Cells and genetics - Natural History Museum
... When the first sperm meets the ovum, enzymes in that sperm’s head break down the ovum jelly and cell membrane so the sperm’s nucleus can enter into the ovum. The sperm’s tail drops away and the nucleus swells. It merges with the nucleus of the ovum and the DNA from the ...
... When the first sperm meets the ovum, enzymes in that sperm’s head break down the ovum jelly and cell membrane so the sperm’s nucleus can enter into the ovum. The sperm’s tail drops away and the nucleus swells. It merges with the nucleus of the ovum and the DNA from the ...
Human Embryology and Natural Stem Cells iPS…..induced
... into a two-way street! Out of 24 potential signals, he found the FOUR that could make it happen - they are today referred to as the ‘Stemness Signals’. CELL REPLACEMENT THERAPY came true thanks to Dolly!! July 7, 2006: Yamanaka announces he has taken somatic cells from the skin of a mouse, inserted ...
... into a two-way street! Out of 24 potential signals, he found the FOUR that could make it happen - they are today referred to as the ‘Stemness Signals’. CELL REPLACEMENT THERAPY came true thanks to Dolly!! July 7, 2006: Yamanaka announces he has taken somatic cells from the skin of a mouse, inserted ...
Generation of functional astrocytes from embryonic stem cells
... Doerenkamp-Zbinden Chair for in vitro alternative methods to animal experiments (Konstanz) (DE) e-mail: philipp.kuegler@uni-konstanz.de Background motivation Deleterious effects of neurotoxicants in the brain are not only caused as a result of direct neurotoxicity, but are also the result of inflamm ...
... Doerenkamp-Zbinden Chair for in vitro alternative methods to animal experiments (Konstanz) (DE) e-mail: philipp.kuegler@uni-konstanz.de Background motivation Deleterious effects of neurotoxicants in the brain are not only caused as a result of direct neurotoxicity, but are also the result of inflamm ...
Cell Structure and Function
... * thylakoids are surrounded by fluid called stroma 4. Stroma contains circular DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes ...
... * thylakoids are surrounded by fluid called stroma 4. Stroma contains circular DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes ...
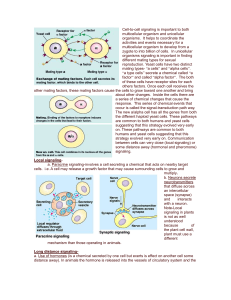
Long distance signaling
... organisms. It helps to coordinate the activities and events necessary for a multicellular organism to develop from a zygote to into billion of cells. In unicellular organisms signaling is important in finding different mating types for sexual reproduction. Yeast cells have two distinct mating types- ...
... organisms. It helps to coordinate the activities and events necessary for a multicellular organism to develop from a zygote to into billion of cells. In unicellular organisms signaling is important in finding different mating types for sexual reproduction. Yeast cells have two distinct mating types- ...
Cell Analogy Project
... storage closets in the school are vacuoles because they are a place for storage of waste or extra materials (which is the function of a vacuole in the cell.) Or, I might say that the administrative office is the nucleus, because that is where the instructions for carrying out school functions are st ...
... storage closets in the school are vacuoles because they are a place for storage of waste or extra materials (which is the function of a vacuole in the cell.) Or, I might say that the administrative office is the nucleus, because that is where the instructions for carrying out school functions are st ...
Document
... Green in color because of chlorophyll, which is a green pigment Double membrane structure ...
... Green in color because of chlorophyll, which is a green pigment Double membrane structure ...
Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... What two organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not? ...
... What two organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not? ...
Ms. E.Russell`s 7th Grade Life Science Classes START DATE
... In the center of the cytoplasm you will need to place a medium sized edible, round nucleus. --Nucleus controls all cell activities, including how the cell grows, develops and divides. Place one or two small, edible pieces in the cytoplasm. These will represent one or two vacuoles. --Vacuoles is a te ...
... In the center of the cytoplasm you will need to place a medium sized edible, round nucleus. --Nucleus controls all cell activities, including how the cell grows, develops and divides. Place one or two small, edible pieces in the cytoplasm. These will represent one or two vacuoles. --Vacuoles is a te ...
Biology SOL REVIEW
... pH because changes in pH cause changes in _______ conformation, resulting in a change in activity. ...
... pH because changes in pH cause changes in _______ conformation, resulting in a change in activity. ...
P014 The role of auxin transport in root hair development Angharad
... shows remarkable consistency both within and between species, with hairs being produced almost exclusively within two hair’s widths from the transverse cell wall closest to the root apex. The transport of the plant hormone auxin from cell to cell through the epidermal cell layer in an apical to basa ...
... shows remarkable consistency both within and between species, with hairs being produced almost exclusively within two hair’s widths from the transverse cell wall closest to the root apex. The transport of the plant hormone auxin from cell to cell through the epidermal cell layer in an apical to basa ...
Plant vs Animal Cell Activity
... Slides (4-6 animal, 4-6 plant) Colored Pencils Activity: Set up microscopes at different stations throughout the room. Each microscope should be labeled using a labeling system that does not indicate which type of cell is in view (i.e. label A-F). On 4-6 of the microscopes, have in focus an animal c ...
... Slides (4-6 animal, 4-6 plant) Colored Pencils Activity: Set up microscopes at different stations throughout the room. Each microscope should be labeled using a labeling system that does not indicate which type of cell is in view (i.e. label A-F). On 4-6 of the microscopes, have in focus an animal c ...
HonoNameKEY Date Period Introduction to Living Things Notes
... Why can’t organisms just live forever? Over time there is damage to the DNA and cells (things wear out despite constant maintenance and repair). Organisms cannot always maintain homeostasis in all environmental conditions. If an organism cannot continue its metabolism and maintain homeostasis – its ...
... Why can’t organisms just live forever? Over time there is damage to the DNA and cells (things wear out despite constant maintenance and repair). Organisms cannot always maintain homeostasis in all environmental conditions. If an organism cannot continue its metabolism and maintain homeostasis – its ...
Plant and Animal Cell
... a granular material called… CHROMATIN Chromatin= DNA + protein Usually spread out in nucleus During cell division, chromatin clumps together or condenses…we call this…. CHROMOSOMES ...
... a granular material called… CHROMATIN Chromatin= DNA + protein Usually spread out in nucleus During cell division, chromatin clumps together or condenses…we call this…. CHROMOSOMES ...
Plant and Animal Cells
... A group of cells in your body work together to form your circulatory system. Another group of cells work together to form your respiratory system. Without cells, you wouldn't be alive! ...
... A group of cells in your body work together to form your circulatory system. Another group of cells work together to form your respiratory system. Without cells, you wouldn't be alive! ...
Organelles - Granbury ISD
... functions for the cell. • The membrane separates and protects the cell from the outside environment. • It regulates all that enters and leaves the cell; in multicellular organisms it allows self recognition. • It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer. ...
... functions for the cell. • The membrane separates and protects the cell from the outside environment. • It regulates all that enters and leaves the cell; in multicellular organisms it allows self recognition. • It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer. ...
Which of the following organisms do NOT have cell walls?
... Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. Endoplasmic reticulum is made up of folded membranes. Ribosomes are sometimes attached to folded membranes. ...
... Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. Endoplasmic reticulum is made up of folded membranes. Ribosomes are sometimes attached to folded membranes. ...
Cells
... • Process by which cells develop different characteristics in structure and function • Differences in outcome – Directed by cell’s DNA – Determined by cell’s position in the body and its ...
... • Process by which cells develop different characteristics in structure and function • Differences in outcome – Directed by cell’s DNA – Determined by cell’s position in the body and its ...
Why do cells need to divide?
... the cell pinches and divides the cytoplasm into two parts two identical separate cells are ...
... the cell pinches and divides the cytoplasm into two parts two identical separate cells are ...
5cpptdd - Cell-as-a
... divide, produce secretary products contacts. They are all about the size of bacteria but others may have a little difference shapes depending on the types of cells. This is like the classrooms. ...
... divide, produce secretary products contacts. They are all about the size of bacteria but others may have a little difference shapes depending on the types of cells. This is like the classrooms. ...
Flow of Matter_04_Sample Quiz Questions_Key
... A protein is a polymer of many monomers called amino acids that are linked together by covalent bonds. The structure of a protein is held together by hydrogen bonds between the amino acids in the polymer (remember primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary protein structure). During digestion, our ...
... A protein is a polymer of many monomers called amino acids that are linked together by covalent bonds. The structure of a protein is held together by hydrogen bonds between the amino acids in the polymer (remember primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary protein structure). During digestion, our ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.