HW 9/14 Two Kinds of Cells
... This brain like organ is called a nucleus (nuke lee us). The nucleus controls how fast a cell grows, how much it eats, and when it reproduces. Your brain has very similar functions (plus a whole lot more). Whether a cell has a nucleus or not is what determines the difference between the two types of ...
... This brain like organ is called a nucleus (nuke lee us). The nucleus controls how fast a cell grows, how much it eats, and when it reproduces. Your brain has very similar functions (plus a whole lot more). Whether a cell has a nucleus or not is what determines the difference between the two types of ...
, A-terminal bud, B-leaf, C-lateraJ bud, 0- stem, E-lateral root, F
... (c) The air space C permits the diffusion of oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour to or from the cells inside the leaf. (d) (i) and (ii) The elongated palisade cells allow the sunlight to penetrate without being absorbed by cell walls. The abundant chloroplasts in the palisade cells absorb and us ...
... (c) The air space C permits the diffusion of oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour to or from the cells inside the leaf. (d) (i) and (ii) The elongated palisade cells allow the sunlight to penetrate without being absorbed by cell walls. The abundant chloroplasts in the palisade cells absorb and us ...
3.2 Looking Inside Cells
... between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell because an animal cell does not have a cell wall • ALL cells have cell membranes • Key concept: “The cell membrane controls what substances come into and out of a cell.” • To survive a cell must get food, oxygen, and as well as let out waste ...
... between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell because an animal cell does not have a cell wall • ALL cells have cell membranes • Key concept: “The cell membrane controls what substances come into and out of a cell.” • To survive a cell must get food, oxygen, and as well as let out waste ...
3-1
... region of high pressure to a region of low pressure. Occurs in kidneys when waste product urea is forced by pressure of blood to cross membrane. ...
... region of high pressure to a region of low pressure. Occurs in kidneys when waste product urea is forced by pressure of blood to cross membrane. ...
Tour of Cell Organelles - kyoussef-mci
... organelles that do this work… cell membrane vacuoles & vesicles lysosomes mitochondria ...
... organelles that do this work… cell membrane vacuoles & vesicles lysosomes mitochondria ...
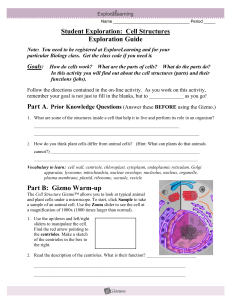
HW Cell Structures Gizmo Gizmo Cell Structures final
... 1. Use the up/down and left/right sliders to manipulate the cell. Find the red arrow pointing to the centrioles. Make a sketch of the centrioles in the box to the right. 2. Read the description of the centrioles. What is their function? ________________________ ______________________________________ ...
... 1. Use the up/down and left/right sliders to manipulate the cell. Find the red arrow pointing to the centrioles. Make a sketch of the centrioles in the box to the right. 2. Read the description of the centrioles. What is their function? ________________________ ______________________________________ ...
Unit 2 - TeacherWeb
... know the cell organelles: rough ER, smooth ER, vacuoles, mitochondria, vesicles, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, centrioles, lysosomes, cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, chromosomes what type of cell has a large, central vacuole? how are plant and animal cells different? (organ ...
... know the cell organelles: rough ER, smooth ER, vacuoles, mitochondria, vesicles, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, centrioles, lysosomes, cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, chromosomes what type of cell has a large, central vacuole? how are plant and animal cells different? (organ ...
Cell Unit Objectives
... Objectives. A student should be able to: Assignments and Resources 1. Explain the three parts of the cell theory. Cell theory notes, Chapter 7-1 2. Identify the important scientists who contributed to the current body of knowledge regarding cells. ...
... Objectives. A student should be able to: Assignments and Resources 1. Explain the three parts of the cell theory. Cell theory notes, Chapter 7-1 2. Identify the important scientists who contributed to the current body of knowledge regarding cells. ...
Chapter 2 - Angelfire
... • Active Transport – the movement of substances through the cell membrane using energy • Endocytosis & Exocytosis – vesicles transport large materials into (endocytosis) and out of (exocytosis) the cell ...
... • Active Transport – the movement of substances through the cell membrane using energy • Endocytosis & Exocytosis – vesicles transport large materials into (endocytosis) and out of (exocytosis) the cell ...
CELLS
... 1. The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life; all organisms are composed of cells. 2. All cells are produced by the division of pre-existing cells (in other words, through reproduction). Each cell contains genetic material that is passed down during this process. 3. All basic chem ...
... 1. The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life; all organisms are composed of cells. 2. All cells are produced by the division of pre-existing cells (in other words, through reproduction). Each cell contains genetic material that is passed down during this process. 3. All basic chem ...
cells
... leaves the cell & also provides protection & support (figure 7-15) -lipid bilayer–a double layered membrane formed when certain kinds of lipids are dissolved in water -embedded proteins-forms channels & pumps that help move materials across the membrane -carbohydrate chains-attach to proteins & aids ...
... leaves the cell & also provides protection & support (figure 7-15) -lipid bilayer–a double layered membrane formed when certain kinds of lipids are dissolved in water -embedded proteins-forms channels & pumps that help move materials across the membrane -carbohydrate chains-attach to proteins & aids ...
How are cells in a multicellular organism organized?
... organism to a unicellular organism? (1) A multicellular organism has organ systems that interact to carry out life functions, while a singlecelled organism carries out life functions without using organ systems. (2) A single-celled organism carries out fewer life functions than each cell of a multic ...
... organism to a unicellular organism? (1) A multicellular organism has organ systems that interact to carry out life functions, while a singlecelled organism carries out life functions without using organ systems. (2) A single-celled organism carries out fewer life functions than each cell of a multic ...
Biology Mitosis/Meiosis Test Review
... have 11. During normal mitotic cell division (mitosis), a parent cell having four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing 12. True/False - Homologous chromosomes may have one chromosome for hair color and another for eye color. ...
... have 11. During normal mitotic cell division (mitosis), a parent cell having four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing 12. True/False - Homologous chromosomes may have one chromosome for hair color and another for eye color. ...
AP Biology, Mrs. Stahl
... paper mache, play dough, etc you need to make sure you give yourself enough time for it to harden and dry correctly so that it won’t fall apart. Please make the replicas colorful, vibrant, and be creative. For helpful hints and other examples, simply Google search it or look on Pinterest. Requiremen ...
... paper mache, play dough, etc you need to make sure you give yourself enough time for it to harden and dry correctly so that it won’t fall apart. Please make the replicas colorful, vibrant, and be creative. For helpful hints and other examples, simply Google search it or look on Pinterest. Requiremen ...
Anti-Myosin 1C antibody ab154498 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 3 Images
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
Plant cells ppt File
... As the plant cell grows, more cellulose fibres are secreted by the protoplast and laid down on the inside of the primary wall forming a secondary wall The cellulose fibres of the secondary wall are closely packed and laid down in an orderly way giving considerable rigidity to the cell wall ...
... As the plant cell grows, more cellulose fibres are secreted by the protoplast and laid down on the inside of the primary wall forming a secondary wall The cellulose fibres of the secondary wall are closely packed and laid down in an orderly way giving considerable rigidity to the cell wall ...
Cells, Solutions, and Characteristics of Living Things Quiz
... 21) Animal cells contain very large main vacuoles that are used for storage. (False) 22) A unicellular organism is capable of all of the jobs necessary for life. (True) 23) Animal cells are usually smaller than plant cells. (True) 24) Sexual reproduction requires two parent cells, each with half of ...
... 21) Animal cells contain very large main vacuoles that are used for storage. (False) 22) A unicellular organism is capable of all of the jobs necessary for life. (True) 23) Animal cells are usually smaller than plant cells. (True) 24) Sexual reproduction requires two parent cells, each with half of ...
Chapter 3 Vocabulary
... A membrane that surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the inside of the cell and the cell’s environment. ...
... A membrane that surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the inside of the cell and the cell’s environment. ...
Cells and Development - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... factors as many tissues and organs interact. Also, can’t see or access many cells. • Tissue explants: cut out a piece, culture it in a nutrient medium • Primary cell culture: dissociate a tissue into individual cells and grow in nutrient medium. Problem: cells are mortal, after about 60 ...
... factors as many tissues and organs interact. Also, can’t see or access many cells. • Tissue explants: cut out a piece, culture it in a nutrient medium • Primary cell culture: dissociate a tissue into individual cells and grow in nutrient medium. Problem: cells are mortal, after about 60 ...
A few weeks ago I had the pleasure of attending the Turner
... or tissue sample and placed in a container with a growth solution. This process is called cell culturing. The cultured cells can then be “harvested”, frozen, and stored indefinitely. Information about the medical and family history of the sample donor is also collected. To protect the privacy of sam ...
... or tissue sample and placed in a container with a growth solution. This process is called cell culturing. The cultured cells can then be “harvested”, frozen, and stored indefinitely. Information about the medical and family history of the sample donor is also collected. To protect the privacy of sam ...
A prokaryote is a simple, unicellular organism that lacks
... localized in a nucleoid, ribosomes, a cell membrane, and a cell wall.The other structures shown are present in some, but not all, bacteria. ...
... localized in a nucleoid, ribosomes, a cell membrane, and a cell wall.The other structures shown are present in some, but not all, bacteria. ...
The Cell Theory
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. (All living things are made of one or more cells, which carry out the life functions.) ...
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. (All living things are made of one or more cells, which carry out the life functions.) ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.