Life*s home: The Cell - Tyler Flisik
... “We, all of us, are what happens when a primordial mixture of hydrogen and helium evolves for so long that it begin to ask where it came from” -Jill Tarter ...
... “We, all of us, are what happens when a primordial mixture of hydrogen and helium evolves for so long that it begin to ask where it came from” -Jill Tarter ...
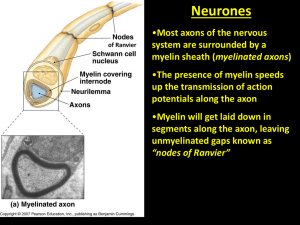
Myelin Sheaths Plant Hormone Intro
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
Lesson Plan Plant Cells
... Summary: In order for students to understand life science they must understand the most basic form of life, which is the cell. They must understand what it is made of and how it functions in order for there to life at all. This lesson is designed to introduce the plant cell along with all of its par ...
... Summary: In order for students to understand life science they must understand the most basic form of life, which is the cell. They must understand what it is made of and how it functions in order for there to life at all. This lesson is designed to introduce the plant cell along with all of its par ...
Shine & Write for teachers
... Cells are the smallest unit of life which can perform the seven characteristics of living things. Different cells are adapted to do different jobs in the bodies of plants and animals. These are called SPECIALISED CELLS ...
... Cells are the smallest unit of life which can perform the seven characteristics of living things. Different cells are adapted to do different jobs in the bodies of plants and animals. These are called SPECIALISED CELLS ...
Station #1: Chemistry
... Which organelle transports ribosomes from one end of the cell to another? Rough ER Which organelle creates ribosomes? Nucleolus Which organelle packages and ships proteins outside of a cell? Golgi body Which organelle creates ATP energy? Mitochondria Which two organelles (besides the nucleus) co ...
... Which organelle transports ribosomes from one end of the cell to another? Rough ER Which organelle creates ribosomes? Nucleolus Which organelle packages and ships proteins outside of a cell? Golgi body Which organelle creates ATP energy? Mitochondria Which two organelles (besides the nucleus) co ...
Plant tissue systems - Science with Stacey
... Cellulose is a polysaccharide made from β glucose monomers. Alternate glucose molecules “flip over” in the chain, forming hydrogen bonds between adjacent cellulose chains. Because cellulose has no side branches the chains can be packed closely which increases the strength of the hydrogen bonds f ...
... Cellulose is a polysaccharide made from β glucose monomers. Alternate glucose molecules “flip over” in the chain, forming hydrogen bonds between adjacent cellulose chains. Because cellulose has no side branches the chains can be packed closely which increases the strength of the hydrogen bonds f ...
Plant Tissues-PPT
... shape. The cell wall is thin & encloses a dense cytoplasm which contains a small nucleus & surrounds a large central vacuole. Occurrence-the parenchyma is widely distributed in stem,roots, FunctionsParenchyma maintain the shape & firmness of the plant due to its turgid cells. The main function of pa ...
... shape. The cell wall is thin & encloses a dense cytoplasm which contains a small nucleus & surrounds a large central vacuole. Occurrence-the parenchyma is widely distributed in stem,roots, FunctionsParenchyma maintain the shape & firmness of the plant due to its turgid cells. The main function of pa ...
Chapter 12 – The Cell Cycle – Pages 215
... In animal cells a cleavage furrow forms and is a pinching in of the two prospective daughter cells. This starts near the metaphase plate and proteins actin and myosin work together as a drawstring to pull the two cells together and then separating into two new cells. In plant cells a cell plate form ...
... In animal cells a cleavage furrow forms and is a pinching in of the two prospective daughter cells. This starts near the metaphase plate and proteins actin and myosin work together as a drawstring to pull the two cells together and then separating into two new cells. In plant cells a cell plate form ...
Unit 2: Cells & Microscope
... Makes lipids and other materials for inside and outside the cell. Breaks down drugs and other harmful chemicals. May be covered with ribosomes (Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum) ...
... Makes lipids and other materials for inside and outside the cell. Breaks down drugs and other harmful chemicals. May be covered with ribosomes (Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum) ...
P014 The role of auxin transport in root hair development Angharad
... shows remarkable consistency both within and between species, with hairs being produced almost exclusively within two hair’s widths from the transverse cell wall closest to the root apex. The transport of the plant hormone auxin from cell to cell through the epidermal cell layer in an apical to basa ...
... shows remarkable consistency both within and between species, with hairs being produced almost exclusively within two hair’s widths from the transverse cell wall closest to the root apex. The transport of the plant hormone auxin from cell to cell through the epidermal cell layer in an apical to basa ...
Cell Theory Lab-honors-bio
... 1. How did observing the cork allow Robert Hooke to begin development of the cell theory? 2. How did observing the diatom help Anton Van Leeuwenhoek to contribute to the cell theory? 3. How did observing plant cells allow Matthias Schleiden contribute to the cell theory? 4. How did observing cheek c ...
... 1. How did observing the cork allow Robert Hooke to begin development of the cell theory? 2. How did observing the diatom help Anton Van Leeuwenhoek to contribute to the cell theory? 3. How did observing plant cells allow Matthias Schleiden contribute to the cell theory? 4. How did observing cheek c ...
KONTRAK KULIAH & STRUKTUR DAN FUNGSI SEL
... • Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration – This process uses the chemical energy in food to make ATP for cellular work ...
... • Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration – This process uses the chemical energy in food to make ATP for cellular work ...
Cell Organelle Flip Book Assignment: Create a flip book of different
... Cell Organelle Flip Book Assignment: Create a flip book of different cell types and organelles for study and reference. Standard: SC.912.L.14.3 compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells. compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. SC.9 ...
... Cell Organelle Flip Book Assignment: Create a flip book of different cell types and organelles for study and reference. Standard: SC.912.L.14.3 compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells. compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. SC.9 ...
The amazing plant cell.
... all living organisms. All organisms are composed of cells All cells arise from other cells (you can’t make cells from scratch, you need a pre-existent cell). ...
... all living organisms. All organisms are composed of cells All cells arise from other cells (you can’t make cells from scratch, you need a pre-existent cell). ...
4-2-pt.1
... Proteins - are attached loosely to the inner or outer membrane. Integral Proteins – extend into, or through the membrane. Transmembrane Proteins – appear at both the inner and outer surface. ...
... Proteins - are attached loosely to the inner or outer membrane. Integral Proteins – extend into, or through the membrane. Transmembrane Proteins – appear at both the inner and outer surface. ...
Tumor Cells and the Onset of Cancer
... IV. Cancer cells may secrete a protein that converts the serum protein plasminogen to the active protease plasmin. V. As the basal lamina degrades, some of the tumor cell will enter the blood stream, but fewer than 1 in 10,000 survive and are able to create a secondary, metastic tumor. ...
... IV. Cancer cells may secrete a protein that converts the serum protein plasminogen to the active protease plasmin. V. As the basal lamina degrades, some of the tumor cell will enter the blood stream, but fewer than 1 in 10,000 survive and are able to create a secondary, metastic tumor. ...
ert 211 biochemical engineering
... found that the end yield was only 15%. The company aims to produce codeine up to 30% in their next operation.As a bioprocess engineer in the company, suggest how to improve the production of codeine to meet the company’s demand. 1) Optimization of culture condition -Find medium that influence both g ...
... found that the end yield was only 15%. The company aims to produce codeine up to 30% in their next operation.As a bioprocess engineer in the company, suggest how to improve the production of codeine to meet the company’s demand. 1) Optimization of culture condition -Find medium that influence both g ...
POGIL Biology I – Introduction to life on earth
... 9. In model 2, which cytoskeletal filaments can be involved with movement of a cell through its environment (motility)? Name any involved structures. ...
... 9. In model 2, which cytoskeletal filaments can be involved with movement of a cell through its environment (motility)? Name any involved structures. ...
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
... • Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) a membrane system of folded sacs and interconnected channels to make carbohydrates and liquids and phospholipids • Phospholipids are an important part of the cell membrane • Does NOT have ribosomes so it is smooth ...
... • Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) a membrane system of folded sacs and interconnected channels to make carbohydrates and liquids and phospholipids • Phospholipids are an important part of the cell membrane • Does NOT have ribosomes so it is smooth ...
Developmental Patterns
... – large egg divided into typical small cells – large increase in number of cells, chromatin, surface membrane ...
... – large egg divided into typical small cells – large increase in number of cells, chromatin, surface membrane ...
WHAT IS “ALIVE?” – Living or Nonliving
... cells (cell theory): all organisms are composed of cells (singlecelled or multi-cellular), all cells come from pre-existing cells, and cells are the basic unit of life. SC.6.L.14.3 Recognize and explore how cells of all organisms undergo similar processes to maintain homeostasis, including extractin ...
... cells (cell theory): all organisms are composed of cells (singlecelled or multi-cellular), all cells come from pre-existing cells, and cells are the basic unit of life. SC.6.L.14.3 Recognize and explore how cells of all organisms undergo similar processes to maintain homeostasis, including extractin ...
Biological background of cell-ECM interactions
... Jones & Wagers, No place like home: Anatomy and function of the stem cell niche, Nature Rev 9, 11-22 (2008) ...
... Jones & Wagers, No place like home: Anatomy and function of the stem cell niche, Nature Rev 9, 11-22 (2008) ...
The Prokaryotes Simplest organisms All unicellular
... 4. Feeding B. Flagella - Solid, unsheathed, protein - Filament, hook, basal body C. Axial Filaments D. Fimbriae and Pili ...
... 4. Feeding B. Flagella - Solid, unsheathed, protein - Filament, hook, basal body C. Axial Filaments D. Fimbriae and Pili ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.