Le Louis - LaPazChirripoColegio2016-2017
... • 2 layers were identified (wrongly) as being two protein layers ...
... • 2 layers were identified (wrongly) as being two protein layers ...
Functions of Plont ond Animol Cell Structures control center ofceII
... Functions of Plont ond Animol Cell Structures Cell ...
... Functions of Plont ond Animol Cell Structures Cell ...
Chapter 1 Cells
... chloroplasts is definitely an advantage that plants have over animals. Chloroplasts allow plants to produce their own food from water, carbon and sunlight. Animals need to consume other organisms in order to survive. ...
... chloroplasts is definitely an advantage that plants have over animals. Chloroplasts allow plants to produce their own food from water, carbon and sunlight. Animals need to consume other organisms in order to survive. ...
Signal Transduction Pathways and the Activation of B Cells
... Most type 1 TI (TI-1) Ags are polyclonal B-cell activators (mitogens); that is, they are able to activate B cells regardless of their antigenic specificity. ...
... Most type 1 TI (TI-1) Ags are polyclonal B-cell activators (mitogens); that is, they are able to activate B cells regardless of their antigenic specificity. ...
Plant Cells
... ● Plant walls have thicker wall than animal cells because plant cells have no structure to keep them in place unlike animal cells which have bones for structure. ● The cells for making energy are at the top of the cell so they are closer to the sun and can get as much of it as possible. ● There are ...
... ● Plant walls have thicker wall than animal cells because plant cells have no structure to keep them in place unlike animal cells which have bones for structure. ● The cells for making energy are at the top of the cell so they are closer to the sun and can get as much of it as possible. ● There are ...
Cell theory states: living things are composed of one or
... things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing cells. Rudolf Virchow later made important contributions to this theory. Schleiden and Schwann proposed spontaneous generation as the method for cell origination, but spontaneous generatio ...
... things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing cells. Rudolf Virchow later made important contributions to this theory. Schleiden and Schwann proposed spontaneous generation as the method for cell origination, but spontaneous generatio ...
Cell Organelles
... Much like a crossing guard, the cell membrane controls traffic. It functions by accepting and releasing materials into and out of the cell. The materials move across the cell membrane using diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport, using flagella or cilia. Flagella has only one or two ...
... Much like a crossing guard, the cell membrane controls traffic. It functions by accepting and releasing materials into and out of the cell. The materials move across the cell membrane using diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport, using flagella or cilia. Flagella has only one or two ...
cells - SCF Faculty Site Homepage
... • Site of Photosynthesis = acquisition of chemical energy from sunlight. Sunlight + CO2 Carbohydrates • A plastid (not part of endomembrane system). • Have their own DNA, RNA, Proteins, and Ribosomes (70-S). • Grow and reproduce independently. • Plants, Protists. ...
... • Site of Photosynthesis = acquisition of chemical energy from sunlight. Sunlight + CO2 Carbohydrates • A plastid (not part of endomembrane system). • Have their own DNA, RNA, Proteins, and Ribosomes (70-S). • Grow and reproduce independently. • Plants, Protists. ...
Cell Specialization and Organization
... Things Vocab Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function together Organ Systems: A group of organs that work together to perfo ...
... Things Vocab Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function together Organ Systems: A group of organs that work together to perfo ...
reproduction
... REPRODUCTION THE MOST IMPORTANT Cell wall – external covering of cells by bacteria, fungi, plants -it determines the shape, protects of external environment Cytoplasmic membrane – it makes elastic and solid covering of all cells -admitted into the cell interior as well as outside of it some substan ...
... REPRODUCTION THE MOST IMPORTANT Cell wall – external covering of cells by bacteria, fungi, plants -it determines the shape, protects of external environment Cytoplasmic membrane – it makes elastic and solid covering of all cells -admitted into the cell interior as well as outside of it some substan ...
Ch. 1 - Cell Organelles Worksheet
... the ER, contain enzymes for modifying proteins and lipids, package finished products into vesicles for transport to the cell membrane (for secretion out of the cell) and within the cell as lysosomes. ...
... the ER, contain enzymes for modifying proteins and lipids, package finished products into vesicles for transport to the cell membrane (for secretion out of the cell) and within the cell as lysosomes. ...
cell organelle WS 2014
... C. Put a check in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both plant & animal cells. ...
... C. Put a check in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both plant & animal cells. ...
The Cell Cycle (2009).
... DNA overload: As a cell gets large, its DNA cannot hold all the information necessary for the cell to run properly. Movement of materials: Materials have to travel too far to get from the cell membrane to the nucleus. The cell becomes inefficient. ...
... DNA overload: As a cell gets large, its DNA cannot hold all the information necessary for the cell to run properly. Movement of materials: Materials have to travel too far to get from the cell membrane to the nucleus. The cell becomes inefficient. ...
Cellular Chemical Reactions
... Carbon atoms and are made up of smaller parts called subunits. An important property of Lipids is that they cannot mix with water. Proteins are needed in the cell for proper cell function. These proteins control chemical reactions, support grown and repair, allow muscles to move, fight infections, d ...
... Carbon atoms and are made up of smaller parts called subunits. An important property of Lipids is that they cannot mix with water. Proteins are needed in the cell for proper cell function. These proteins control chemical reactions, support grown and repair, allow muscles to move, fight infections, d ...
The nonliving outer covering of plant cells
... Cell walls are not found in animal cells because animal cells do not need structure and support. B. A cell without a nucleus could still undergo normal functions. C. A cell’s cytoplasm does not have a specific function. D. A human muscle cell should contain more mitochondria than a human skin cell b ...
... Cell walls are not found in animal cells because animal cells do not need structure and support. B. A cell without a nucleus could still undergo normal functions. C. A cell’s cytoplasm does not have a specific function. D. A human muscle cell should contain more mitochondria than a human skin cell b ...
Virus and Kingdom Overview
... reproducing along with the cell and its offspring. Within the cell’s offspring, referred to as daughter cells, the viral DNA creates RNA replicas of itself. ...
... reproducing along with the cell and its offspring. Within the cell’s offspring, referred to as daughter cells, the viral DNA creates RNA replicas of itself. ...
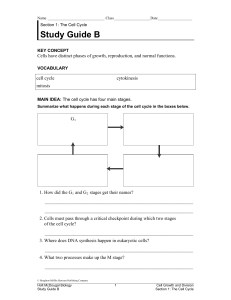
Study Guide B
... 2. Cells must pass through a critical checkpoint during which two stages of the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where does DNA synthesis happen in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________________________ 4. What two processes ma ...
... 2. Cells must pass through a critical checkpoint during which two stages of the cell cycle? _______________________________________________________________ 3. Where does DNA synthesis happen in eukaryotic cells? _______________________________________________________________ 4. What two processes ma ...
The Living Cell
... The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells ...
... The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells ...
Genetics/Zoology Semester Exam Review
... Work can be repeated, experimental procedures can be reviewed, others can try to reproduce the ...
... Work can be repeated, experimental procedures can be reviewed, others can try to reproduce the ...
cells final - educ399portfolioedwinawilson
... Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. ...
... Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.