Discovery and the Cell Theory
... Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes. Prokaryotes are primitive cells which have simple structure and organisation. Bacterial and Blue-green Algae (Cyanobacteria) are included in this group. Eukaryotes on the other hand are well organised complex cells which are highly evolved. Fungi, Algae and higher organis ...
... Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes. Prokaryotes are primitive cells which have simple structure and organisation. Bacterial and Blue-green Algae (Cyanobacteria) are included in this group. Eukaryotes on the other hand are well organised complex cells which are highly evolved. Fungi, Algae and higher organis ...
Help to T cells
... Central role in the immune system Coordination of the immune response Cytotoxic functions Suppression of the immune responses ...
... Central role in the immune system Coordination of the immune response Cytotoxic functions Suppression of the immune responses ...
Cells
... with organelles that have a membrane around them. You will find out more about organelles below. Plant cells and animal cells are eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are cells that do not have organelles with membranes around them. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells that live just about everywhere on Ea ...
... with organelles that have a membrane around them. You will find out more about organelles below. Plant cells and animal cells are eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are cells that do not have organelles with membranes around them. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells that live just about everywhere on Ea ...
Multicellular Organisms
... groups (colonies) that performed specialize jobs to benefit the entire group as a whole. • These colonies may have continued to evolve to into an individual who have parts that have become specialized. ...
... groups (colonies) that performed specialize jobs to benefit the entire group as a whole. • These colonies may have continued to evolve to into an individual who have parts that have become specialized. ...
cell cycle staging from fluorecence dapi images
... in S phase and green cluster to cells in G2 phase. The EM algorithm is highly sensitive to the amount and distribution of the input data. This sensitivity is strongly related with the determinant of matrix Σ! involved in Equation (3) that can be ill-conditioned, especially if the number of elements ...
... in S phase and green cluster to cells in G2 phase. The EM algorithm is highly sensitive to the amount and distribution of the input data. This sensitivity is strongly related with the determinant of matrix Σ! involved in Equation (3) that can be ill-conditioned, especially if the number of elements ...
Biology Passage 2 - HCC Learning Web
... whereas water freely diffuses through the lipid bilayer. Thus, a solution (solvent) can be considered hyper-tonic (more solute), hypo-tonic (less solute) or isotonic (same concentration) to the cell it surrounds. In addition, the flux of solvent in an effort to achieve equilibrium of solute concentr ...
... whereas water freely diffuses through the lipid bilayer. Thus, a solution (solvent) can be considered hyper-tonic (more solute), hypo-tonic (less solute) or isotonic (same concentration) to the cell it surrounds. In addition, the flux of solvent in an effort to achieve equilibrium of solute concentr ...
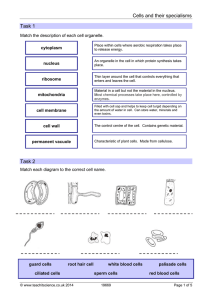
Cells and their specialisms Task 1 Task 2
... Adapted to engulf and digest ‘foreign’ cells. Produce antibodies to help fight foreign antigens. ...
... Adapted to engulf and digest ‘foreign’ cells. Produce antibodies to help fight foreign antigens. ...
Unit5testCells
... ____ 51. Animal cells a. do not contain mitochondria. b. have a cell wall instead of a cell membrane. c. have a large vacuole instead of a Golgi apparatus. d. have mitochondria but no cell wall. ____ 52. Which of the following is the correct order of organization of structures in living things, from ...
... ____ 51. Animal cells a. do not contain mitochondria. b. have a cell wall instead of a cell membrane. c. have a large vacuole instead of a Golgi apparatus. d. have mitochondria but no cell wall. ____ 52. Which of the following is the correct order of organization of structures in living things, from ...
Chapter 43.
... Destroying cells gone bad! Natural Killer Cells perforate cells release perforin protein insert into membrane of target cell forms pore allowing fluid to flow in & out of cell natural killer cell cell ruptures (lysis) ...
... Destroying cells gone bad! Natural Killer Cells perforate cells release perforin protein insert into membrane of target cell forms pore allowing fluid to flow in & out of cell natural killer cell cell ruptures (lysis) ...
7th Grade Science Marking Period 2 Cell Organelle Project The
... The purpose of this project is for the students to strengthen their knowledge of a cell and its many structures by making a physical model. First, students are to choose between the two types of eukaryotic cells, an animal cell and a plant cell. Then students are to represent their cell and its vari ...
... The purpose of this project is for the students to strengthen their knowledge of a cell and its many structures by making a physical model. First, students are to choose between the two types of eukaryotic cells, an animal cell and a plant cell. Then students are to represent their cell and its vari ...
File
... Single celled organisms, like the amoeba, are simple organisms and are able of carrying out all of the essential life functions to survive on their own. Complex, multicellular organisms, like plants and animals divide the tasks needed for survival into groups of _____________ __________________. Fol ...
... Single celled organisms, like the amoeba, are simple organisms and are able of carrying out all of the essential life functions to survive on their own. Complex, multicellular organisms, like plants and animals divide the tasks needed for survival into groups of _____________ __________________. Fol ...
7.2 Cell Structure
... molecules lysosomes: small organelles filled with enzymes that break down large molecules and organelles that are no longer useful the cytoskeleton: a network of protein filaments; it helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in movement centrioles: organelles made from tubulins; they help o ...
... molecules lysosomes: small organelles filled with enzymes that break down large molecules and organelles that are no longer useful the cytoskeleton: a network of protein filaments; it helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in movement centrioles: organelles made from tubulins; they help o ...
Unit 4 Power Point
... The cell membrane regulates/controls what is transported into (absorption) and out of the cell ...
... The cell membrane regulates/controls what is transported into (absorption) and out of the cell ...
Ch. 4 Guided Reading
... 11. There are a couple of ways that the surface area-to-volume and surface area-to-mass ratios be increased in a large cell. Describe one of them.(Hints: cells will do this when they reach a certain size. Also, how can you fit something large into smaller space????) ...
... 11. There are a couple of ways that the surface area-to-volume and surface area-to-mass ratios be increased in a large cell. Describe one of them.(Hints: cells will do this when they reach a certain size. Also, how can you fit something large into smaller space????) ...
Assessment of DNA oxidation by nitroheterocyclic compounds using
... metronidazole and nitrofurantoin, antimicrobial agents widely used in human and veterinary medicine. In order to further study whether their interaction with cellular DNA is linked to the generation of reactive oxygen species we investigated the effects of metronidazole and nitrofurantoin on UV-C in ...
... metronidazole and nitrofurantoin, antimicrobial agents widely used in human and veterinary medicine. In order to further study whether their interaction with cellular DNA is linked to the generation of reactive oxygen species we investigated the effects of metronidazole and nitrofurantoin on UV-C in ...
Observing Protozoa - Science
... ¸ Amoeba - move by making their cytoplasm flow in a certain direction. This pushes one part of the organism (called a PSEUDOPOD) away from the rest of the organism, and then pulls its body along with the pseudopod. ¸ Ciliates - move by beating tiny, hair like structures called CILIA. The cilia are a ...
... ¸ Amoeba - move by making their cytoplasm flow in a certain direction. This pushes one part of the organism (called a PSEUDOPOD) away from the rest of the organism, and then pulls its body along with the pseudopod. ¸ Ciliates - move by beating tiny, hair like structures called CILIA. The cilia are a ...
RG_Talk5PM_Nov6-1
... • Goal: To find dependable ways to unite the data available at various scales into coherent pictures for particular plants in particular contexts. Generalizations/hypotheses may follow. • Difficulty: There are no complete data sets, and the mechanistic bases for the data that are available are not f ...
... • Goal: To find dependable ways to unite the data available at various scales into coherent pictures for particular plants in particular contexts. Generalizations/hypotheses may follow. • Difficulty: There are no complete data sets, and the mechanistic bases for the data that are available are not f ...
Discovery of Cells PPT - Ms. George`s Science Class
... were able to magnify up to 270 times! These more powerful microscopes led to the discovery that there were many very small organisms that did not belong in the Animal or Plant Kingdoms. Before this time, people did not know that there were organisms smaller than plants or animals! ...
... were able to magnify up to 270 times! These more powerful microscopes led to the discovery that there were many very small organisms that did not belong in the Animal or Plant Kingdoms. Before this time, people did not know that there were organisms smaller than plants or animals! ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Notes
... each original chromosome (1 copy each of 23 chromosomes). This means that each daughter cell possesses only half as many chromosomes as the original parent cell. ...
... each original chromosome (1 copy each of 23 chromosomes). This means that each daughter cell possesses only half as many chromosomes as the original parent cell. ...
Homeostasis and Transport
... easiest time moving across a lipid bilayer? 3. Name some molecules that may have difficulty entering or leaving a cell. 4. What organelles (aside from the cell membrane) have one or more lipid bilayers? ...
... easiest time moving across a lipid bilayer? 3. Name some molecules that may have difficulty entering or leaving a cell. 4. What organelles (aside from the cell membrane) have one or more lipid bilayers? ...
Cell Transport Mechanisms
... Active Transport Moves molecules __________ the concentration gradient from areas of _________ concentration to areas of __________ concentration. Restores ________ Takes _______ to “go _______” ...
... Active Transport Moves molecules __________ the concentration gradient from areas of _________ concentration to areas of __________ concentration. Restores ________ Takes _______ to “go _______” ...
Title: Using context to decipher a poem
... 9-11 LS1C Cells contain specialized parts for determining essential functions such as regulation of cellular activities, energy capture and release, formation of proteins, waste disposal, the transfer of information, and movement. 9-11 LS1D The cell is surrounded by a membrane that separates the int ...
... 9-11 LS1C Cells contain specialized parts for determining essential functions such as regulation of cellular activities, energy capture and release, formation of proteins, waste disposal, the transfer of information, and movement. 9-11 LS1D The cell is surrounded by a membrane that separates the int ...
Cell Observation Exercise - Mr. Hill`s Science Website
... Possible structures that could be identified: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, mitochondria, vacuoles. Answer all the questions on the data sheet and turn in. 4. Complete Part III on your worksheet. ...
... Possible structures that could be identified: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, mitochondria, vacuoles. Answer all the questions on the data sheet and turn in. 4. Complete Part III on your worksheet. ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Study Guide:
... Chromosome copied cell divides much like mitosis, but then divides again without making another copy resulting in 4 daughter cells with ½ the chromosomes of the parent cells. These cells become sex cells and are used in sexual reproduction resulting in offspring that is unique to both parents as eac ...
... Chromosome copied cell divides much like mitosis, but then divides again without making another copy resulting in 4 daughter cells with ½ the chromosomes of the parent cells. These cells become sex cells and are used in sexual reproduction resulting in offspring that is unique to both parents as eac ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.