
Plant Cells - New Brigden School
... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protests such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. The entire process is called photosynthesi ...
... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protests such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. The entire process is called photosynthesi ...
Chromosomes
... • The type of cell division depends on the type of cell. – Prokaryotes divide differently than eukaryotes. - ...
... • The type of cell division depends on the type of cell. – Prokaryotes divide differently than eukaryotes. - ...
Document
... This diagram shows a cell in a solution. The black dots represent solute molecules. 16. This shows a cell is in a ________tonic solution. ...
... This diagram shows a cell in a solution. The black dots represent solute molecules. 16. This shows a cell is in a ________tonic solution. ...
Cell Notes PPT - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... • Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living things • All cells are produced from other cells ...
... • Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living things • All cells are produced from other cells ...
cell cycle - user web page
... The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of at least one cell. Most cells are very small and invisible without using a microscope.There are two main types or of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, which is made of a doubl ...
... The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of at least one cell. Most cells are very small and invisible without using a microscope.There are two main types or of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, which is made of a doubl ...
Year 9 Cells Quick Quiz
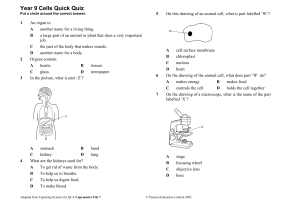
... a collection of tissues that do the same job. C a collection of organs that help us breathe. D a way of counting the number of organs in the body. The heart contains: A muscle, fat and nerve tissues. B only muscle tissue. C muscle and bone tissues. D muscle, nerve and palisade tissues. Which organ s ...
... a collection of tissues that do the same job. C a collection of organs that help us breathe. D a way of counting the number of organs in the body. The heart contains: A muscle, fat and nerve tissues. B only muscle tissue. C muscle and bone tissues. D muscle, nerve and palisade tissues. Which organ s ...
Integrated Science
... Plants are stiff and rigid. How does their cellular structure contribute to this characteristic? ...
... Plants are stiff and rigid. How does their cellular structure contribute to this characteristic? ...
Plant Cell
... The cytosol (cytoplasm) is the "soup" within which all the other cell organelles reside and where most of the cellular metabolism occurs full of proteins that control cell metabolism including signal transduction pathways, glycolysis, intracellular receptors, and transcription factors. ...
... The cytosol (cytoplasm) is the "soup" within which all the other cell organelles reside and where most of the cellular metabolism occurs full of proteins that control cell metabolism including signal transduction pathways, glycolysis, intracellular receptors, and transcription factors. ...
Cells Alive Tutorial 08-09
... page, or hit your back button) For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? ...
... page, or hit your back button) For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? ...
Document
... Define the cell cycle: Click mitosis List the stages of mitosis beginning with interphase. Discuss 3 events that are unique and occur in each of these phases. ...
... Define the cell cycle: Click mitosis List the stages of mitosis beginning with interphase. Discuss 3 events that are unique and occur in each of these phases. ...
Principles of Cell Biology
... 60-70% Divided into two compartments: o Intracellular fluid (ICF) – o Extracellular fluid (ECF) – ...
... 60-70% Divided into two compartments: o Intracellular fluid (ICF) – o Extracellular fluid (ECF) – ...
organ system - Scholieren.com
... Plants and animals are made up of small parts: cells. These are tiny building blocks. You can’t see them with the naked eye so you need a microscope. When you look at the cells through a microscope the cells seem to be flat, but in reality they are a kind of boxes because something is in it. There a ...
... Plants and animals are made up of small parts: cells. These are tiny building blocks. You can’t see them with the naked eye so you need a microscope. When you look at the cells through a microscope the cells seem to be flat, but in reality they are a kind of boxes because something is in it. There a ...
Topic 2 revision notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... biconcave shape (for greater surface area); flexible (so they fit through small capillaries). ...
... biconcave shape (for greater surface area); flexible (so they fit through small capillaries). ...
Student_Work_files/how cells keep us alive[1]
... The cytoplasm holds all the organelles in a cell in place. ...
... The cytoplasm holds all the organelles in a cell in place. ...
ch1 FA11 - Cal State LA
... Intro to Cell & Molecular Biology • How do we study cell biology? – Reductionist view • Cells as tiny complex machines • Sum of parts = whole • Your goal: – be able to explain the roles various molecular parts play in cell biological processes ...
... Intro to Cell & Molecular Biology • How do we study cell biology? – Reductionist view • Cells as tiny complex machines • Sum of parts = whole • Your goal: – be able to explain the roles various molecular parts play in cell biological processes ...
Plasma Membrane
... means predicting how a cell will react in a solution (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic) ...
... means predicting how a cell will react in a solution (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic) ...
Differences between unicellular and multicellular - Grade-56G
... Differences between unicellular and multicellular 1. Unicellular is an organism with one cell ( unicellular is also called single cell organism ) 2. Multicellular is an organism with two or more cells like humans, dogs and cats. 3. Multicellular have lots of cells in their body. 4. Unicellular's bod ...
... Differences between unicellular and multicellular 1. Unicellular is an organism with one cell ( unicellular is also called single cell organism ) 2. Multicellular is an organism with two or more cells like humans, dogs and cats. 3. Multicellular have lots of cells in their body. 4. Unicellular's bod ...
普通生物學 - 高雄師範大學生物科技系
... 16. In comparing the typical life cycles of plants and animals, a stage found in plant but not in animals is a (a) gamete (b) zygote (c) multicellular diploid (d) multicellular haploid (e) none of all above. 17. Synthesis of a new DNA strand usually begins with (a) an RNA primer (b) a DNA primer (c) ...
... 16. In comparing the typical life cycles of plants and animals, a stage found in plant but not in animals is a (a) gamete (b) zygote (c) multicellular diploid (d) multicellular haploid (e) none of all above. 17. Synthesis of a new DNA strand usually begins with (a) an RNA primer (b) a DNA primer (c) ...
Transport of Materials
... • Companion cells provide the energy for the tube cells. • The end walls of the tube cells have pores through which food is transported from cell to cell in the form of dissolved sugars ...
... • Companion cells provide the energy for the tube cells. • The end walls of the tube cells have pores through which food is transported from cell to cell in the form of dissolved sugars ...
Genetics Utah Research
... 5. What name is given to cells that only contain one set of chromosomes? 6. How many cells are formed when a cell divides through meiosis? ...
... 5. What name is given to cells that only contain one set of chromosomes? 6. How many cells are formed when a cell divides through meiosis? ...
Types of Asexual Reproduction
... When some bacteria, micro-organisms and fungi can form spores - single cells that can grow into a whole new organism. through mitosis ...
... When some bacteria, micro-organisms and fungi can form spores - single cells that can grow into a whole new organism. through mitosis ...
All About Cells - Exploring Nature
... like hormones. Lysosomes are vesicles that have digestive enzymes inside them and break down the things that the cell doesn’t need. They also kill bacteria that invades the body. Vacuoles are membrane sacs for storing things. Mitochondria have a double membrane that folds in on itself forming little ...
... like hormones. Lysosomes are vesicles that have digestive enzymes inside them and break down the things that the cell doesn’t need. They also kill bacteria that invades the body. Vacuoles are membrane sacs for storing things. Mitochondria have a double membrane that folds in on itself forming little ...
The Cell Membrane
... The first big difference is that plant cells have both a cell wall and cell membrane. But the animal cell has only a cell membrane. This is because an animal cell doesn’t need the structure of a cell wall because it has a cytoskeleton. The next thing is that plant cell have chloroplast and an animal ...
... The first big difference is that plant cells have both a cell wall and cell membrane. But the animal cell has only a cell membrane. This is because an animal cell doesn’t need the structure of a cell wall because it has a cytoskeleton. The next thing is that plant cell have chloroplast and an animal ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.











![Student_Work_files/how cells keep us alive[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008096061_1-3bccda7a250f4b6d053f03d6cd844694-300x300.png)










