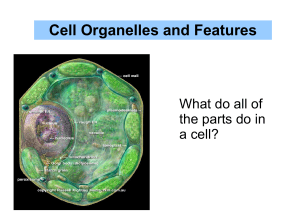
Cells
... The basic unit of all living things. Are made up of “little organs” called organelles. ...
... The basic unit of all living things. Are made up of “little organs” called organelles. ...
Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize
... rRNA synthesis occur here and it requires DNA instructions Proteins imported from the cytoplasm are assembled with rRNA into large and small subunit of ribosomes These subunit of ribosomes will eventually assemble in to a ribosome = protein synthesis machinery . Process will begin upon contact with ...
... rRNA synthesis occur here and it requires DNA instructions Proteins imported from the cytoplasm are assembled with rRNA into large and small subunit of ribosomes These subunit of ribosomes will eventually assemble in to a ribosome = protein synthesis machinery . Process will begin upon contact with ...
Prokaryotic Cells – Single-celled organisms that do not
... Reassessment Review Directions • Click “Slideshow” then “From Beginning” to view this presentation properly. • Take detailed notes. • STUDY and quiz your self over the information. ...
... Reassessment Review Directions • Click “Slideshow” then “From Beginning” to view this presentation properly. • Take detailed notes. • STUDY and quiz your self over the information. ...
Anatomy_of_Cells - Northwest ISD Moodle
... (1/12,000 of an inch) in to 10cm or more in the largest cell. The typical human cell is about 10 micrometers. The largest, the fertilized egg, is nearly 100 micrometers in diameter. • Lengths range from a few micrometers to a meter or more. Some skeletal muscle cells are 30cm long, and the nerve cel ...
... (1/12,000 of an inch) in to 10cm or more in the largest cell. The typical human cell is about 10 micrometers. The largest, the fertilized egg, is nearly 100 micrometers in diameter. • Lengths range from a few micrometers to a meter or more. Some skeletal muscle cells are 30cm long, and the nerve cel ...
Kingdom Review Project
... For each, bacteria, plant, and animal kingdoms, choose an organism to “zoom in” on. Draw a picture depicting a typical cell for each organism. Your cell drawings should include all major structures typically found in each cell. It should also include a written description of each structure’s funct ...
... For each, bacteria, plant, and animal kingdoms, choose an organism to “zoom in” on. Draw a picture depicting a typical cell for each organism. Your cell drawings should include all major structures typically found in each cell. It should also include a written description of each structure’s funct ...
Unit 3 Powerpoint
... 14.swf::Mitosis%20and%20Cytokinesis 5. Cancer – cells duplicate without control •Tissue is called tumor, growth, neoplasm •Oncology – The study of •Cancerous is called malignant •Non-cancerous is benign – does not spread to other parts and may be removed ...
... 14.swf::Mitosis%20and%20Cytokinesis 5. Cancer – cells duplicate without control •Tissue is called tumor, growth, neoplasm •Oncology – The study of •Cancerous is called malignant •Non-cancerous is benign – does not spread to other parts and may be removed ...
Homework Questions – Unit 1 – Biochemistry Section: The Cell
... Why does your body manufacture cholesterol even if you do not eat any food that contain cholesterol? ...
... Why does your body manufacture cholesterol even if you do not eat any food that contain cholesterol? ...
7th Grade Science Cells Study Guide You will have a Cell Test on
... 9. What is the structure of a Bacteria (Prokaryote) cell. Draw a picture from page 64. Bacteria have a nucleoid where a single strand of DNA floats inside. 10.Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the organism. Organization of the cell. (pages ...
... 9. What is the structure of a Bacteria (Prokaryote) cell. Draw a picture from page 64. Bacteria have a nucleoid where a single strand of DNA floats inside. 10.Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the organism. Organization of the cell. (pages ...
22. Myxobacterial Differentiation
... b. The length of the amoeboid cell allows orientation in a gradient, so they can (and do) respond to spatial gradients. 2. a. Myxobacteria feed in packs and move slowly. they can use cell surface signals rather than small diffusible molecules. The use of cell surface macromolecules as attractants ...
... b. The length of the amoeboid cell allows orientation in a gradient, so they can (and do) respond to spatial gradients. 2. a. Myxobacteria feed in packs and move slowly. they can use cell surface signals rather than small diffusible molecules. The use of cell surface macromolecules as attractants ...
Slide 1
... nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. Endoplasmic Reticulum - The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of sacs that manufactures, processes, and transports chemical compounds for use inside and outside of the cell. It is connected to the double-layered nuclear envelope, prov ...
... nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. Endoplasmic Reticulum - The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of sacs that manufactures, processes, and transports chemical compounds for use inside and outside of the cell. It is connected to the double-layered nuclear envelope, prov ...
Cells
... All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
Ch.4 Cell Notes - Milan Area Schools
... Puts finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER Packages finished material for shipment to ...
... Puts finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER Packages finished material for shipment to ...
Inflammation
... ③ Emigrating It refers to the process by which motile white cells migrate out of blood vessels. Although all leukocytes are more or less motile, the most active are the neutrophils and monocytes; the most sluggish are the lymphocytes. While cell emigration is an active, energy-dependent process. * ...
... ③ Emigrating It refers to the process by which motile white cells migrate out of blood vessels. Although all leukocytes are more or less motile, the most active are the neutrophils and monocytes; the most sluggish are the lymphocytes. While cell emigration is an active, energy-dependent process. * ...
Animal Cell Structure and functions
... Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane that encloses their contents. These membranes also regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cells. Ribosomes - non non--membraneous, spherical bodies composed of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and protein enzymes. It is the site of protein ...
... Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane that encloses their contents. These membranes also regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cells. Ribosomes - non non--membraneous, spherical bodies composed of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and protein enzymes. It is the site of protein ...
Reprogramming somatic cells without fusion or ethical confusion
... clones also clustered them closer to ESCs than MEFs and fibroblasts; however, their signature was still distinct from ESCs. The authors also examined epigenetic marks of these reprogrammed clones. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses showed that the promoters of Oct3/4 and Nanog had increased acet ...
... clones also clustered them closer to ESCs than MEFs and fibroblasts; however, their signature was still distinct from ESCs. The authors also examined epigenetic marks of these reprogrammed clones. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses showed that the promoters of Oct3/4 and Nanog had increased acet ...
Battle Royale game
... explanations (IQIA). • Lists must be written in order (answers only) • The point will be awarded for the team with the correct, complete answer that puts their pen down first. • Candy for the winning team!!! ...
... explanations (IQIA). • Lists must be written in order (answers only) • The point will be awarded for the team with the correct, complete answer that puts their pen down first. • Candy for the winning team!!! ...
The Cell
... Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. What are eukaryotes? Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular, but they all have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. ...
... Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. What are eukaryotes? Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular, but they all have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. ...
REVIEW QUESTIONS- Structure and Function of
... What is one difference between the cells of plants and animals? A. Animal cells have a cell membrane, and plant cells do not. B. Plant cells have a cell wall, and animal cells do not. C. Plant cells have ribosomes, and animal cells do not. D. Plant cells have a mitochondrion, and animal cells do not ...
... What is one difference between the cells of plants and animals? A. Animal cells have a cell membrane, and plant cells do not. B. Plant cells have a cell wall, and animal cells do not. C. Plant cells have ribosomes, and animal cells do not. D. Plant cells have a mitochondrion, and animal cells do not ...
Chapter 7.4: The Diversity of Cellular Life
... 2. Self-sufficient (can grow, respond to environment, use energy, reproduce) 3. Most numerous types of organisms on Earth Example: Bacteria ...
... 2. Self-sufficient (can grow, respond to environment, use energy, reproduce) 3. Most numerous types of organisms on Earth Example: Bacteria ...
New Data, Research and Tools at genome.ucsc.edu
... • Theory later disproved by better microscopes. ...
... • Theory later disproved by better microscopes. ...
Explain how cell size and shape affect the overall rate of nutrient
... Note: Emergent properties arise from the interaction of component parts: the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.The concept of emergent properties has many implications in biology. Life itself can be viewed as an emergent property, and the nature of life could be discussed in the light of th ...
... Note: Emergent properties arise from the interaction of component parts: the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.The concept of emergent properties has many implications in biology. Life itself can be viewed as an emergent property, and the nature of life could be discussed in the light of th ...
What structures of living things are cells involved?
... involved? 5. What functions of living things are cells involved? ...
... involved? 5. What functions of living things are cells involved? ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.