What is a cell?
... Remember, a theory is not just a hunch, it is an idea supported by a considerable amount of experimental evidence. ...
... Remember, a theory is not just a hunch, it is an idea supported by a considerable amount of experimental evidence. ...
cells - Warren Hills Regional School District
... Although ALL living things are made of cells, organisms may be: Unicellular – composed of one cell Multicellular – composed of many cells that may organize into tissues, etc. Cell Diversity Typical cells range from 5 to 50 micrometers (microns) in diameter Smallest cell mycoplasma bacteria ...
... Although ALL living things are made of cells, organisms may be: Unicellular – composed of one cell Multicellular – composed of many cells that may organize into tissues, etc. Cell Diversity Typical cells range from 5 to 50 micrometers (microns) in diameter Smallest cell mycoplasma bacteria ...
a molecule necessary and complementary to life. What elements are
... Use the diagram to compute the relative ATP production by glycolysis and the electron transport chain. Take a deep breath. Just where is that oxygen going to be used? What by-product of respiration will be the result? ...
... Use the diagram to compute the relative ATP production by glycolysis and the electron transport chain. Take a deep breath. Just where is that oxygen going to be used? What by-product of respiration will be the result? ...
Development and Apoptosis
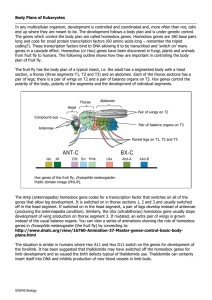
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
學生: 徐綜遠 - 分子與細胞生物學研究所 - National Taiwan University
... HuC-positive neuron cells, but rather, partial GFAP-positive glia cells, suggesting that some glia cells and immature neural stem cells in brain may be the most sensitive in their response to heat stress. Therefore, we concluded that transgenic line Tg(KY43-3) carrying human uORFchop might be an exc ...
... HuC-positive neuron cells, but rather, partial GFAP-positive glia cells, suggesting that some glia cells and immature neural stem cells in brain may be the most sensitive in their response to heat stress. Therefore, we concluded that transgenic line Tg(KY43-3) carrying human uORFchop might be an exc ...
Clonetics™ Dermal Fibroblast Cell Systems
... followed. The performance of cells is not guaranteed if any modifications are made to the complete Cell System. Cryopreserved NHDF are assured to be viable and functional when thawed and maintained ...
... followed. The performance of cells is not guaranteed if any modifications are made to the complete Cell System. Cryopreserved NHDF are assured to be viable and functional when thawed and maintained ...
Cell Processes Review
... through a membrane from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration, the process is called active transport ...
... through a membrane from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration, the process is called active transport ...
Cell Theory, Cell Structure and Cellular Transport
... employ RNA as their hereditary material. Prokaryotic DNA is organized as a circular chromosome contained in an area known as a nucleoid. Eukaryotic DNA is organized in linear structures, the eukaryotic chromosomes, which are associations of DNA and histone proteins contained within a double membrane ...
... employ RNA as their hereditary material. Prokaryotic DNA is organized as a circular chromosome contained in an area known as a nucleoid. Eukaryotic DNA is organized in linear structures, the eukaryotic chromosomes, which are associations of DNA and histone proteins contained within a double membrane ...
Cell Lecture I
... nucleus where ribosomes are produced Nuclear envelope – double membrane layer surrounding the nucleus (aka. Nuclear membrane) ...
... nucleus where ribosomes are produced Nuclear envelope – double membrane layer surrounding the nucleus (aka. Nuclear membrane) ...
How does the food you eat provide energy to cells in
... things. they can live ill a wide variety of environments. "They are able to grow very large - as large as a whale or a Douglas fir. Multicellular animals can obtain their energy from a wide variety of foods. "Their bodies are more complex. By specializing ill particular functions, each cell in a mul ...
... things. they can live ill a wide variety of environments. "They are able to grow very large - as large as a whale or a Douglas fir. Multicellular animals can obtain their energy from a wide variety of foods. "Their bodies are more complex. By specializing ill particular functions, each cell in a mul ...
CP Bio Study Guide
... Stores water for the cell. Plant cells have one large central. Animal cells small and numerous. Transports membrane and secretory proteins inside of a cell from the nucleus to the Golgi Body via transport vesicles. Nucleolus 1. List the 4 structures that are common to all cells (both prokaryotic and ...
... Stores water for the cell. Plant cells have one large central. Animal cells small and numerous. Transports membrane and secretory proteins inside of a cell from the nucleus to the Golgi Body via transport vesicles. Nucleolus 1. List the 4 structures that are common to all cells (both prokaryotic and ...
Cell Structure and Function 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v
... Feel free to pause the video whenever you need to and remember to write down any questions you have and ASK them when you get to class. All questions should be answered in your bill book. What was Robert Hooke observing when he coined the term cells? What is the cell theory? ...
... Feel free to pause the video whenever you need to and remember to write down any questions you have and ASK them when you get to class. All questions should be answered in your bill book. What was Robert Hooke observing when he coined the term cells? What is the cell theory? ...
The Cell
... 3. As a cell grows, its need for oxygen increases faster than its ability to get oxygen. So the cell must divide or suffocate ...
... 3. As a cell grows, its need for oxygen increases faster than its ability to get oxygen. So the cell must divide or suffocate ...
Inner life of a cell http://www.aimediaserver.com
... • The nonpolar (water hating) tails make up the interior of the bilayer, and the polar (water loving) heads make up the outer layer. ...
... • The nonpolar (water hating) tails make up the interior of the bilayer, and the polar (water loving) heads make up the outer layer. ...
CELLS
... Composed of a phospholipid bilayer that has proteins embedded in it Cholesterol is also an important component of cell membranes since it keeps the membrane intact yet fluid The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and leave the cell ...
... Composed of a phospholipid bilayer that has proteins embedded in it Cholesterol is also an important component of cell membranes since it keeps the membrane intact yet fluid The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and leave the cell ...
National 4 & 5 BIOlogy – multicellular organisms
... found within many tissues of the body • - can form specialised cells of a particular tissue • - e.g. Hematopoietic cells can form any type of blood cell • - adult stem cells can only form cells of a certain type • Stem Cells Video • Stem Cell therapies video ...
... found within many tissues of the body • - can form specialised cells of a particular tissue • - e.g. Hematopoietic cells can form any type of blood cell • - adult stem cells can only form cells of a certain type • Stem Cells Video • Stem Cell therapies video ...
Pre-Bio LP 1.23-2.2
... What do you need to study the most? Make two T-chart that identifies the differences between 1) prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and 2) plant cells and animal cells Question/Answer in class discussion (verbal) I can describe the purpose of the major cellular organelles & cellular structures. I can differ ...
... What do you need to study the most? Make two T-chart that identifies the differences between 1) prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and 2) plant cells and animal cells Question/Answer in class discussion (verbal) I can describe the purpose of the major cellular organelles & cellular structures. I can differ ...
Eukaryotic Cells – Cells that have a true nucleus. A nuclear
... Mitochondria - Spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae). The mitochondrion “converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP” (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. These are known as the Powe ...
... Mitochondria - Spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae). The mitochondrion “converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP” (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. These are known as the Powe ...
Cell Cycle Regulation
... only a partial genome! • M-phase checkpoint: makes sure all kinetochores are attached to spindle fibers before going on to anaphase (Apart). This is important because we can’t have a cell in the body that’s missing a chromosome! What if that cell needs to transcribe a gene located ...
... only a partial genome! • M-phase checkpoint: makes sure all kinetochores are attached to spindle fibers before going on to anaphase (Apart). This is important because we can’t have a cell in the body that’s missing a chromosome! What if that cell needs to transcribe a gene located ...
PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Organelle
... A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles. The control center of the cell. Contains the DNA Surrounds the nucleus. A round struc ...
... A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles. The control center of the cell. Contains the DNA Surrounds the nucleus. A round struc ...
CELL CITY PROJECT
... between your metaphors and the function of the organelles o Remember: A Plant City* has a cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuoles - An Animal City does not. BE CREATIVE! A cell is also like a theme park, factory, school, store and much more… POINTS POSSIBLE ...
... between your metaphors and the function of the organelles o Remember: A Plant City* has a cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuoles - An Animal City does not. BE CREATIVE! A cell is also like a theme park, factory, school, store and much more… POINTS POSSIBLE ...
Biology 1406 Chapter 7 Lecture Notes
... This cellular pump moves sodium ions from an area of low concentration (inside your cells) to an area of high concentration (outside your cells) and at the same time moves potassium ions from an area of low concentration (outside your cells) to an area of high concentration (inside your cells). ATP ...
... This cellular pump moves sodium ions from an area of low concentration (inside your cells) to an area of high concentration (outside your cells) and at the same time moves potassium ions from an area of low concentration (outside your cells) to an area of high concentration (inside your cells). ATP ...
Model - Sitka School District
... Plant and Animal Cells GLE SC2.1 Diversity of Life The student demonstrates an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles and diversity of living organisms by describing the basic structure and function of plant and animal cells. ...
... Plant and Animal Cells GLE SC2.1 Diversity of Life The student demonstrates an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles and diversity of living organisms by describing the basic structure and function of plant and animal cells. ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.