLE
... The Key Roles of Cell Division 1. Understand that cell division functions in reproduction, growth, renewal and repair. 2. Explain how chromatin, chromosomes and genomes relate to one another 3. Describe the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete. The Mitotic Cell Cycle 1. Describe the proces ...
... The Key Roles of Cell Division 1. Understand that cell division functions in reproduction, growth, renewal and repair. 2. Explain how chromatin, chromosomes and genomes relate to one another 3. Describe the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete. The Mitotic Cell Cycle 1. Describe the proces ...
Chapter 2 notes- cells
... shows a distinct cloudy nucleus filled with chromatin. 1. G1 (growth 1)- after a cell is created it enters this stage and performs its specialized function 2. S (synthesis)- DNA is copied so there are two sets of chromosomes 3. G2 (growth 2)- cell continues to grow and prepare for cell division ...
... shows a distinct cloudy nucleus filled with chromatin. 1. G1 (growth 1)- after a cell is created it enters this stage and performs its specialized function 2. S (synthesis)- DNA is copied so there are two sets of chromosomes 3. G2 (growth 2)- cell continues to grow and prepare for cell division ...
File
... Hypotonic: (think hippo) solute concentrations inside are higher than outside the cell. When hypotonic, water moves inside the cell and it swells ...
... Hypotonic: (think hippo) solute concentrations inside are higher than outside the cell. When hypotonic, water moves inside the cell and it swells ...
Team Publications
... show that release of short MTs from the centrosome is frequent in migrating cells and that their transport toward the cell periphery is blocked when dynein activity is impaired. We further show that MT release, but not MT nucleation or polymerization dynamics, is abolished by overexpression of the c ...
... show that release of short MTs from the centrosome is frequent in migrating cells and that their transport toward the cell periphery is blocked when dynein activity is impaired. We further show that MT release, but not MT nucleation or polymerization dynamics, is abolished by overexpression of the c ...
Cell Structure Review
... Organelles that cause the release of energy by using oxygen to break down sugars. Usually round or tube shaped Releases food molecules that supply energy to the cell; it is known as the powerhouse of the cell. Usually more than one in a cell ...
... Organelles that cause the release of energy by using oxygen to break down sugars. Usually round or tube shaped Releases food molecules that supply energy to the cell; it is known as the powerhouse of the cell. Usually more than one in a cell ...
NAME DATE___________ CHAPTER 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND
... Below is a diagram showing the process of osmosis in two different cell types. The arrows represent the movement of water. ...
... Below is a diagram showing the process of osmosis in two different cell types. The arrows represent the movement of water. ...
monocellular eukaryote
... Function in yeast (and Function in other multicellular eukaryotes in bacteria monocellular eukaryotes) Function ...
... Function in yeast (and Function in other multicellular eukaryotes in bacteria monocellular eukaryotes) Function ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.