Basic Cell Biology
... water and other materials. They store nutrients and enzymes needed by cells. They provide a storage space for waste materials given off by the cell. ...
... water and other materials. They store nutrients and enzymes needed by cells. They provide a storage space for waste materials given off by the cell. ...
Cells - St. Ambrose School
... They are organized structures that help living things carry on the activities of life, such as digestion, movement, growth and reproduction ...
... They are organized structures that help living things carry on the activities of life, such as digestion, movement, growth and reproduction ...
File
... Matthias Jakob Schleiden, a German botanist, concluded that all plant tissues are composed of cells and that a plant arose from a single cell. He declared that the cell is the basic building block of all plant matter. This statement of Schleiden was the first generalizations concerning cells. Born i ...
... Matthias Jakob Schleiden, a German botanist, concluded that all plant tissues are composed of cells and that a plant arose from a single cell. He declared that the cell is the basic building block of all plant matter. This statement of Schleiden was the first generalizations concerning cells. Born i ...
Guided Notes on Cell Parts Fill in the blank on your Sheet
... especially a whip like extension of certain cells. • It functions as an organ of locomotion. ...
... especially a whip like extension of certain cells. • It functions as an organ of locomotion. ...
The Body in Motion
... and Virchow contributed to this theory Each cell is a microcosm of life ...
... and Virchow contributed to this theory Each cell is a microcosm of life ...
6th Grade Science
... are considerably ________________ than those in plant cells. In animal cells, vacuoles may store food that needs to be ____________________. Vacuoles can also store the indigestible __________________ until they can ________________ with the cell membrane and squirt the wastes outside. The cell sap ...
... are considerably ________________ than those in plant cells. In animal cells, vacuoles may store food that needs to be ____________________. Vacuoles can also store the indigestible __________________ until they can ________________ with the cell membrane and squirt the wastes outside. The cell sap ...
Exam 2 Short Answers Ch 4-8.doc
... from the light dependent reactions to completely reduce carbon dioxide to glucose in the Calvin cycle. 11. During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, the synthesis of ______________ is coupled to the diffusion of protons. 12. The _________________ is composed of a light-harvesting compl ...
... from the light dependent reactions to completely reduce carbon dioxide to glucose in the Calvin cycle. 11. During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, the synthesis of ______________ is coupled to the diffusion of protons. 12. The _________________ is composed of a light-harvesting compl ...
Study Guide for the LS
... cell wall: a structure made from cellulose that surrounds the cell membrane of some cells and provides strength and support to the cell (not in animal cells) chloroplast: found in plants and algae/ make food using the energy of the sun chlorophyll: the pigment that makes chloroplasts green D ...
... cell wall: a structure made from cellulose that surrounds the cell membrane of some cells and provides strength and support to the cell (not in animal cells) chloroplast: found in plants and algae/ make food using the energy of the sun chlorophyll: the pigment that makes chloroplasts green D ...
Cell WEBQUEST: An interactive
... You will be asked to use the web to research what cells are and what cells are made of. You will complete conventional worksheets completing information on the cell, as well completed a detailed, colored drawing of an animal cell. ...
... You will be asked to use the web to research what cells are and what cells are made of. You will complete conventional worksheets completing information on the cell, as well completed a detailed, colored drawing of an animal cell. ...
Cell Organelles
... rough and smooth. My rough parts are responsible for packaging proteins. The ribosomes on my sides make me rough. My smooth parts are the smooth tubes that store spare ions and other chemicals the cell might need later. You can find me near the nucleus and throughout the cytoplasm.” 4) “I look like ...
... rough and smooth. My rough parts are responsible for packaging proteins. The ribosomes on my sides make me rough. My smooth parts are the smooth tubes that store spare ions and other chemicals the cell might need later. You can find me near the nucleus and throughout the cytoplasm.” 4) “I look like ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... • Somatic cells (body cells) of a multicellular organism perform specialized functions to keep the organism functioning • Life cycle of a cell is called the Cell Cycle – Interphase – Mitosis ...
... • Somatic cells (body cells) of a multicellular organism perform specialized functions to keep the organism functioning • Life cycle of a cell is called the Cell Cycle – Interphase – Mitosis ...
Cell Notes - Fort Bend ISD
... All living things are composed of cells. If its not made up of at least one cell, it is NOT living! Cells carry on similar functions like obtaining energy and removing waste ...
... All living things are composed of cells. If its not made up of at least one cell, it is NOT living! Cells carry on similar functions like obtaining energy and removing waste ...
CELLS PLUS VOLUME
... • all energy flow (metabolism & biochemistry) of life occurs within cells • cells contain DNA as genetic info - (for subsequent generations) ...
... • all energy flow (metabolism & biochemistry) of life occurs within cells • cells contain DNA as genetic info - (for subsequent generations) ...
Cells Alive - Net Start Class
... a. In this animation, what is the smallest object illustrated? ____________________________________ b. How big is it? ___________________________ c. What is the size relationship between ragweed pollen and Staphylococcus bacteria? _____________________________________________________________________ ...
... a. In this animation, what is the smallest object illustrated? ____________________________________ b. How big is it? ___________________________ c. What is the size relationship between ragweed pollen and Staphylococcus bacteria? _____________________________________________________________________ ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... A) moves sodium and potassium opposite to the direction of their electrochemical gradients. B) depends on a hydrogen gradient for energy. C) must reestablish ion concentrations after each action potential. D) transports potassium ions out of the cell during repolarization. E) transports sodium ions ...
... A) moves sodium and potassium opposite to the direction of their electrochemical gradients. B) depends on a hydrogen gradient for energy. C) must reestablish ion concentrations after each action potential. D) transports potassium ions out of the cell during repolarization. E) transports sodium ions ...
Cell Specialization - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The shape of animal cells provides a clue to their function. Many of the features of unicellular organisms can be found in animal cells as you can see in Figure 2. Figure 2 Some specialized cells found in human bodies. ...
... The shape of animal cells provides a clue to their function. Many of the features of unicellular organisms can be found in animal cells as you can see in Figure 2. Figure 2 Some specialized cells found in human bodies. ...
Mitosis (cell division)
... • Cell spends the majority of life in interphase – G1: Cells grow to mature size (growth phase) – S: Cell’s DNA is copied (synthesis phase) – G2: Cell prepares for division – G0: Cell exits cell cycle. Cells are not copying DNA or preparing to divide. (The vast majority of the body’s cells are in G0 ...
... • Cell spends the majority of life in interphase – G1: Cells grow to mature size (growth phase) – S: Cell’s DNA is copied (synthesis phase) – G2: Cell prepares for division – G0: Cell exits cell cycle. Cells are not copying DNA or preparing to divide. (The vast majority of the body’s cells are in G0 ...
Cells Powerpoint - Class on the Moon
... • Mitochondria & chloroplasts divide independent of rest of eukaryotic cell • Mitochondria & chloroplasts have separate, circular ring of ...
... • Mitochondria & chloroplasts divide independent of rest of eukaryotic cell • Mitochondria & chloroplasts have separate, circular ring of ...
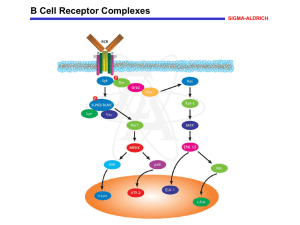
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
... homeostasis of reversible tyrosine phosphorylation in the resting B cell. Members of the Src family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads ...
... homeostasis of reversible tyrosine phosphorylation in the resting B cell. Members of the Src family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads ...
Name Class Date Cell Differentiation (Foldable) Make Up #20
... Stem Cells and Development During an organism’s development, some cells differentiate to become a wide variety of body cells. A fertilized egg and the first few cells in an embryo are able to form any kind of cell and tissue. Such a cell is termed totipotent. A blastocyst is an embryonic stage that ...
... Stem Cells and Development During an organism’s development, some cells differentiate to become a wide variety of body cells. A fertilized egg and the first few cells in an embryo are able to form any kind of cell and tissue. Such a cell is termed totipotent. A blastocyst is an embryonic stage that ...
Link to Unit 4 - Lake County Schools
... SC.6.L.14.4 (AA): Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. SC.6.L.14.3: Recognize and explore how cells of all organisms undergo similar processes t ...
... SC.6.L.14.4 (AA): Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. SC.6.L.14.3: Recognize and explore how cells of all organisms undergo similar processes t ...
Outline --- Programmed Cell Death 1. Apoptosis An overview: the
... An overview: the establishment of the concept/field Morphological observations (concept/hypothesis) Medicine/cancer (Bcl-2, the founder of a new class of oncogene) Basic research (proof of the concept by C. elegans genetics) In-depth discussion of certain topics Mitochondria-mediated caspase act ...
... An overview: the establishment of the concept/field Morphological observations (concept/hypothesis) Medicine/cancer (Bcl-2, the founder of a new class of oncogene) Basic research (proof of the concept by C. elegans genetics) In-depth discussion of certain topics Mitochondria-mediated caspase act ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.