Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
... Key Words: cell, living, single-celled, celled, multi multi-cellular, organism, homeostasis Essential Questions: ...
... Key Words: cell, living, single-celled, celled, multi multi-cellular, organism, homeostasis Essential Questions: ...
1.4 The Cell Cycle
... Some cells are encouraged to divide, while others are encouraged to “stay as they are” ...
... Some cells are encouraged to divide, while others are encouraged to “stay as they are” ...
Slide 1
... The cilia are bathed in nasal mucus. The mucus moisturizes the air but also, like fly paper, filters dust , pollen, chemicals, bacteria and viruses that enter our nose as we breath. The cilia are always refreshing the mucus coating of the nose. In coordinated waves, they sweep a layer of mucus to th ...
... The cilia are bathed in nasal mucus. The mucus moisturizes the air but also, like fly paper, filters dust , pollen, chemicals, bacteria and viruses that enter our nose as we breath. The cilia are always refreshing the mucus coating of the nose. In coordinated waves, they sweep a layer of mucus to th ...
Cell wall - s3.amazonaws.com
... How do Microscopes Work? Some microscopes use lenses to focus light onto an object The lenses in light microscopes are similar to the clear curved pieces of glass used in eyeglasses ...
... How do Microscopes Work? Some microscopes use lenses to focus light onto an object The lenses in light microscopes are similar to the clear curved pieces of glass used in eyeglasses ...
Unit 5 – Reproduction and Development Review Sheet Vocabulary
... - What organ provides nutrients for the fetus? How do nutrients pass through this organ? Placenta; diffusion - What else, besides nutrients, can pass through the placenta? How can these substances influence fetal development? Toxins, such as nicotine and alcohol; these substances can harm the fetus, ...
... - What organ provides nutrients for the fetus? How do nutrients pass through this organ? Placenta; diffusion - What else, besides nutrients, can pass through the placenta? How can these substances influence fetal development? Toxins, such as nicotine and alcohol; these substances can harm the fetus, ...
Cell Mates
... ● Job: perform _______________________________ ● ___________________________ molecules _____________________ sunlight, and convert water and CO2 into ________________. ● _____________________________ theory: were once free living organisms that became parts of modern cells. ...
... ● Job: perform _______________________________ ● ___________________________ molecules _____________________ sunlight, and convert water and CO2 into ________________. ● _____________________________ theory: were once free living organisms that became parts of modern cells. ...
Cell Communication
... – How did you recognize where to go? – How does this model cell communication? – What effect did joining the pathway have on you? – What problems did you encounter? – What would have happened if someone did not do their job or simply were not present? ...
... – How did you recognize where to go? – How does this model cell communication? – What effect did joining the pathway have on you? – What problems did you encounter? – What would have happened if someone did not do their job or simply were not present? ...
millionaire cells
... Cells performing different functions and cooperate to allow an organism to perform functions beyond one cell type. ...
... Cells performing different functions and cooperate to allow an organism to perform functions beyond one cell type. ...
Bio392-Chapter 10-1
... Why are cells so small? Cells are found in every living organism, ranging from unicellular (onecelled) organisms, such as amoebas, to multicellular (many-celled) organisms, such as human beings. Even though each organism is very unique, their cells are typically about the same small size. This simil ...
... Why are cells so small? Cells are found in every living organism, ranging from unicellular (onecelled) organisms, such as amoebas, to multicellular (many-celled) organisms, such as human beings. Even though each organism is very unique, their cells are typically about the same small size. This simil ...
topic 1.6 quiz - Peoria Public Schools
... What are the structures and stage of mitosis? Stage of mitosis ...
... What are the structures and stage of mitosis? Stage of mitosis ...
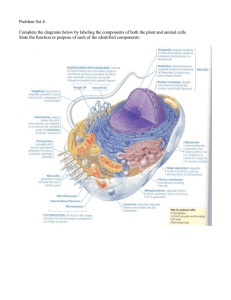
Problem Set 4:
... Complete the diagrams below by labeling the components of both the plant and animal cells. State the function or purpose of each of the identified components: ...
... Complete the diagrams below by labeling the components of both the plant and animal cells. State the function or purpose of each of the identified components: ...
Slide 1
... • Cells affected by diseases caused by “broken” genes can be aided by the addition of “working” genes • Working genes are carried by a vector, in most cases an altered virus, into an individual’s cells ...
... • Cells affected by diseases caused by “broken” genes can be aided by the addition of “working” genes • Working genes are carried by a vector, in most cases an altered virus, into an individual’s cells ...
Q: True or False? Cells do everything needed for life. Q: What are all
... A: 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. ...
... A: 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. ...
The Cell and Its Structures
... Topic 3 - The Cell and Its Structure Practice Quiz 1. Many single-celled (unicellular) organisms have different ways of moving, obtaining food and carrying out other essential functions for living. Structures, that unicellular organisms, such as a euglena, or a chlamydomonas have for movement are ca ...
... Topic 3 - The Cell and Its Structure Practice Quiz 1. Many single-celled (unicellular) organisms have different ways of moving, obtaining food and carrying out other essential functions for living. Structures, that unicellular organisms, such as a euglena, or a chlamydomonas have for movement are ca ...
12/10/09
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
The Cell Membrane
... a. The phospholipid bilayer is a double layer of lipids (fat). Each lipid has a phosphate molecule attached. The lipids are hydrophobic, which means that they repel water. The phosphate molecules are hydrophilic and attract water. This maintains the water inside the cell as well as sep ...
... a. The phospholipid bilayer is a double layer of lipids (fat). Each lipid has a phosphate molecule attached. The lipids are hydrophobic, which means that they repel water. The phosphate molecules are hydrophilic and attract water. This maintains the water inside the cell as well as sep ...
Inexpensive Cell Migration- Pre-lab presentation
... Inexpensive Cell Migration Inquiry Lab using Danio rerio – Kate M. Cooper ...
... Inexpensive Cell Migration Inquiry Lab using Danio rerio – Kate M. Cooper ...
Levels of Organization
... Before a human being develops, an egg and sperm unite to form a zygote. A zygote is a fertilized egg. It is made of just one cell. Then the zygote begins to divide, and the cells that it forms also divide. This process continues for a few weeks. The cells that form during this time are called embryo ...
... Before a human being develops, an egg and sperm unite to form a zygote. A zygote is a fertilized egg. It is made of just one cell. Then the zygote begins to divide, and the cells that it forms also divide. This process continues for a few weeks. The cells that form during this time are called embryo ...
Plant & Animal Cells
... cells under a microscope and thought they looked like the cells monks lived in within their monasteries. As our microscopes became more powerful over the years, we have learned a great deal more about the inner workings of the cell. ...
... cells under a microscope and thought they looked like the cells monks lived in within their monasteries. As our microscopes became more powerful over the years, we have learned a great deal more about the inner workings of the cell. ...
# Unit 4 LT1
... Create a model to illustrate how prokaryotic DNA is divided for cell reproduction. What is this process called? How are the two cells related to each other genetically? ...
... Create a model to illustrate how prokaryotic DNA is divided for cell reproduction. What is this process called? How are the two cells related to each other genetically? ...
congratulations!!! you have found the vacuole!
... forms that are usable by the mitochondria during ATP synthesis. Vacuoles bring their stored material to any organelle inside the cell that needs it or to other cells if they need the stored material. Vacuoles in plant and animal cells are different in size and numbers but they ultimately have the sa ...
... forms that are usable by the mitochondria during ATP synthesis. Vacuoles bring their stored material to any organelle inside the cell that needs it or to other cells if they need the stored material. Vacuoles in plant and animal cells are different in size and numbers but they ultimately have the sa ...
BMT+Treatment+of+Infectious+Diseasespost
... Penicillin kills bacteria by interfering with the ability to synthesize cell wall. In this sequence, Escherichia coli were incubated in penicillin for 30 minutes. The bacteria lengthen, but cannot divide. Eventually the weak cell wall ruptures (last panel). ...
... Penicillin kills bacteria by interfering with the ability to synthesize cell wall. In this sequence, Escherichia coli were incubated in penicillin for 30 minutes. The bacteria lengthen, but cannot divide. Eventually the weak cell wall ruptures (last panel). ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.