Abstract
... ITO-Si heterojunction solar cell with nanocrystal line CdTe thin films grown by magnetron sputtering are studied. The electrical and optical properties of these solar cell devices, as determined by current–voltage and photovoltage spectroscopy, were found to change with temperature over a range of 8 ...
... ITO-Si heterojunction solar cell with nanocrystal line CdTe thin films grown by magnetron sputtering are studied. The electrical and optical properties of these solar cell devices, as determined by current–voltage and photovoltage spectroscopy, were found to change with temperature over a range of 8 ...
44401 Molecular biology of the cell
... targeting of peroxisomal proteins, peroxisome functions. Specific protein synthesis and vesicular traffic in hematopoietic cells and in the defence against microorganisms. 4.Structure and function of the nucleus. Structure of the nuclear envelope and lamina, link between cytosol cytoskeleton and chr ...
... targeting of peroxisomal proteins, peroxisome functions. Specific protein synthesis and vesicular traffic in hematopoietic cells and in the defence against microorganisms. 4.Structure and function of the nucleus. Structure of the nuclear envelope and lamina, link between cytosol cytoskeleton and chr ...
Key Card for Plant Cell
... of hydrogen peroxide, a molecule that would cause serious damage if it were released into the cytoplasm ...
... of hydrogen peroxide, a molecule that would cause serious damage if it were released into the cytoplasm ...
An introduction to cells and tissues
... • Control exchange of materials between cell & its surrounding environment • Sensing and responding to changes in surrounding environment • Reproduction – Exception, Nerve cells and muscle cells lose their ability to reproduce during their early development ...
... • Control exchange of materials between cell & its surrounding environment • Sensing and responding to changes in surrounding environment • Reproduction – Exception, Nerve cells and muscle cells lose their ability to reproduce during their early development ...
Cells Part 1 Powerpoint
... • The three major parts of all cells • The structure and function of a cell membrane • The distinction between a cell membrane and cell wall • The nature of diffusion and osmosis • The three types of membrane transport • Bulk transport and ionic transport in cells ...
... • The three major parts of all cells • The structure and function of a cell membrane • The distinction between a cell membrane and cell wall • The nature of diffusion and osmosis • The three types of membrane transport • Bulk transport and ionic transport in cells ...
Dynamic Plant – BI 103
... Where are the cultural origins of agriculture and what type of food did each contribute? E.g. where did the grains originate? Apples? Potatoes? Rules of scientific names and examples. i.e. Genus species. Parts of a microscope and how do you obtain magnification level? Know the types of microscopes a ...
... Where are the cultural origins of agriculture and what type of food did each contribute? E.g. where did the grains originate? Apples? Potatoes? Rules of scientific names and examples. i.e. Genus species. Parts of a microscope and how do you obtain magnification level? Know the types of microscopes a ...
Cell structure part B
... Synthesis of phospholipids and cholesterol Synthesis of steroid hormones Synthesis and storage of triglycerides Synthesis and storage of glycogen Storage of ions ( e.g. Ca++ in muscle) Detoxification and inactivation of drugs ...
... Synthesis of phospholipids and cholesterol Synthesis of steroid hormones Synthesis and storage of triglycerides Synthesis and storage of glycogen Storage of ions ( e.g. Ca++ in muscle) Detoxification and inactivation of drugs ...
Chapter 4: The Characteristics of Prokaryotic and
... Flagella, Cilia, Pseudopodia(Amoeboid Movement), Cell Wall ...
... Flagella, Cilia, Pseudopodia(Amoeboid Movement), Cell Wall ...
Cells - Effingham County Schools
... activities & carries info for cell reproduction cytoplasm: gel-like material that spreads around the internal parts of the cell Organelle: structure that has a specific task within the cell *for example: mitochondria (energy), vacuoles ...
... activities & carries info for cell reproduction cytoplasm: gel-like material that spreads around the internal parts of the cell Organelle: structure that has a specific task within the cell *for example: mitochondria (energy), vacuoles ...
CHROMOSOMES - Bishop Montgomery High School
... Bacteria reproduce using __________________________________ ...
... Bacteria reproduce using __________________________________ ...
Lecture 4 - Harford Community College
... • Rod-shaped organelles that derived from a bacterium that invaded a host cell • The powerhouse of the cell! • Only organelle other than the nucleus to house DNA – Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has unique genes in their DNA that are lacking in nuclear DNA ...
... • Rod-shaped organelles that derived from a bacterium that invaded a host cell • The powerhouse of the cell! • Only organelle other than the nucleus to house DNA – Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has unique genes in their DNA that are lacking in nuclear DNA ...
Aim: What is a cell? Do Now: On your paper. Notes are in
... grow to be a meter long (3 ¼ feet)! Thiomargarita namibiensis is the largest bacteria on Earth- it’s 0.75 mm in diameter- so big you can see it with only your eye!! ...
... grow to be a meter long (3 ¼ feet)! Thiomargarita namibiensis is the largest bacteria on Earth- it’s 0.75 mm in diameter- so big you can see it with only your eye!! ...
Review Guide Cells
... Oxygen regulation O2 levels must be regulated according to activity level. The more active the body/cells then more oxygen needed. During periods of slower activity level less oxygen is needed. Rate is controlled by the brain/brain stem to make sure carbon dioxide and oxygen levels are suitable for ...
... Oxygen regulation O2 levels must be regulated according to activity level. The more active the body/cells then more oxygen needed. During periods of slower activity level less oxygen is needed. Rate is controlled by the brain/brain stem to make sure carbon dioxide and oxygen levels are suitable for ...
Cell junctions
... These are formed from proteins in the cell membranes that form hollow tubes through which small molecules and ions (with a molecular mass below 1000) electrochemical signals, such as Ca2+ (a second messenger) or Na+ can be delivered from one cell to its neighbours. If you touch a single cell in an e ...
... These are formed from proteins in the cell membranes that form hollow tubes through which small molecules and ions (with a molecular mass below 1000) electrochemical signals, such as Ca2+ (a second messenger) or Na+ can be delivered from one cell to its neighbours. If you touch a single cell in an e ...
BioBoot Camp – Cells
... BIO.A.1.2.2 Describe and interpret relationships between structures and function at various levels of biological organization (ie organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and multicellular organisms) Cell – smallest unit that can perform all life’s processes. o Organelles - inside of cell ...
... BIO.A.1.2.2 Describe and interpret relationships between structures and function at various levels of biological organization (ie organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and multicellular organisms) Cell – smallest unit that can perform all life’s processes. o Organelles - inside of cell ...
Cell Growth and Division
... ____________________ is the process by which new cells are produced from pre-existing cells. Each “daughter” cell gets an ______________ copy of the DNA and half of the cytoplasm and organelles. Cell Reproduction--Prokaryotes In ___________________, cell division takes the form of BINARY FISSION ...
... ____________________ is the process by which new cells are produced from pre-existing cells. Each “daughter” cell gets an ______________ copy of the DNA and half of the cytoplasm and organelles. Cell Reproduction--Prokaryotes In ___________________, cell division takes the form of BINARY FISSION ...
What traits define what it means to be living?
... Living organisms consist of highly organized systems that interact. Topic: ...
... Living organisms consist of highly organized systems that interact. Topic: ...
Cell powerpoint 1 Cells PP Final
... • Cells are the building blocks of life • Cells tissues organs organ systems organisms • Organelles each have a different job • Prokaryotic cells don’t have a nucleus; Eukaryotic cells do. ...
... • Cells are the building blocks of life • Cells tissues organs organ systems organisms • Organelles each have a different job • Prokaryotic cells don’t have a nucleus; Eukaryotic cells do. ...
Cells! - Personal
... form channels (pores) for transport of substances across the membrane. • Integral proteins also may lie partly submerged in one side or the other. They have several functions. – Some integral proteins serve as cell surface enzymes. – Integral proteins bound to carbohydrates may form receptor sites f ...
... form channels (pores) for transport of substances across the membrane. • Integral proteins also may lie partly submerged in one side or the other. They have several functions. – Some integral proteins serve as cell surface enzymes. – Integral proteins bound to carbohydrates may form receptor sites f ...
Content Outline
... b. A cell membrane allows ________ and _____________ into the cell and waste products out of the cell. 3. Cytoplasm–gelatin like substance inside cell membrane a. _________________–scaffolding-like structure in cytoplasm which helps cell keep its shape b. In the cytoplasm, eukaryotic cells have ____ ...
... b. A cell membrane allows ________ and _____________ into the cell and waste products out of the cell. 3. Cytoplasm–gelatin like substance inside cell membrane a. _________________–scaffolding-like structure in cytoplasm which helps cell keep its shape b. In the cytoplasm, eukaryotic cells have ____ ...
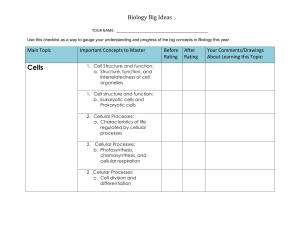
Biology Standards Checklist
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
Cells - Seattle Central College
... • How does the cell move stuff in and out? • How does it eat, drink and defend itself? ...
... • How does the cell move stuff in and out? • How does it eat, drink and defend itself? ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.