UpdatedCumulativeStudyGuide
... transport chain. These electrons then gradually lose their energy as they are shuttled from one membrane protein to the next and as they do this, this energy is used to pump hydrogen ions UP their concentration gradient. As the hydrogen ions enter back into the cell via ATPases, ATP is generated in ...
... transport chain. These electrons then gradually lose their energy as they are shuttled from one membrane protein to the next and as they do this, this energy is used to pump hydrogen ions UP their concentration gradient. As the hydrogen ions enter back into the cell via ATPases, ATP is generated in ...
CH - TeacherWeb
... Each channel is specific to an ion and the direction they move is determined by either their concentration or voltage across the membrane. Facilitated Diffusion – has substances going from an area of High concentration to an area of Low concentration, but requires a CARRIER. These carriers are spec ...
... Each channel is specific to an ion and the direction they move is determined by either their concentration or voltage across the membrane. Facilitated Diffusion – has substances going from an area of High concentration to an area of Low concentration, but requires a CARRIER. These carriers are spec ...
... – Porous, absorbable synthetic or natural polymers • CELLS (Autologous or Allogeneic) – Differentiated cells of same type as tissue – Stem cells (e.g., bone marrow-derived) – Other cell types (e.g., dermal cells) • REGULATORS – Growth factors or their genes – Mechanical loading – Static versus dynam ...
Ch 18 - protists
... 1. Spores transferred to humans through mosquito saliva 2. Spores grow in liver and blood cells, causing them to lyse, releasing toxins (creates fever, chills) ...
... 1. Spores transferred to humans through mosquito saliva 2. Spores grow in liver and blood cells, causing them to lyse, releasing toxins (creates fever, chills) ...
VII
... Instructions: Write each question on your own paper. You are to hand in both the worksheet and your answer sheet before you leave class today. Do as many questions as you can correctly in the class period. Biology - Section 7.1 Study Questions 1. What three things does the cell theory state? 2. What ...
... Instructions: Write each question on your own paper. You are to hand in both the worksheet and your answer sheet before you leave class today. Do as many questions as you can correctly in the class period. Biology - Section 7.1 Study Questions 1. What three things does the cell theory state? 2. What ...
Cell Bio Syllabus
... In parenthesis are the Biology learning outcomes to which each objective pertains. These outcomes may be found on the last page of the syllabus. Upon successful completion of this course students will be able to: 1. Identify the major organelles of the cell in eukaryotes and prokaryotes and enumerat ...
... In parenthesis are the Biology learning outcomes to which each objective pertains. These outcomes may be found on the last page of the syllabus. Upon successful completion of this course students will be able to: 1. Identify the major organelles of the cell in eukaryotes and prokaryotes and enumerat ...
cells - Bremen High School District 228
... No nuclei, but contain DNA within cytoplasm Most are single-celled organisms- smaller & simpler All bacteria are prokaryotes Carry out every activity associated with life o Grow, reproduce, respond to changes in ...
... No nuclei, but contain DNA within cytoplasm Most are single-celled organisms- smaller & simpler All bacteria are prokaryotes Carry out every activity associated with life o Grow, reproduce, respond to changes in ...
Hypersensitivity Reaction
... * Three classes of mediators derived from mast cells: 1) Preformed mediators stored in granules (histamine) 2) Newly sensitized mediators: leukotrienes, prostaglandins, platelets activating factor 3) Cytokines produced by activated mast cells, basophils e.g. TNF, IL3, IL-4, IL-5 IL-13, chemokines * ...
... * Three classes of mediators derived from mast cells: 1) Preformed mediators stored in granules (histamine) 2) Newly sensitized mediators: leukotrienes, prostaglandins, platelets activating factor 3) Cytokines produced by activated mast cells, basophils e.g. TNF, IL3, IL-4, IL-5 IL-13, chemokines * ...
f9 What advantage accrues to a cud-chewer? - e
... network of cellulose and pectin. This cell wall can be mechanically rent by chewing and stomach churning in mammals (in reptiles aided often by gastroliths; in birds by grit in the crop) but it cannot be digested away except by organisms that produce a mixture of synergistically acting enzymes as de ...
... network of cellulose and pectin. This cell wall can be mechanically rent by chewing and stomach churning in mammals (in reptiles aided often by gastroliths; in birds by grit in the crop) but it cannot be digested away except by organisms that produce a mixture of synergistically acting enzymes as de ...
Why do cancer cells have too many centrosomes?
... Suzy Prosser and Andrew Fry Department of Biochemistry, University of Leicester Introduction Cell division is the biological basis of life, allowing a single fertilised egg cell to become a multicellular organism containing trillions of cells. This process is strictly regulated as uncontrolled cel ...
... Suzy Prosser and Andrew Fry Department of Biochemistry, University of Leicester Introduction Cell division is the biological basis of life, allowing a single fertilised egg cell to become a multicellular organism containing trillions of cells. This process is strictly regulated as uncontrolled cel ...
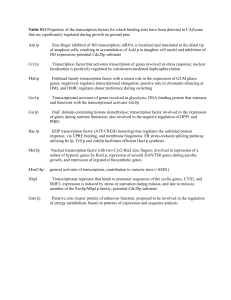
Table S11 Properties of the transcription factors for which binding
... bZIP transcription factor (ATF/CREB1 homolog) that regulates the unfolded protein response, via UPRE binding, and membrane biogenesis; ER stress-induced splicing pathway utilizing Ire1p, Trl1p and Ada5p facilitates efficient Hac1p synthesis ...
... bZIP transcription factor (ATF/CREB1 homolog) that regulates the unfolded protein response, via UPRE binding, and membrane biogenesis; ER stress-induced splicing pathway utilizing Ire1p, Trl1p and Ada5p facilitates efficient Hac1p synthesis ...
BSCI 124: LECTURE 2
... • Each cell is functionally independent – it can live on its own under the right conditions – Uses sugars to get energy and stay alive – Contains all necessary info to replicate produce a multicellular organism – Can make a whole plant from a single cell! ...
... • Each cell is functionally independent – it can live on its own under the right conditions – Uses sugars to get energy and stay alive – Contains all necessary info to replicate produce a multicellular organism – Can make a whole plant from a single cell! ...
Part D: Observing Prokaryotic Cells
... All bacteria are prokaryotic. This means that they lack an organized nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. To find bacteria, smear a very small portion of yogurt across a slide using a toothpick. Add a small drop of water to make a wet mount slide. Have your instructor put a very tiny amount of met ...
... All bacteria are prokaryotic. This means that they lack an organized nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. To find bacteria, smear a very small portion of yogurt across a slide using a toothpick. Add a small drop of water to make a wet mount slide. Have your instructor put a very tiny amount of met ...
Cell Membranes - WordPress.com
... •__________________________________ endocytosis is very ____________________ in terms of what a cell takes in. ___________________ on the outside of a cell bind to a specific molecule. In biology, a general term for any molecule that binds is called a _____________________. Receptor-mediated endocy ...
... •__________________________________ endocytosis is very ____________________ in terms of what a cell takes in. ___________________ on the outside of a cell bind to a specific molecule. In biology, a general term for any molecule that binds is called a _____________________. Receptor-mediated endocy ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... cell body Axon: extension of cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body. ...
... cell body Axon: extension of cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body. ...
Chapter 4 Section 2 Cell Structure and Function
... • Do you know why the cell is described this way? – Example: brick house ...
... • Do you know why the cell is described this way? – Example: brick house ...
Uncovering the Unexpected Site of Biosynthesis of a Major Cell Wall
... form a gel-like matrix during cellular expansion (Kiemle et al., 2014). The biosynthesis of cell wall polysaccharides takes place via the action of two classes of enzymes: polysaccharide synthases (enzymes of the carbohydrate active enzymes [CAZy] family GT2, with multiple membrane-spanning domains ...
... form a gel-like matrix during cellular expansion (Kiemle et al., 2014). The biosynthesis of cell wall polysaccharides takes place via the action of two classes of enzymes: polysaccharide synthases (enzymes of the carbohydrate active enzymes [CAZy] family GT2, with multiple membrane-spanning domains ...
Diabetes in Native Americans: The interaction between diet and genes
... vesicles fuse to form first flat sacks of Golgi apparatus ...
... vesicles fuse to form first flat sacks of Golgi apparatus ...
CumulativeStudyGuide
... transport chain. These electrons then gradually lose their energy as they are shuttled from one membrane protein to the next and as they do this, this energy is used to pump hydrogen ions UP their concentration gradient. As the hydrogen ions enter back into the cell via ATPases, ATP is generated in ...
... transport chain. These electrons then gradually lose their energy as they are shuttled from one membrane protein to the next and as they do this, this energy is used to pump hydrogen ions UP their concentration gradient. As the hydrogen ions enter back into the cell via ATPases, ATP is generated in ...
COTM0211 - California Tumor Tissue Registry
... Histologically, LCA is characterized by a proliferation of anastomosing vascular conduits lined by tall or histiocytoid, bland-appearing cells having either central or eccentrically located nuclei and distinctly clear cytoplasm. Mitotic figures are usually rarely encountered. Pseudopapillary configu ...
... Histologically, LCA is characterized by a proliferation of anastomosing vascular conduits lined by tall or histiocytoid, bland-appearing cells having either central or eccentrically located nuclei and distinctly clear cytoplasm. Mitotic figures are usually rarely encountered. Pseudopapillary configu ...
Plant Cell Structures
... Mitochondria are sometimes called the “powerhouses” of the cell. They basically act like a digestive system that takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy. This the making of the cells energy, and is known also as cellular respiration. Most of the chemical reactions involved in cellu ...
... Mitochondria are sometimes called the “powerhouses” of the cell. They basically act like a digestive system that takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy. This the making of the cells energy, and is known also as cellular respiration. Most of the chemical reactions involved in cellu ...
Cytoskeleton
... • In spite of their differences, both cilia and flagella have the same ultrastructure. – Both have a core of microtubules sheathed by the plasma membrane. – Nine doublets of microtubules arranged around a pair at the center, the “9 + 2” pattern. – Flexible “wheels” of proteins connect outer doublet ...
... • In spite of their differences, both cilia and flagella have the same ultrastructure. – Both have a core of microtubules sheathed by the plasma membrane. – Nine doublets of microtubules arranged around a pair at the center, the “9 + 2” pattern. – Flexible “wheels” of proteins connect outer doublet ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.