cell - No Brain Too Small
... dormant - a period of time when seeds do not germinate epidermis - outer layer of cells excretion - getting rid of waste substances made in the body by chemical reactions. features - characteristics fertilisation - joining of a male sex cell (gamete) with a female sex cell (gamete) filament - part o ...
... dormant - a period of time when seeds do not germinate epidermis - outer layer of cells excretion - getting rid of waste substances made in the body by chemical reactions. features - characteristics fertilisation - joining of a male sex cell (gamete) with a female sex cell (gamete) filament - part o ...
The Cell Theory Notes
... hundreds of scientists. It has been proven true so many times some scientists call it a concept. The term “cell” was first used by English scientist Robert Hooke as he observed thin slices of cork under the microscope. He used the word cell because the compartments he saw in the cork reminded him of ...
... hundreds of scientists. It has been proven true so many times some scientists call it a concept. The term “cell” was first used by English scientist Robert Hooke as he observed thin slices of cork under the microscope. He used the word cell because the compartments he saw in the cork reminded him of ...
Stages of the cell cycle
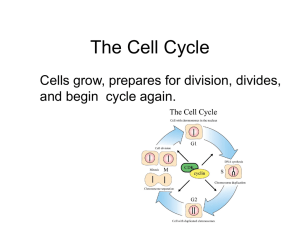
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
Vacuoles
... They are found in the cytoplasm of cells. Found in both plant and animal cells. A good example can be seen in most plant cells. ...
... They are found in the cytoplasm of cells. Found in both plant and animal cells. A good example can be seen in most plant cells. ...
Cell Wall Ribosomes Nucleus Chloroplast Cytoplasm Endoplasmic
... The cell membrane is on the outside of an The lysosomes have special digestive enzymes that are The major difference between plant and animal cells is animal cell and is found just underneath the used to digest old cell parts. It's like a garbage disposal that plant cells have cell walls and chlorop ...
... The cell membrane is on the outside of an The lysosomes have special digestive enzymes that are The major difference between plant and animal cells is animal cell and is found just underneath the used to digest old cell parts. It's like a garbage disposal that plant cells have cell walls and chlorop ...
GCSE worksheet on cell structure and organelle function worksheet.
... building. There are many small power stations that ‘power’ the entire city by releasing energy from sugar. The sugar is grown by plants in giant greenhouses near to the power stations. The energy is used by buildings within the city to make a variety of products. One such building is the Gucci cloth ...
... building. There are many small power stations that ‘power’ the entire city by releasing energy from sugar. The sugar is grown by plants in giant greenhouses near to the power stations. The energy is used by buildings within the city to make a variety of products. One such building is the Gucci cloth ...
Intro to cells
... the synthesis and packaging of proteins. Some of those proteins might be used in the cell and some are sent ...
... the synthesis and packaging of proteins. Some of those proteins might be used in the cell and some are sent ...
V. Lecture Section 5 A. Review of the mitotic cell cycle and cell death
... 1. Internal activation of apoptosis = Intrinsic apoptotic pathway 2. External activation of apopotosis = Extrinsic apoptotic pathway 3. Activation of Caspase Cascade 4. Characteristics include cessation of DNA repair mechanisms, cell shrinkage, nuclear membrane blebbing, DNA fragmentation, and death ...
... 1. Internal activation of apoptosis = Intrinsic apoptotic pathway 2. External activation of apopotosis = Extrinsic apoptotic pathway 3. Activation of Caspase Cascade 4. Characteristics include cessation of DNA repair mechanisms, cell shrinkage, nuclear membrane blebbing, DNA fragmentation, and death ...
Level The Cell and the City of Bling: using analogies to teach cell
... The energy is used by buildings within the city to make a variety of products. One such building is the Gucci clothes factory. This factory manufactures many different clothes that are all desig ...
... The energy is used by buildings within the city to make a variety of products. One such building is the Gucci clothes factory. This factory manufactures many different clothes that are all desig ...
novel in vitro pemf exposure system for a large - ETH E
... MC-3T3-E1 cells indicate a decrease or delay in differentiation as determined by ALP activity (Figure 1). But the underlying mechanisms are still unclear and the clinical success of PEMF treatment is in contrast with reports on in vitro experiments [3]. Consequently reliable identification and repli ...
... MC-3T3-E1 cells indicate a decrease or delay in differentiation as determined by ALP activity (Figure 1). But the underlying mechanisms are still unclear and the clinical success of PEMF treatment is in contrast with reports on in vitro experiments [3]. Consequently reliable identification and repli ...
Cell Ultrastructure
... New parts of a cell • The cytoplasm was basically anything which didn’t include the nucleus or cell membrane • It contains: • Mitochondria • Endoplasmic reticulum • Vesicles • Golgi apparatus ...
... New parts of a cell • The cytoplasm was basically anything which didn’t include the nucleus or cell membrane • It contains: • Mitochondria • Endoplasmic reticulum • Vesicles • Golgi apparatus ...
The World of Cells
... holds the cell together. It helps control what enters and leaves the cell ...
... holds the cell together. It helps control what enters and leaves the cell ...
Lesson 4 Organisms Made of Cells
... 2. Where is the nucleolus found, and what does it produce? The nucleolus is found inside the nucleus, and it produces ribosomes. ...
... 2. Where is the nucleolus found, and what does it produce? The nucleolus is found inside the nucleus, and it produces ribosomes. ...
Cell analogy Organizer
... major product or something that comes out of that system (it doesn’t literally have to be a tangible/concrete object) ...
... major product or something that comes out of that system (it doesn’t literally have to be a tangible/concrete object) ...
Background Information Cloning According to the University of Utah
... Artificial embryo twinning uses the same approach, but it occurs in a Petri dish instead of in the mother's body. This is accomplished by manually separating a very early embryo into individual cells, and then allowing each cell to divide and develop on its own. The resulting embryos are placed into ...
... Artificial embryo twinning uses the same approach, but it occurs in a Petri dish instead of in the mother's body. This is accomplished by manually separating a very early embryo into individual cells, and then allowing each cell to divide and develop on its own. The resulting embryos are placed into ...
Cell Division*Mitosis Notes
... • DNA codes the proteins our cells need to survive. The larger the cell, the more protein it would need and DNA could not keep up! • Surface Area to Volume Ratio – the larger the cell, the more volume it has. More is needed and more waste is produced. It would need more surface area than the membran ...
... • DNA codes the proteins our cells need to survive. The larger the cell, the more protein it would need and DNA could not keep up! • Surface Area to Volume Ratio – the larger the cell, the more volume it has. More is needed and more waste is produced. It would need more surface area than the membran ...
Year 7: Living World-‐ Cells
... • Include advantages and disadvantages of each First-‐hand investigation(s): Using a microscope Prepare a wet mount slide to examine letters of a newspaper First-‐hand investigation(s): Observing and drawing cells ...
... • Include advantages and disadvantages of each First-‐hand investigation(s): Using a microscope Prepare a wet mount slide to examine letters of a newspaper First-‐hand investigation(s): Observing and drawing cells ...
1. To enter or leave a cell, substances must pass through a. a
... a. its need for enough surface area for exchange with its environment. b. the number of organelles that can be packed inside. c. the materials needed to build it. d. the amount of flexibility it needs to be able to move. e. the amount of food it needs to survive. 4. You would expect a cell with an e ...
... a. its need for enough surface area for exchange with its environment. b. the number of organelles that can be packed inside. c. the materials needed to build it. d. the amount of flexibility it needs to be able to move. e. the amount of food it needs to survive. 4. You would expect a cell with an e ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... • Cells need to communicate to each other. There are many challenges in how they accomplish this communication. • With your group, draw a picture of an ‘ideal cell’ and diagram or explain at least 5 ways that your cell could communicate with other cells • Try to make it realistic, but you don’t nece ...
... • Cells need to communicate to each other. There are many challenges in how they accomplish this communication. • With your group, draw a picture of an ‘ideal cell’ and diagram or explain at least 5 ways that your cell could communicate with other cells • Try to make it realistic, but you don’t nece ...
Observing the Intellectual Landscape and New Developments of
... 9,760 bibliographic records based on document co-citation analysis. According to the cluster visualizations, research works related to induced pluripotent stem cell and myocardial infarction shape the foundation of the intellectual landscape. Research works related to platform technologies reflect t ...
... 9,760 bibliographic records based on document co-citation analysis. According to the cluster visualizations, research works related to induced pluripotent stem cell and myocardial infarction shape the foundation of the intellectual landscape. Research works related to platform technologies reflect t ...
Cell Biology - rci.rutgers.edu
... i. Large in growing cells c. Associated with chromatin region associated with DNA coding for rRNA i. Nuclear organizing regions (DNA regions) 3. Chromatin—DNA + globular histone a. Nucleosome—fundamental unit of chromatin i. Units of eight wrapped by DNA molecule b. Chromosomes: prior to cell divisi ...
... i. Large in growing cells c. Associated with chromatin region associated with DNA coding for rRNA i. Nuclear organizing regions (DNA regions) 3. Chromatin—DNA + globular histone a. Nucleosome—fundamental unit of chromatin i. Units of eight wrapped by DNA molecule b. Chromosomes: prior to cell divisi ...
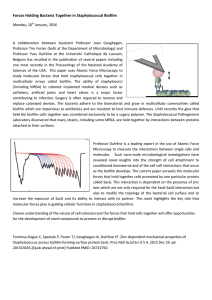
Forces Holding Bacteria Together in Staphylococcal Biofilm
... Microscopy to measure the interactions between single cells and molecules. Such nano-scale microbiological investigations have revealed novel insights into the strength of cell attachment to conditioned biomaterial and of the cell-cell interactions that occur as the biofilm develops. The current pap ...
... Microscopy to measure the interactions between single cells and molecules. Such nano-scale microbiological investigations have revealed novel insights into the strength of cell attachment to conditioned biomaterial and of the cell-cell interactions that occur as the biofilm develops. The current pap ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.