Introduction - Cedar Crest College
... Cells in multicellular organisms must divide only when appropriate. They must respond to external signals, controls called growth factors. ...
... Cells in multicellular organisms must divide only when appropriate. They must respond to external signals, controls called growth factors. ...
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life
... Very large fluid-filled structure that holds water, waste and food. Much larger in plants than animals due to Turgor Pressure. ...
... Very large fluid-filled structure that holds water, waste and food. Much larger in plants than animals due to Turgor Pressure. ...
human Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptor Cell Line
... The recommended media catalogue number and supplier reference information are listed in this Product Technical Data Sheet (last page). Media composition is specifically defined for each cell type and receptor expression selection. The use of incorrect media or component substitutions can lead to red ...
... The recommended media catalogue number and supplier reference information are listed in this Product Technical Data Sheet (last page). Media composition is specifically defined for each cell type and receptor expression selection. The use of incorrect media or component substitutions can lead to red ...
Parts of a Cell
... Perixomes are very similar to lysosomes. They also digest material, but they are better at breaking down fatty acids and toxic material, like alcohol. What if a cell has too much food? Or what if the organelles produce waste that can contaminate the rest of the cell? That’s when the organelles calle ...
... Perixomes are very similar to lysosomes. They also digest material, but they are better at breaking down fatty acids and toxic material, like alcohol. What if a cell has too much food? Or what if the organelles produce waste that can contaminate the rest of the cell? That’s when the organelles calle ...
development - World of Teaching
... – The embryo floats free for several days, nourished by fluids from glands in the ...
... – The embryo floats free for several days, nourished by fluids from glands in the ...
Drivers of Cancer
... In metastasis, cancer cells break away from where they first formed (primary cancer), travel through the blood or lymph system, and form new tumors (metastatic tumors) in other parts of the body. The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. A cancer that has spread from the ...
... In metastasis, cancer cells break away from where they first formed (primary cancer), travel through the blood or lymph system, and form new tumors (metastatic tumors) in other parts of the body. The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. A cancer that has spread from the ...
Structure of the Cell Membrane
... imat/lipids/membrane%20fluidity.swf from water. Carbohydrate cell markers ...
... imat/lipids/membrane%20fluidity.swf from water. Carbohydrate cell markers ...
IMPORTANT PREFIXES, SUFFIXES AND ROOT WORDS
... MESENCHYMAL: Embryonic tissue (one of three types), muscle and fat are derived from this. METAPLASIA: Reversible change in which one mature cell type is replaced by another. METASTASIS: In cancer, the appearance of secondary tumors in parts of the body remote from the primary tumor. MONOMORPHIC: One ...
... MESENCHYMAL: Embryonic tissue (one of three types), muscle and fat are derived from this. METAPLASIA: Reversible change in which one mature cell type is replaced by another. METASTASIS: In cancer, the appearance of secondary tumors in parts of the body remote from the primary tumor. MONOMORPHIC: One ...
Cell Transport
... Based on the amount of solute in the solution Hypertonic: higher levels of solute Isotonic: equal amounts of solute Hypotonic: lower levels of solution Water moves from an area that is hypotonic to hypertonic until they are isotonic Osmosis Animation ...
... Based on the amount of solute in the solution Hypertonic: higher levels of solute Isotonic: equal amounts of solute Hypotonic: lower levels of solution Water moves from an area that is hypotonic to hypertonic until they are isotonic Osmosis Animation ...
image - Filament Games
... of the cell from harmful agents around the cell and controls what moves in and out of the cell. breaks down waste materials in an animal cell. ...
... of the cell from harmful agents around the cell and controls what moves in and out of the cell. breaks down waste materials in an animal cell. ...
Working in the third dimension - biomed
... On the bottom of the well a collagen type IV matrix allows a coculture of smooth muscle cells and stromal cells. The membrane of the insert is coated with laminin, an important component of the basement membrane that enables epithelial polarization. The differentiated, polarized epithelial cells on ...
... On the bottom of the well a collagen type IV matrix allows a coculture of smooth muscle cells and stromal cells. The membrane of the insert is coated with laminin, an important component of the basement membrane that enables epithelial polarization. The differentiated, polarized epithelial cells on ...
Is the living cell simple or complex?
... The major components, such as some enzymes, were present in cells before aerobic metabolism evolved. The Krebs cycle may have been built using existing genes and proteins to produce a new biochemical pathway. ...
... The major components, such as some enzymes, were present in cells before aerobic metabolism evolved. The Krebs cycle may have been built using existing genes and proteins to produce a new biochemical pathway. ...
Plant genes involved in giant cell formation induced by
... associations with a wide range of mutualistic and parasitic biotrophic organisms, it is quite conceivable that these biotrophic interactions might have evolved certain common core components affecting cellular functions such as cell-wall reorganisation, membrane synthesis, metabolite fluxes or cyto ...
... associations with a wide range of mutualistic and parasitic biotrophic organisms, it is quite conceivable that these biotrophic interactions might have evolved certain common core components affecting cellular functions such as cell-wall reorganisation, membrane synthesis, metabolite fluxes or cyto ...
Difference Between Cytosol and Cytoplasm
... the other contents that float about in the cytosol. Cytosol is the part of the cytoplasm that is not held by any of the organelles in the cell. On the other hand, cytoplasm is the part of the cell which is contained within the entire cell membrane. It is the total content within the cell membrane ot ...
... the other contents that float about in the cytosol. Cytosol is the part of the cytoplasm that is not held by any of the organelles in the cell. On the other hand, cytoplasm is the part of the cell which is contained within the entire cell membrane. It is the total content within the cell membrane ot ...
A Closer Look at Cell Membranes
... Many types of molecules and ions diffuse across a lipid bilayer only with the help of specific transport proteins. A. Passive Transport Requires no energy input Some passive transporters are open channels Other passive transporters are gated and change shape when a specific molecule binds to the ...
... Many types of molecules and ions diffuse across a lipid bilayer only with the help of specific transport proteins. A. Passive Transport Requires no energy input Some passive transporters are open channels Other passive transporters are gated and change shape when a specific molecule binds to the ...
Hypertrophy
... Hypertrophy is an increase in the size of cells resulting in increase in the size of the organ. In contrast, hyperplasia (discussed next) is characterized by an increase in cell number. Stated another way, in pure hypertrophy there are no new cells, just bigger cells, enlarged by an increased amount ...
... Hypertrophy is an increase in the size of cells resulting in increase in the size of the organ. In contrast, hyperplasia (discussed next) is characterized by an increase in cell number. Stated another way, in pure hypertrophy there are no new cells, just bigger cells, enlarged by an increased amount ...
Osmosis in Red Blood Cells
... A water molecule is a ‘polar’ molecule because it has a partial negative charge on one side and a partial positive charge on the other side. When the Hydrogen atom of one water molecule is attracted to the oxygen atoms of another water molecule a hydrogen bond is formed. Lipids are Nonpolar molecule ...
... A water molecule is a ‘polar’ molecule because it has a partial negative charge on one side and a partial positive charge on the other side. When the Hydrogen atom of one water molecule is attracted to the oxygen atoms of another water molecule a hydrogen bond is formed. Lipids are Nonpolar molecule ...
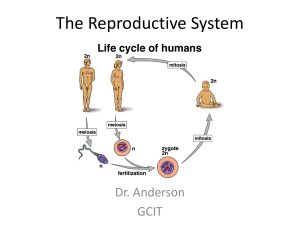
The Reproductive System
... HPV and Cervical Cancer • How women can protect themselves – Gardasil – Regular visits to gynecologist if sexually active to check for abnormal cervical cells • Pap smear ...
... HPV and Cervical Cancer • How women can protect themselves – Gardasil – Regular visits to gynecologist if sexually active to check for abnormal cervical cells • Pap smear ...
Name: : :__
... Part I. Use the website http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm to answer the questions about animal and plant cells. Click on “Animal Cell” underneath the diagram to view an animal cell. 1. Click on “Nucleus.” What is found within the nucleus? ...
... Part I. Use the website http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm to answer the questions about animal and plant cells. Click on “Animal Cell” underneath the diagram to view an animal cell. 1. Click on “Nucleus.” What is found within the nucleus? ...
Cells_Library_Quest
... Part I. Use the website http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm to answer the questions about animal and plant cells. Click on “Animal Cell” underneath the diagram to view an animal cell. 1. Click on “Nucleus.” What is found within the nucleus? ...
... Part I. Use the website http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm to answer the questions about animal and plant cells. Click on “Animal Cell” underneath the diagram to view an animal cell. 1. Click on “Nucleus.” What is found within the nucleus? ...
Modeling Cellular Activation Using Visual Formalism
... A type of white blood cell that is of crucial importance to the immune system protecting you from viral infections; helping other cells fight bacterial and fungal infections; producing antibodies; fighting cancers; and coordinating the activities of other cells in the immune system. ...
... A type of white blood cell that is of crucial importance to the immune system protecting you from viral infections; helping other cells fight bacterial and fungal infections; producing antibodies; fighting cancers; and coordinating the activities of other cells in the immune system. ...
Gas Reference Cells Overview
... offers alkali reference cells that contain sodium, potassium, rubidium, and cesium. In alkali atom reference cells, the bulk of the material in the cell will be coalesced in a solid or liquid form on the cell walls. However, since the cell was sealed with vacuum conditions inside the cell, alkali va ...
... offers alkali reference cells that contain sodium, potassium, rubidium, and cesium. In alkali atom reference cells, the bulk of the material in the cell will be coalesced in a solid or liquid form on the cell walls. However, since the cell was sealed with vacuum conditions inside the cell, alkali va ...
File - Anna DrewE
... Cancer is a disease where mitosis does not occur properly. Mutations in the sequence of DNA cause cell cycle genes to behave improperly. These cell cycle genes are no longer able to control the rate of mitosis, and the mutated cancer cells undergo rapid mitosis—they divide out of control, forming ab ...
... Cancer is a disease where mitosis does not occur properly. Mutations in the sequence of DNA cause cell cycle genes to behave improperly. These cell cycle genes are no longer able to control the rate of mitosis, and the mutated cancer cells undergo rapid mitosis—they divide out of control, forming ab ...
Cell junction
... b) Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes connect epithelial cells to their basement membrane and adjacent cells ...
... b) Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes connect epithelial cells to their basement membrane and adjacent cells ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.