ISCI/FRM/004 – hES Cell Details
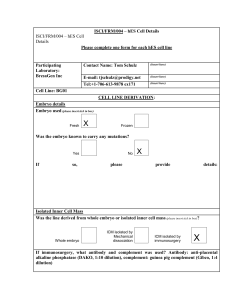
... Karyotype of cells – please include passage level(s) at which karyotyping was performed (If you have data on multiple passage levels, please provide) Normal male karyotype observed when cells were maintained by microdissection passaging. Mulitple parallel cultures, mulitple time points. Normal kary ...
... Karyotype of cells – please include passage level(s) at which karyotyping was performed (If you have data on multiple passage levels, please provide) Normal male karyotype observed when cells were maintained by microdissection passaging. Mulitple parallel cultures, mulitple time points. Normal kary ...
Chapter 4
... • some plants add a secondary cell wall between the PM and the primary cell wall • plants use the plasmodesmata - channels in the cell wall - strands of cytoplasm connect one cell to another ...
... • some plants add a secondary cell wall between the PM and the primary cell wall • plants use the plasmodesmata - channels in the cell wall - strands of cytoplasm connect one cell to another ...
Unit 2
... surrounds vacuole 8. Explain the role of Peroxisomes in eukaryotic cells. These grab hydrogen and oxygen to form hydrogen peroxide, they break toxic waste apart. this grows through the incorporation of proteins and lipids from the cytosol and split when they reach a certain size. 9. Describe the str ...
... surrounds vacuole 8. Explain the role of Peroxisomes in eukaryotic cells. These grab hydrogen and oxygen to form hydrogen peroxide, they break toxic waste apart. this grows through the incorporation of proteins and lipids from the cytosol and split when they reach a certain size. 9. Describe the str ...
AP Biology Cell Poster
... 4. (50 pts) Create a chart that resembles the chart below on a separate sheet of paper (you may type it or write it on notebook paper). You will staple this to your poster. It must include all 15 chosen items. Cell Structure: Animal Cell EXAMPLE: Nucleus ...
... 4. (50 pts) Create a chart that resembles the chart below on a separate sheet of paper (you may type it or write it on notebook paper). You will staple this to your poster. It must include all 15 chosen items. Cell Structure: Animal Cell EXAMPLE: Nucleus ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... There are many different types of cells. For example, in you there are blood cells and skin cells and bone cells and even bacteria. Here we have drawings of bacteria and human cells. Can you tell which depicts various types of bacteria? All cells - whether from bacteria, human, or any other organism ...
... There are many different types of cells. For example, in you there are blood cells and skin cells and bone cells and even bacteria. Here we have drawings of bacteria and human cells. Can you tell which depicts various types of bacteria? All cells - whether from bacteria, human, or any other organism ...
Mitosis and Meiosis
... Why Do Cells Divide? The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on it's DNA. It also has more trouble moving enough food and wastes across its cell membrane. ...
... Why Do Cells Divide? The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on it's DNA. It also has more trouble moving enough food and wastes across its cell membrane. ...
CH 6 CQ
... Brefeldin A is a drug that disrupts transport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. What other organelles and membranes are affected? a) lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane b) lysosomes, peroxisomes, plasma membrane c) vacuoles, mitochondria, plasma membrane ...
... Brefeldin A is a drug that disrupts transport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. What other organelles and membranes are affected? a) lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane b) lysosomes, peroxisomes, plasma membrane c) vacuoles, mitochondria, plasma membrane ...
Q4 Describe the factors that affect the flux of
... Plasma K levels à as per Fick’s Law of Diffusion, the diffusion of a substance across a semipermeable membrane is directly proportional to the concentration gradient across the membrane. Temperature à ...
... Plasma K levels à as per Fick’s Law of Diffusion, the diffusion of a substance across a semipermeable membrane is directly proportional to the concentration gradient across the membrane. Temperature à ...
Chromosomes
... (gender) of an organism Autosomes: does not determine gender Every cell has two copies of each autosome – 1 from mother and 1 from father called homologous chromosomes or homologues Homologous chromosomes carry the same type of genetic information but it may not be identical • Every cell has 2 sex c ...
... (gender) of an organism Autosomes: does not determine gender Every cell has two copies of each autosome – 1 from mother and 1 from father called homologous chromosomes or homologues Homologous chromosomes carry the same type of genetic information but it may not be identical • Every cell has 2 sex c ...
September 8 2014 APBiology
... membrane. Glycolipids - protective and assist in various functions. Glycoproteins - have an attached carbohydrate chain of sugar that projects externally ...
... membrane. Glycolipids - protective and assist in various functions. Glycoproteins - have an attached carbohydrate chain of sugar that projects externally ...
B2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... • Percen.le – The value of a variable below which a certain percentage of observaBons fall. • Stem Cell – An unspecialised cell that can divide to produce more stem cells or different kinds of specialised cells • Differen.ate – Specialise, develop into different kinds of cell, as in cells that bec ...
... • Percen.le – The value of a variable below which a certain percentage of observaBons fall. • Stem Cell – An unspecialised cell that can divide to produce more stem cells or different kinds of specialised cells • Differen.ate – Specialise, develop into different kinds of cell, as in cells that bec ...
Engage students to continuously learn, question, define and solve
... What do you think might happen if phospholipids did not form a bilayer? How might they arrange themselves in an aqueous environment? See Figures 3.20 in your book for drawings of phospholipids. The hydrophilic head and the hydrophobic tail of phospholipids allow them to have an “inside” that resists ...
... What do you think might happen if phospholipids did not form a bilayer? How might they arrange themselves in an aqueous environment? See Figures 3.20 in your book for drawings of phospholipids. The hydrophilic head and the hydrophobic tail of phospholipids allow them to have an “inside” that resists ...
FOSS Diversity of Life Course Glossary 1 FOSS
... Food: A substance that provides nutrients for organisms. Photosynthetic organisms produce their own food; all other organisms must consume food. Food is used by organisms for growth, repair, cellular processes, and energy. Fruit: The ripened ovary of a plant containing the seeds. Fungus (fungi, pl.) ...
... Food: A substance that provides nutrients for organisms. Photosynthetic organisms produce their own food; all other organisms must consume food. Food is used by organisms for growth, repair, cellular processes, and energy. Fruit: The ripened ovary of a plant containing the seeds. Fungus (fungi, pl.) ...
1 Subject: Plant morphogenesis in vivo and in vitro 4 0 26 30 Staff
... (polysomatic and nonpolysomatic plants). Endoreduplication in plant development. Tissue- and organspecific endopolyploidization patterns. Polysomatic and nonpolysomatic plant in in vitro culture. Somaclonal variation – chromosomal aberration in cultured cells and regenerated plant. Methods of nuclea ...
... (polysomatic and nonpolysomatic plants). Endoreduplication in plant development. Tissue- and organspecific endopolyploidization patterns. Polysomatic and nonpolysomatic plant in in vitro culture. Somaclonal variation – chromosomal aberration in cultured cells and regenerated plant. Methods of nuclea ...
slides - IUN.edu
... • Influx of Ca+2 is tightly regulated, since Ca+2 binds molecules (enzymes) and alters their activities (activation or inhibition). • Influx of Ca+2 through Ca+2 channels is often used as a signal to trigger other intracellular events (muscle contraction). • The cell maintains a low concentration, s ...
... • Influx of Ca+2 is tightly regulated, since Ca+2 binds molecules (enzymes) and alters their activities (activation or inhibition). • Influx of Ca+2 through Ca+2 channels is often used as a signal to trigger other intracellular events (muscle contraction). • The cell maintains a low concentration, s ...
Cell Organelles - Shelton School District
... • Prokaryotic Cell: A cell that is lacking a nucleus and most organelles • Eukaryotic Cell: A cell that contains a membrane bound nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. • Organelles: “mini-organ” part of the cell with a specific job. ...
... • Prokaryotic Cell: A cell that is lacking a nucleus and most organelles • Eukaryotic Cell: A cell that contains a membrane bound nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. • Organelles: “mini-organ” part of the cell with a specific job. ...
Cell injury, death and adaptation yemen
... • Pathogenesis: steps in the development of disease…… cellular and molecular changes . • Morphology: macroscopic and microscopic changes. ...
... • Pathogenesis: steps in the development of disease…… cellular and molecular changes . • Morphology: macroscopic and microscopic changes. ...
Course Guide - Universitat de València
... After completing this course, students will be able to: • Know the plant and animal cell structure • Understand how different cellular processes and basic cell signaling systems are performed and where they place on in the cell. • Understand and manage the basic scientific terminology related to the ...
... After completing this course, students will be able to: • Know the plant and animal cell structure • Understand how different cellular processes and basic cell signaling systems are performed and where they place on in the cell. • Understand and manage the basic scientific terminology related to the ...
There are 2 types of cells.
... 3. they include: - bacteria - blue-green algae 4. some move using: or flagella ...
... 3. they include: - bacteria - blue-green algae 4. some move using: or flagella ...
Section: 2.6 Name:
... While some cells have an easy time keeping the water in balance, other types of organisms have a much harder time adjusting. For example, unicellular organisms that live in freshwater are in a hypotonic condition, where water freely moves into their cells. Therefore, these organisms must use a _____ ...
... While some cells have an easy time keeping the water in balance, other types of organisms have a much harder time adjusting. For example, unicellular organisms that live in freshwater are in a hypotonic condition, where water freely moves into their cells. Therefore, these organisms must use a _____ ...
Chapter_7PP - biologywithbengele
... Allow steady supply of nutrients into the cell Examples- oxygen, water, glucose Allow wastes and products of cell metabolism to leave the cell Examples- carbon dioxide, water, wastes Demonstrate the function of the cell membrane and explain its role in maintaining homeostasis ...
... Allow steady supply of nutrients into the cell Examples- oxygen, water, glucose Allow wastes and products of cell metabolism to leave the cell Examples- carbon dioxide, water, wastes Demonstrate the function of the cell membrane and explain its role in maintaining homeostasis ...
Cell Theory Lab. - Kihei Charter STEM Academy Middle School
... same conclusion about animals. These two ideas gave us the first part of the three part cell theory. Then in 1855 a doctor who was studying how diseases affect living things came to the conclusion that cells can only come from other cells. These ideas along with the research of modern scientists giv ...
... same conclusion about animals. These two ideas gave us the first part of the three part cell theory. Then in 1855 a doctor who was studying how diseases affect living things came to the conclusion that cells can only come from other cells. These ideas along with the research of modern scientists giv ...
Characteristics of Living Things (Essay
... sensory neuron (pressure, temperature) vs. motor neuron/neuro-muscular junction structure and function of neurons: axons/dendrites/myelin ”resting potential” vs. “action potential”: difference in polarity (charge across cell membrane). o What transmembrane proteins involved to maintain the cha ...
... sensory neuron (pressure, temperature) vs. motor neuron/neuro-muscular junction structure and function of neurons: axons/dendrites/myelin ”resting potential” vs. “action potential”: difference in polarity (charge across cell membrane). o What transmembrane proteins involved to maintain the cha ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.























