Differential stimulation of IL-6 secretion following apical and
... Elan Corporation Research In?i.tute, Trinity College, Dublin 2. ’BiochemistryDepartment, T m t y College, Dublin 2, Ireland. IL-1 is a classic pro-inflammatory cytokine[l). Its biological effects are shared by two functionally active forms ILl a and IL-Ip[l]. In humans the primary source of IL-1 is ...
... Elan Corporation Research In?i.tute, Trinity College, Dublin 2. ’BiochemistryDepartment, T m t y College, Dublin 2, Ireland. IL-1 is a classic pro-inflammatory cytokine[l). Its biological effects are shared by two functionally active forms ILl a and IL-Ip[l]. In humans the primary source of IL-1 is ...
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
... Read these passages from the text and answer the questions that follow. Two Types of Cells There is a basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and ...
... Read these passages from the text and answer the questions that follow. Two Types of Cells There is a basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and ...
Cell Foldable
... On a different section of your foldable you must write out three important facts about the type of cell you drew. These facts need to show some form of gained knowledge and cannot be facts you learned from 8th grade! The fourth section you will describe the process of binary fission and conjugation ...
... On a different section of your foldable you must write out three important facts about the type of cell you drew. These facts need to show some form of gained knowledge and cannot be facts you learned from 8th grade! The fourth section you will describe the process of binary fission and conjugation ...
5.1 The Cell Cycle TEKS 5A
... • The main stages of the cell cycle are gap 1, synthesis, gap 2, and mitosis. – Gap 1 (G1): cell growth and normal functions – DNA synthesis (S): copies DNA – Gap 2 (G2): additional growth – Mitosis (M): includes division of the cell nucleus (mitosis) and division of the cell cytoplasm (cytokinesis) ...
... • The main stages of the cell cycle are gap 1, synthesis, gap 2, and mitosis. – Gap 1 (G1): cell growth and normal functions – DNA synthesis (S): copies DNA – Gap 2 (G2): additional growth – Mitosis (M): includes division of the cell nucleus (mitosis) and division of the cell cytoplasm (cytokinesis) ...
Cell Foldable
... On a different section of your foldable you must write out three important facts about the type of cell you drew. These facts need to show some form of gained knowledge and cannot be facts you learned from 8th grade! The fourth section you will describe the process of binary fission and conjugation ...
... On a different section of your foldable you must write out three important facts about the type of cell you drew. These facts need to show some form of gained knowledge and cannot be facts you learned from 8th grade! The fourth section you will describe the process of binary fission and conjugation ...
Lecture 4 (BY 14)
... Why Are Cells So Small? • _______-__-______ ratio • The bigger a cell is, the less surface area there is per unit volume • Above a certain size, material cannot be moved in or out of cell fast enough ...
... Why Are Cells So Small? • _______-__-______ ratio • The bigger a cell is, the less surface area there is per unit volume • Above a certain size, material cannot be moved in or out of cell fast enough ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... and extensive internal membranes occur in bacteria and archaea that perform photosynthesis. The photosynthetic membranes arise as invaginations of the plasma membrane. As the plasma membrane folds in, either vesicles pinch off or the types of flattened stacks shown in Figure 7.5 form. The internal p ...
... and extensive internal membranes occur in bacteria and archaea that perform photosynthesis. The photosynthetic membranes arise as invaginations of the plasma membrane. As the plasma membrane folds in, either vesicles pinch off or the types of flattened stacks shown in Figure 7.5 form. The internal p ...
1. Cell Membrane It protects, supports, and controls movement of
... waste, enzymes, etc; “locker” ...
... waste, enzymes, etc; “locker” ...
SkMC Skeletal Muscle Cell Systems CC-45-6
... Lonza guarantees the performance of its cells only if ...
... Lonza guarantees the performance of its cells only if ...
Name - Humble ISD
... 5. To compare and contrast different types of specialized cells. 6. To observe plasmolysis in a plant cell. Scientific Drawings: Although it is not necessary to be artistic to make good biological drawings, you do need to be accurate and invest the time needed to do a good job. 1. Obtain a plain, wh ...
... 5. To compare and contrast different types of specialized cells. 6. To observe plasmolysis in a plant cell. Scientific Drawings: Although it is not necessary to be artistic to make good biological drawings, you do need to be accurate and invest the time needed to do a good job. 1. Obtain a plain, wh ...
3-2 summary levels of organization
... What is the process by which cells become specialized? A. photosynthesis B. vascular development C. prokaryotic process D. cell differentiation ...
... What is the process by which cells become specialized? A. photosynthesis B. vascular development C. prokaryotic process D. cell differentiation ...
worksheet prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure
... Evolve from much smaller prokaryotic cells___________________________________ Contain DNR______________________________________________________________ DNR is visible as a long irregularly shaped molecule_______________________________ DNR is packaged together with special proteins, called chromosom ...
... Evolve from much smaller prokaryotic cells___________________________________ Contain DNR______________________________________________________________ DNR is visible as a long irregularly shaped molecule_______________________________ DNR is packaged together with special proteins, called chromosom ...
Plants Up Close
... • Using the 40x objective lens, students should be able to see that onion cells are rectangular in shape and that the cells stack together neatly. The round dots inside of the cells are nuclei; they control heredity and cell division. • Review with the class what Students should also be able to see ...
... • Using the 40x objective lens, students should be able to see that onion cells are rectangular in shape and that the cells stack together neatly. The round dots inside of the cells are nuclei; they control heredity and cell division. • Review with the class what Students should also be able to see ...
Learning Target
... 6. Recognize the type of daughter cells formed through mitosis and their chromosome number as compared to the parent cell. ...
... 6. Recognize the type of daughter cells formed through mitosis and their chromosome number as compared to the parent cell. ...
Cells
... Structures inside that perform special jobs for the cell (example: ribosomes=make protein, etc.) ...
... Structures inside that perform special jobs for the cell (example: ribosomes=make protein, etc.) ...
Biology_Plant & Animal Cell Notes_06
... Changes chemical energy in food to compounds more convenient for cell to use Has 2 membranes Outer- surrounds the organelle Inner- increases surface area because of folds; this is where cellular respiration takes place; folds are called cristae ...
... Changes chemical energy in food to compounds more convenient for cell to use Has 2 membranes Outer- surrounds the organelle Inner- increases surface area because of folds; this is where cellular respiration takes place; folds are called cristae ...
Tissue - scienceathawthorn
... tissue functions to produce force and cause motion, either locomotion or movement within internal organs. Muscle tissue is separated into three distinct categories: visceral or smooth muscle, which is found in the inner linings of organs; skeletal muscle, in which is found attached to bone providing ...
... tissue functions to produce force and cause motion, either locomotion or movement within internal organs. Muscle tissue is separated into three distinct categories: visceral or smooth muscle, which is found in the inner linings of organs; skeletal muscle, in which is found attached to bone providing ...
學習目標
... • TGF-β and activins may be involved in terminating hepatocyte replication. • Intrahepatic stem or progenitor cells do not play a role in the compensatory growth that occurs after partial hepatotectomy. ...
... • TGF-β and activins may be involved in terminating hepatocyte replication. • Intrahepatic stem or progenitor cells do not play a role in the compensatory growth that occurs after partial hepatotectomy. ...
Mitosis (cell division)
... • The work of the cell occurs at the boundaries – cells have biochemical needs proportional to their size, and the membrane is the means by which things move in and out - and the cell membrane grows more slowly than the volume as cell size increases. • What if Anchorage doubled in size but it didn’t ...
... • The work of the cell occurs at the boundaries – cells have biochemical needs proportional to their size, and the membrane is the means by which things move in and out - and the cell membrane grows more slowly than the volume as cell size increases. • What if Anchorage doubled in size but it didn’t ...
Special topics in electrical and systems engineering
... • There are specialized receptors on the cell surface • Receptors transduce signals (binding of their ligand) into the cytosol (the inside of the cell) • Signaling cascades originate in the initial binding event • Complicated networks of multistep phosphorylation ...
... • There are specialized receptors on the cell surface • Receptors transduce signals (binding of their ligand) into the cytosol (the inside of the cell) • Signaling cascades originate in the initial binding event • Complicated networks of multistep phosphorylation ...
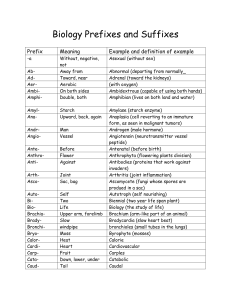
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... for a given trait) histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyperthyroidism (condition resulting from the ...
... for a given trait) histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyperthyroidism (condition resulting from the ...
Name: Date:______ Period
... Many cells grow until they reach a certain size and then divide. Why don’t cells grow indefinitely until they become the size of basketballs? What problems arise when a cell grows larger? Why does a cell divide into two smaller cells when it reaches a certain size? These are all questions that scien ...
... Many cells grow until they reach a certain size and then divide. Why don’t cells grow indefinitely until they become the size of basketballs? What problems arise when a cell grows larger? Why does a cell divide into two smaller cells when it reaches a certain size? These are all questions that scien ...
PP text version
... IGF for skeletal system) receptors for growth factors are present or active on some cells and not on others. e.g. Speeman & Mangold’s organizer ...
... IGF for skeletal system) receptors for growth factors are present or active on some cells and not on others. e.g. Speeman & Mangold’s organizer ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.