Slide 1
... A vesicle is like a mail truck because it picks up materials and delivers them somewhere else OBJECTIVE Explain the importance of each cell organelle by creating a Frayer vocabulary model for each. ...
... A vesicle is like a mail truck because it picks up materials and delivers them somewhere else OBJECTIVE Explain the importance of each cell organelle by creating a Frayer vocabulary model for each. ...
Cells Building Blocks
... Cells with different functions often vary in shape. They may also vary in size. However, all cells are very small. Even the largest organisms have microscopic cells. Cells are so small that their diameter is measured in micrometers. A micrometer is just one-millionth of a meter. Use the sliding scal ...
... Cells with different functions often vary in shape. They may also vary in size. However, all cells are very small. Even the largest organisms have microscopic cells. Cells are so small that their diameter is measured in micrometers. A micrometer is just one-millionth of a meter. Use the sliding scal ...
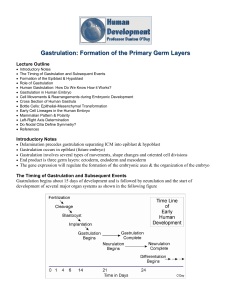
Gastrulation: Formation of the Primary Germ Layers
... Inner Cell Mass (ICM) delaminates to form hypoblast and epiblast Occurs just prior to implantation & gastrulation Epiblast (green cells) is 2-layered (i.e., it is bilaminate) disc of approximately cuboidal cells & will form the embryo proper Flatter hypoblast cells lie below the epiblast and will ...
... Inner Cell Mass (ICM) delaminates to form hypoblast and epiblast Occurs just prior to implantation & gastrulation Epiblast (green cells) is 2-layered (i.e., it is bilaminate) disc of approximately cuboidal cells & will form the embryo proper Flatter hypoblast cells lie below the epiblast and will ...
Section 1.2: Microscopes allow us to see inside the cell
... The microscope is an important tool • Different types of microscopes are used to observe different things Compound Light microscope- allow scientists to see living cells Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM)produce a 3-D image of a cell’s surface Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)produce a 2-D im ...
... The microscope is an important tool • Different types of microscopes are used to observe different things Compound Light microscope- allow scientists to see living cells Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM)produce a 3-D image of a cell’s surface Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)produce a 2-D im ...
REVISION: CELL DIVISION 20 MARCH 2013 Key Concepts
... At the beginning of interphase the cell grows quickly. More organelles are made and there is an increase in the number of chemical reactions. The cell may become specialised for its function in the body or it may store nutrients and get ready for mitosis. Towards the end of interphase the chromatin ...
... At the beginning of interphase the cell grows quickly. More organelles are made and there is an increase in the number of chemical reactions. The cell may become specialised for its function in the body or it may store nutrients and get ready for mitosis. Towards the end of interphase the chromatin ...
G. Cell Surfaces and Junctions
... Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) are useful for studying surface structures. The sample surface is covered with a thin film of gold. The beam excites electrons on the surface. These secondary electrons are collected and focused on a screen. The SEM has great depth of field, resulting i ...
... Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) are useful for studying surface structures. The sample surface is covered with a thin film of gold. The beam excites electrons on the surface. These secondary electrons are collected and focused on a screen. The SEM has great depth of field, resulting i ...
Chapter 10 Cell Divison
... Internal signals - Family of proteins called cyclins - Increase and decrease as cell cycle continues - Without them cycle stops at G1, M or G2 - Allows time for any damage to be repaired ...
... Internal signals - Family of proteins called cyclins - Increase and decrease as cell cycle continues - Without them cycle stops at G1, M or G2 - Allows time for any damage to be repaired ...
In Vitro Bioassays Technical Sheet
... • Transgenic products in vivo [e.g., green fluorescent protein (GFP)] • Enzyme activity • Phosphoprotein analysis • Apoptosis/viability • Cell cycle analyses • Changes in intracellular pH, calcium and glutathione • Various combinations (DNA/surface antigens, etc.) • In-process quality contro ...
... • Transgenic products in vivo [e.g., green fluorescent protein (GFP)] • Enzyme activity • Phosphoprotein analysis • Apoptosis/viability • Cell cycle analyses • Changes in intracellular pH, calcium and glutathione • Various combinations (DNA/surface antigens, etc.) • In-process quality contro ...
The Incredible Edible Cell Model
... #7 Write and perform a song about cells. Must include information about most organelles. #8 Create a ride at an amusement park that would simulate traveling through a cell as though the riders were microscopic in size. Describe the organelles as you find them during the trip. #9 Write a short story ...
... #7 Write and perform a song about cells. Must include information about most organelles. #8 Create a ride at an amusement park that would simulate traveling through a cell as though the riders were microscopic in size. Describe the organelles as you find them during the trip. #9 Write a short story ...
III. Circulatory System
... 1. Theories tie together many scientific facts, hypotheses and laws. 2. Common Mistake: “Theories are things that are opinions, or are not proven.” This is an incorrect use of the word “theory” in a scientific context. A scientific theory is not a simple guess or conjecture, and is strongly supporte ...
... 1. Theories tie together many scientific facts, hypotheses and laws. 2. Common Mistake: “Theories are things that are opinions, or are not proven.” This is an incorrect use of the word “theory” in a scientific context. A scientific theory is not a simple guess or conjecture, and is strongly supporte ...
Objective: You will be able to list the parts of the cell theory.
... Objective: You will be able to give the functions of the cell organelles. Do Now: • Look at the cell organelle sheet • Give the function for as many of the cell organelles as you can remember ...
... Objective: You will be able to give the functions of the cell organelles. Do Now: • Look at the cell organelle sheet • Give the function for as many of the cell organelles as you can remember ...
CD14 MicroBeads - Miltenyi Biotec
... prevent capping of antibodies on the cell surface and non-specific cell labeling. ▲ Volumes for magnetic labeling given below are for up to 10⁷ total cells. When working with fewer than 10⁷ cells, use the same volumes as indicated. When working with higher cell numbers, scale up all reagent volumes ...
... prevent capping of antibodies on the cell surface and non-specific cell labeling. ▲ Volumes for magnetic labeling given below are for up to 10⁷ total cells. When working with fewer than 10⁷ cells, use the same volumes as indicated. When working with higher cell numbers, scale up all reagent volumes ...
Lisa
... Both control the cell/body and contains information that the cell/body needs. The nervous system senses changes in the environment and fixes whatever is needed to make sure the body is healthy. Like the nervous system, the nucleus controls reactions and senses changes in the cell. ...
... Both control the cell/body and contains information that the cell/body needs. The nervous system senses changes in the environment and fixes whatever is needed to make sure the body is healthy. Like the nervous system, the nucleus controls reactions and senses changes in the cell. ...
A. diffuser - WordPress.com
... _____2. During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration _____3. When the concentration of ...
... _____2. During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration _____3. When the concentration of ...
Pathologic hyperplasia
... incapable of cell division • Hyperplasia: increased cell numbers in response to hormones and other growth factors; occurs in tissues whose cells are able to divide or contain abundant tissue stem cells • Atrophy: decreased cell and organ size, as a result of decreased nutrient supply or disuse; asso ...
... incapable of cell division • Hyperplasia: increased cell numbers in response to hormones and other growth factors; occurs in tissues whose cells are able to divide or contain abundant tissue stem cells • Atrophy: decreased cell and organ size, as a result of decreased nutrient supply or disuse; asso ...
A. diffuser
... _____2. During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration _____3. When the concentration of ...
... _____2. During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration _____3. When the concentration of ...
Osmosis and Diffusion
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Biology II – Chapter 4 Key Terms
... 2. carrier protein – a membrane protein that facilitates the diffusion of specific substances across the membrane 3. cell wall – a layer of material, normally made up of cellulose or cellulose-like materials, that is outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, bacteria, and some protists 4. channe ...
... 2. carrier protein – a membrane protein that facilitates the diffusion of specific substances across the membrane 3. cell wall – a layer of material, normally made up of cellulose or cellulose-like materials, that is outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, bacteria, and some protists 4. channe ...
Classification
... • A few fungi, such as yeast, are unicellular eukaryotes. Most fungi are multicellular eukaryotes. Hyphae are branching, threadlike tubes that make-up the bodies. What a fungus looks like depends on the arrangement of its hyphae. • First, the fungus grows hyphae into a food source. Then digestive ch ...
... • A few fungi, such as yeast, are unicellular eukaryotes. Most fungi are multicellular eukaryotes. Hyphae are branching, threadlike tubes that make-up the bodies. What a fungus looks like depends on the arrangement of its hyphae. • First, the fungus grows hyphae into a food source. Then digestive ch ...
3D Cell Rubric
... Some information is accurate Size of cell part is somewhat accurate relative to the class model ...
... Some information is accurate Size of cell part is somewhat accurate relative to the class model ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.