CS 8.1, CS 8.2, CS 8.3, CS 8.4 Unit Plan
... - show relationships between cells-tissue-organs and organ systems - identify organ systems in the body and state purpose - explain how the body organ systems work together- interdependent - explain how personal lifestyle choices impact the body and the body systems/ external and internal stimuli - ...
... - show relationships between cells-tissue-organs and organ systems - identify organ systems in the body and state purpose - explain how the body organ systems work together- interdependent - explain how personal lifestyle choices impact the body and the body systems/ external and internal stimuli - ...
Animal Cell Anatomy
... The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of cells (or in some cases, a single cell). Most cells are very small; most are invisible without using a microscope. Cells are covered by a cell membrane and come in many different shapes. The contents of a cell are called the cytoplasm. ...
... The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of cells (or in some cases, a single cell). Most cells are very small; most are invisible without using a microscope. Cells are covered by a cell membrane and come in many different shapes. The contents of a cell are called the cytoplasm. ...
B2.12.2 Cells Diffusion SOW May 2013
... 3. Know that oxygen required for respiration passes through cell membranes by diffusion. ...
... 3. Know that oxygen required for respiration passes through cell membranes by diffusion. ...
Cell City Analogy - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... Part B:Cell City Analogy Directions: Read the story, then match each underlined part with the cell organelle that has the same or similar job. In a far away city called Redmen City, the main export and production product is the steel widget. The entire town is below sea level and is filled with a w ...
... Part B:Cell City Analogy Directions: Read the story, then match each underlined part with the cell organelle that has the same or similar job. In a far away city called Redmen City, the main export and production product is the steel widget. The entire town is below sea level and is filled with a w ...
Mitosis Powerpoint
... of a new cell wall between the daughter cells then occurs at the cell plate. ...
... of a new cell wall between the daughter cells then occurs at the cell plate. ...
Cell Biology Overview
... the cytoplasm where ribosomes are located because ribosomes are the structures where messenger RNA is translated (translation). Ribosomes along with transfer-RNA translate the genetic information into a protein by adding one amino acid per three mRNA bases (codons). Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic c ...
... the cytoplasm where ribosomes are located because ribosomes are the structures where messenger RNA is translated (translation). Ribosomes along with transfer-RNA translate the genetic information into a protein by adding one amino acid per three mRNA bases (codons). Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic c ...
lets get organized reading
... busy manufacturing plant. Anything that works, works best if someone is in control. Most things that work need energy to keep things humming along. A cell, like a manufacturer, transforms simple materials into complex substances and packages them to be delivered where they are needed. These are just ...
... busy manufacturing plant. Anything that works, works best if someone is in control. Most things that work need energy to keep things humming along. A cell, like a manufacturer, transforms simple materials into complex substances and packages them to be delivered where they are needed. These are just ...
2.3 Cellular Transport
... Do NOW • What is passive transport? • What are 2 examples of passive transport? • Explain what happens when you put a sugar cube in your tea in regards to diffusion. ...
... Do NOW • What is passive transport? • What are 2 examples of passive transport? • Explain what happens when you put a sugar cube in your tea in regards to diffusion. ...
Cell Full Notes
... • Digestive 'plant' for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates • Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal • Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes ...
... • Digestive 'plant' for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates • Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal • Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes ...
The Life Cycle of Sporocytophaga
... of this family (Myxococcus, Chondrococcus) by the absence of fruiting-body formation. The formation of microcysts, which Stanier considers to be the main point of resemblance, is shared by many apparently unrelated groups of bacteria (Bisset, 1949, 1 9 5 0 ~ ) .In the details of the nuclear cycle, m ...
... of this family (Myxococcus, Chondrococcus) by the absence of fruiting-body formation. The formation of microcysts, which Stanier considers to be the main point of resemblance, is shared by many apparently unrelated groups of bacteria (Bisset, 1949, 1 9 5 0 ~ ) .In the details of the nuclear cycle, m ...
Review-Introduction to Plant-Animal Cell
... Proteins are manufactured by the ______________. The __________ ____________ surrounds the nucleus and controls what enters and leaves it. Storage chambers within the cell are called _____________. Found mostly in animal cells, the ______________ plays a role in cell division. Located within the nuc ...
... Proteins are manufactured by the ______________. The __________ ____________ surrounds the nucleus and controls what enters and leaves it. Storage chambers within the cell are called _____________. Found mostly in animal cells, the ______________ plays a role in cell division. Located within the nuc ...
Anatomy of the Pea Plant
... anatomy by becoming familiar with the anatomy of just one plant, the pea (Pisum sativum). Compared to the anatomy of most animals, the anatomy of vascular plants is relatively simple; there are only four major organs (leaves, stems, roots and flowers) and four major types of tissues (epidermis, pare ...
... anatomy by becoming familiar with the anatomy of just one plant, the pea (Pisum sativum). Compared to the anatomy of most animals, the anatomy of vascular plants is relatively simple; there are only four major organs (leaves, stems, roots and flowers) and four major types of tissues (epidermis, pare ...
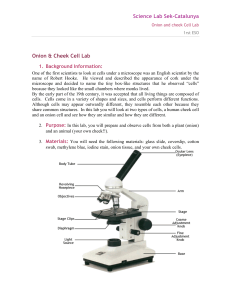
Onion and cheek Cell Lab
... name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny box-like structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted that all living th ...
... name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny box-like structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted that all living th ...
UNIT 3: Cellular Biology 3A: Origin of Life The Big Picture Evidence
... The following information is found in your completed note packet. By the conclusion of this unit, you should know the following: 1. Scientific evidence indicates that organic molecules and cells may have formed spontaneously on ancient Earth. 2. Earth’s life forms evolved from earlier and distinctl ...
... The following information is found in your completed note packet. By the conclusion of this unit, you should know the following: 1. Scientific evidence indicates that organic molecules and cells may have formed spontaneously on ancient Earth. 2. Earth’s life forms evolved from earlier and distinctl ...
SOL 5.5 Living Systems – Study Guide 1. What is a cell? 2. What is
... food. Chloroplasts contain the green chlorophyll used to make food during photosynthesis. ...
... food. Chloroplasts contain the green chlorophyll used to make food during photosynthesis. ...
Homeostasis and Transport Notes
... • Cells ingest molecules using ATP after they bond to special receptor proteins on the cell’s surface. ...
... • Cells ingest molecules using ATP after they bond to special receptor proteins on the cell’s surface. ...
The non-proteic extrusive secondary metabolites in ciliated protists F
... particular group of protists, the ciliated protozoa. Many of non-proteic extrusive secondary metabolites in ciliates function for chemical offense or defense in prey-predator interactions against unicellular or/and multicellular organisms. It is worthy of note that at least some of these secondary m ...
... particular group of protists, the ciliated protozoa. Many of non-proteic extrusive secondary metabolites in ciliates function for chemical offense or defense in prey-predator interactions against unicellular or/and multicellular organisms. It is worthy of note that at least some of these secondary m ...
1 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... Cells with different functions often vary in shape. They may also vary in size. However, all cells are very small. Even the largest organisms have microscopic cells. Cells are so small that their diameter is measured in micrometers. A micrometer is just one-millionth of a meter. Use the sliding scal ...
... Cells with different functions often vary in shape. They may also vary in size. However, all cells are very small. Even the largest organisms have microscopic cells. Cells are so small that their diameter is measured in micrometers. A micrometer is just one-millionth of a meter. Use the sliding scal ...
2.5 : Cells are grouped into tissue - study
... chains of cells, sieve-tube members. •These are alive at functional maturity, although they lack the nucleus, ribosomes, and a distinct vacuole. •The end walls, the sieve plates, have pores that presumably facilitate the flow of fluid between cells. ...
... chains of cells, sieve-tube members. •These are alive at functional maturity, although they lack the nucleus, ribosomes, and a distinct vacuole. •The end walls, the sieve plates, have pores that presumably facilitate the flow of fluid between cells. ...
Osmosis Diffusion Notes
... Cell Membarane • Also known as Plasma Membrane and Phospholipid Bi-layer • Defines the shape of the cell. • Maintains Homeostasis (controls what goes in and out) ...
... Cell Membarane • Also known as Plasma Membrane and Phospholipid Bi-layer • Defines the shape of the cell. • Maintains Homeostasis (controls what goes in and out) ...
Notes: The Eukaryotic Cell
... Notes: The Eukaryotic Cell On the sketch of a prokaryotic cell, label each of these features and give its function or description. cell wall plasma membrane bacterial chromosome nucleoid cytoplasm flagella Why are cells so small? Explain the relationship of surface area to volume. ...
... Notes: The Eukaryotic Cell On the sketch of a prokaryotic cell, label each of these features and give its function or description. cell wall plasma membrane bacterial chromosome nucleoid cytoplasm flagella Why are cells so small? Explain the relationship of surface area to volume. ...
The Incredible Cell Analogy Project Cells need to carry on the same
... The Incredible Cell Analogy Project Cells need to carry on the same basic functions as we do to sustain life; the difference is cells do this with much smaller parts. These smaller structures that allow the cell to function are called organelles – “tiny organs.” Also plant and animal cells have some ...
... The Incredible Cell Analogy Project Cells need to carry on the same basic functions as we do to sustain life; the difference is cells do this with much smaller parts. These smaller structures that allow the cell to function are called organelles – “tiny organs.” Also plant and animal cells have some ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... CDKs & cyclin drive cell from one phase to next in cell cycle ...
... CDKs & cyclin drive cell from one phase to next in cell cycle ...
Lec.3
... difficult to cultivate and usually require a medium that is solidified with agar as well as having the right osmotic strength. L forms are produced more readily with penicillin than with lysozyme, suggesting the need for residual peptidoglycan. Some L forms can revert to the normal bacillary form up ...
... difficult to cultivate and usually require a medium that is solidified with agar as well as having the right osmotic strength. L forms are produced more readily with penicillin than with lysozyme, suggesting the need for residual peptidoglycan. Some L forms can revert to the normal bacillary form up ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.