answers - Biology Resources
... 4 (a) Plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus and chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
... 4 (a) Plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus and chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
Cells: basic unit of Life
... They need a way to dispose of waste They need to reproduce and create more cells They need an environment that is suited to their survival. ...
... They need a way to dispose of waste They need to reproduce and create more cells They need an environment that is suited to their survival. ...
Test Review: Unit 4 Cells and microscopes What is a prokaryote
... 16. Which organelle contains the instructions that built these cells? Why aren’t the cells all the same? ...
... 16. Which organelle contains the instructions that built these cells? Why aren’t the cells all the same? ...
Cells - Weebly
... Directs all cell activities Contains instructions for everything the cell does These instructions are found on a hereditary material called DNA ...
... Directs all cell activities Contains instructions for everything the cell does These instructions are found on a hereditary material called DNA ...
AP Biology - Mitosis and Meiosis Experiments
... 4. Calculate the percentage of cells in each phase and the time (in minutes) that the onion cells are in each phase to accurately describe the cell cycle of onion apical meristem cells. 5. Repeat this process for the prepared slides of fish blastula cells. 6. Compare and contrast the cell cycles and ...
... 4. Calculate the percentage of cells in each phase and the time (in minutes) that the onion cells are in each phase to accurately describe the cell cycle of onion apical meristem cells. 5. Repeat this process for the prepared slides of fish blastula cells. 6. Compare and contrast the cell cycles and ...
Structure and Function of the Cell
... What discoveries led to the development of the cell theory? Who was Robert Hooke and what did he ...
... What discoveries led to the development of the cell theory? Who was Robert Hooke and what did he ...
2.2 – Prokaryotic Cells
... Cytoplasm - The region where metabolic reaction occur which are essential for life. Mesosome - Permeable boundary that allows for entry and exit of nutrients and waste, and may play a role in DNA replication. Cell/ Plasma Membrane - This is a barrier across which all nutrients and waste products mus ...
... Cytoplasm - The region where metabolic reaction occur which are essential for life. Mesosome - Permeable boundary that allows for entry and exit of nutrients and waste, and may play a role in DNA replication. Cell/ Plasma Membrane - This is a barrier across which all nutrients and waste products mus ...
Product Information
... phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active cells, the cells’ death occurs only after 3 to 7 days. The recommended concentration at G 418-BC in the medium has for euka ...
... phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active cells, the cells’ death occurs only after 3 to 7 days. The recommended concentration at G 418-BC in the medium has for euka ...
01 - Cobb Learning
... 2. organelles that break down sugar to produce energy. 4. a combination of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific job in the body 5. organelles that make proteins 6. a group of similar cells that perform a common function 8. cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles ...
... 2. organelles that break down sugar to produce energy. 4. a combination of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific job in the body 5. organelles that make proteins 6. a group of similar cells that perform a common function 8. cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles ...
ch-3-crossword-puzzle
... 2. organelles that break down sugar to produce energy. 4. a combination of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific job in the body 5. organelles that make proteins 6. a group of similar cells that perform a common function 8. cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles ...
... 2. organelles that break down sugar to produce energy. 4. a combination of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific job in the body 5. organelles that make proteins 6. a group of similar cells that perform a common function 8. cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles ...
Name Date The Structure and Function of Cells Cell Part Structure
... Place where proteins are primarily of RNA; may be made attached to endoplasmic reticulum or floating free in cytoplasm; produced in nucleolus Rod shaped organelle; located in the cytoplasm; has a smooth outer membrane and a greatly folded inner membrane ...
... Place where proteins are primarily of RNA; may be made attached to endoplasmic reticulum or floating free in cytoplasm; produced in nucleolus Rod shaped organelle; located in the cytoplasm; has a smooth outer membrane and a greatly folded inner membrane ...
File
... Pus is an accumulation dead bacteria and phagocytes of Natural Killer (NK) cells virus infected cells and cancer cells ...
... Pus is an accumulation dead bacteria and phagocytes of Natural Killer (NK) cells virus infected cells and cancer cells ...
Print here - Ecosystemforkids.com
... 2. ____________________ plasma membrane 3. ____________________ mitochondrion 4. ____________________ ...
... 2. ____________________ plasma membrane 3. ____________________ mitochondrion 4. ____________________ ...
lesson_10
... Unit 10 Unit Title: Cell Growth and Division Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to ex ...
... Unit 10 Unit Title: Cell Growth and Division Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to ex ...
Prof. Dinko Mitrecic, MD, PhD Laboratory for Stem Cells
... Professor Elena N Kozlova,PhD Laboratory of Regenerative Neurobiology Uppsala University, Sweden ...
... Professor Elena N Kozlova,PhD Laboratory of Regenerative Neurobiology Uppsala University, Sweden ...
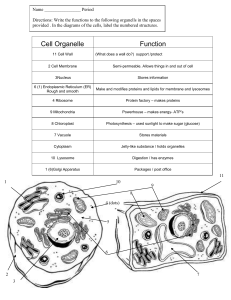
Cell Organelle
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
Cell Organelles
... • Carbohydrate chains –act as “ID” tags for the cell • Cholesterol – provides stability for the membrane ...
... • Carbohydrate chains –act as “ID” tags for the cell • Cholesterol – provides stability for the membrane ...
The Cell Unit
... • In 1838, a botanist named Matthias Schleiden, concluded that plants are made of cells. • In 1839, a zoologist named Theodor Schwann, concluded that all animal tissue is made of cells. • In 1858, a doctor named Rudolf Virchow, stated that cells could only come from other cells. ...
... • In 1838, a botanist named Matthias Schleiden, concluded that plants are made of cells. • In 1839, a zoologist named Theodor Schwann, concluded that all animal tissue is made of cells. • In 1858, a doctor named Rudolf Virchow, stated that cells could only come from other cells. ...
Cell Content Statement 1 Study Guide
... Know the Parts of the Modern Cell Theory All known living things are made up of cells. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. All cells are made of the same ...
... Know the Parts of the Modern Cell Theory All known living things are made up of cells. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. All cells are made of the same ...
Cell structure and Function Practice Quiz
... A thick liquid that carries cell building blocks like amino acids, ions and nucleic acids A thin liquid that only carries ions. A solid gel that holds the DNA None of the above ...
... A thick liquid that carries cell building blocks like amino acids, ions and nucleic acids A thin liquid that only carries ions. A solid gel that holds the DNA None of the above ...
Name: Date: Block: Science 8 Chapter 1 Review Answer the
... 14. Muscle cells have a greater number of mitochondria than other animal cells. Using the function of the mitochondria, explain why this is. 15. What is cellular respiration? 16. Explain the roles of the following organelles in the production of proteins: ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi ...
... 14. Muscle cells have a greater number of mitochondria than other animal cells. Using the function of the mitochondria, explain why this is. 15. What is cellular respiration? 16. Explain the roles of the following organelles in the production of proteins: ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.